Introduction
Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) Holdings is one of the largest international banking and finance corporations. It was able to achieve financial success through a competent business strategy and calculated investments. This analytical report seeks to investigate HSBC’s history as a company and determine the critical strategies and decisions that enabled it to achieve a trajectory of financial growth and success. The report will explore the company from its inception, but will primarily focus on modern-day events that saw an exponential expansion of assets and services. HSBC Holdings is unique in its continuous innovation as well as its ability to adapt corporate values and strategy to the dynamic climate of financial markets.
Report Summary
Starting out as a regional East Asian banking corporation, HSBC Holdings was able to expand its global presence through a series of strategic acquisitions. The corporation slowly increased its market presence by purchasing smaller banking corporations around the world. It has utilized a clientele-driven approach and its global presence to establish itself in the areas of trade finance and retail-banking operations. Recently, the corporation has faced a crisis of leadership as it has readjusted its strategy, and unsuccessfully attempted to enter new sectors such as investment banking. However, HSBC remains a well-respected and highly successful enterprise.
In analyzing the trajectory of HSBC Holdings’ development and growth, it is evident that competent business decision-making and long-term investment strategy has allowed the corporation to succeed. Throughout its history and in the modern-day, HSBC has prospered due to unceasing innovation and its accountability to clients, which direct the company strategy to recognize and address any potential shortcomings at the highest corporate levels. This report seeks to analyze HSBC Holdings’ corporate history to determine the applicable business strategies and strengths that aided in achieving its financial success.
Unlike most major banking corporations, HSBC’s primary focus is on client-oriented services, including retail and commercial banking, global banking, and private banking, which together make up the majority of the company’s profits. It has focused on developing its network based on international trade and investment on local scales. It seeks growth opportunities by ensuring stability and building capital through a low-risk and diversified investment and banking model. HSBC achieved its success in finance through the following strategies:
- Cultural competency that helps to establish a global presence while continuously evaluating the financial risk of its presence in new markets.
- Accountability for business decisions and attempts to improve the business.
- A financial strategy that focuses on client-based profitability and stability in its banking services.
Company History
The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation was formed in 1865 by the Englishman Thomas Sutherland as a response to the demand for local banking facilities. It became one of the established banks in the Asia-Pacific region and continued its expansion through the 20th century. The bank developed significant expertise in trade finance and local business. It led to the formation of banking industries in various East Asian countries and established a reputation for public investment.
During times of crisis in the 20th century, the bank continued to survive and thrive under competent management by maintaining reserves that could be used for further operation. Towards the end of the 20th century, HSBC initiated an expansion strategy that entailed acquiring subsidiaries or smaller financial organizations that shared similar values and expertise. The most prominent acquisition came in the 1980s with the purchase of Marine Midland Bank, which allowed HSBC to expand to Europe and the United States and led to the establishment of a new headquarters in London (HSBC, n.d.). It soon became the most prominent bank in England and one of the largest financial organizations in the world by expanding into new markets.
During the 2008 financial crisis, HSBC remained one of the banks that could guarantee stability and surprisingly emerged from the economic downturn as a profitable enterprise. The holding group has faced difficult challenges in its history, including the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s, unprofitable acquisitions, and accusations of laundering money and violating regulations. Since 2013, the corporation has attempted to streamline its operations by focusing on its most profitable regions.
After money laundering investigations related to illegal international activities, HSBC admitted its shortcomings and paid mandatory fines, and also vowed to reexamine its banking structures and oversight of the financial activity. Currently, HSBC is facing the challenge of finding a CEO after a series of departures from the company and managing the difficult transition of the United Kingdom, leaving the European Union.
Strategies
HSBC has positioned itself as a “world bank” that is based on its culture of providing local banking to customers around the world. It has followed the principles of being perceptive and responsive by adapting to culturally diverse customer needs. This is an essential point of value that the organization strives to uphold, thereby securing its position in the commercial banking sector and high-reliability ratings despite any potential crisis that the company might undergo.
The bank has sought to adapt its practices and infrastructure to secure its financial practice in any given country, thus becoming a universal banking institution (Kynston & Roberts, 2015). HSBC has also practiced corporate social responsibility by investing in projects which benefited various populations. This helped earn the corporation its respected reputation since it was willing to support small-scale businesses and other projects even during financial crises.
In the 21st century, there is a strong demand for corporate responsibility, which HSBC exhibits in activities for the improvement of society (Houssain & Khan, 2016). In the midst of various allegations and investigations that HSBC has faced in recent years, the corporation accepted full accountability for the lack of oversight and improper practices. It has relied solely on its reserves to pay out fines and has not relied on government bail-outs. It has shifted its priorities to taking a new direction to ensure proper banking practices, which is critical for the institution to maintain a strong reputation and remain successful in the future.
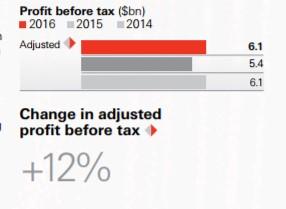
Commercial banking was at the core of the trade finance expertise of HSBC and involved everything from small businesses to relatively large companies. By acquiring regional banks and reconfiguring them into a single enterprise, HSBC was able to increase its prominence and service significantly within the commercial banking sector. As evident from its financial report, commercial banking is increasing profits for HSBC year over year.
In the last several years of severe financial challenges, it is the only sector that has remained profitable for the organization (HSBC Holdings plc., 2017). Retaining business customers has become a priority for HSBC to preserve stability. This has become difficult, with various challenges arising from its competition. The financial industry is rapidly evolving, and HSBC needs to enhance its international network through technology and partnerships (Trudeau & McLarney, 2017).
This is an unusual trend for an international banking conglomerate, considering that most other international organizations derive a majority of their profits from investment banking, a sector where HSBC is struggling to breakthrough.
As part of its strategy going forward, HSBC plans to expand its international network through the support of trade and capital flow among its client base. It plans to continue reinvesting its capital in local markets and retail businesses to support its acquisitions. As part of its attempt to reform the company, HSBC executives have decided to simplify the business by selling branches in various countries that are draining assets.
This is a direct response to some of the failures the company had in expanding into Latin America. Being able to innovate in times of crisis is critical for a corporation. Its decision to withdraw from unprofitable markets initiated massive cost-savings and allowed management to focus on optimizing the company’s presence in regions demanding more resources.
Conclusion
HSBC began as a relatively small financial organization and grew into an international corporation by focusing on its expertise and practicing customer-based values in all its endeavors. As with any large company, it is affected by geopolitical and economic factors as well as instances of poor strategic decision-making. However, appropriate redistribution of priorities and optimization of its services has helped HSBC to continue profiting from its primary focus on commercial banking.
It is evident that the company’s management is seeking methods to increase its global presence and expand its international network in order to benefit customers and shareholders. The company is driven by innovation rather than a desire to maximize profit, which has been a successful long-term business strategy to ensure HSBC’s ability to compete in the global market.
Recommendations and Personal Contribution
The elements identified as essential to the success of HSBC can be practiced at a company on any level or in any sector. However, it is difficult for a financial organization in the modern economic climate to emulate them. Smaller companies may not have the luxury of losing profits in order to drive their mission. Despite such challenges, a company should practice a customer-based approach. HSBC is unique because it has been able to expand commercial and individual banking.
Local banking organizations would profit tremendously by applying such principles in their practice to attract customers. Ensuring financial stability and calculated risk management is critical to establish a valuable reputation for the banking business. Furthermore, management should always be mindful of the company strategy. In order to prosper, a corporation must be able to adapt and continuously optimize its services with the utmost efficiency.
My personal contribution if working in an ambitious financial organization would be to reexamine its mission and the financial strategy to achieve its goals. Often, companies have a good public mission statement but fail to follow it in practice.
For a local banking company, it might be necessary to support regional and community businesses. Similar to the approach of HSBC, if customers choose to conduct small business finances with an organization, they are most likely to transfer personal accounts as well. Achieving a widespread local network will help to establish a base that can be used for expansion and diversification of the organization’s portfolio. There may be elements of risk involved, which can be mitigated by competent management and constant oversight of results for any attempted innovations.
Final Thoughts
The report shows that based on the example of HSBC, a successful trajectory for a corporation lies in an ability to adapt to financial challenges and in loyalty to its customer base. A business strategy that is implemented in consideration of corporate values is more likely to be beneficial in the long term. Furthermore, stability is a critical factor for any financial organization to attract investment.
References
Houssain, K., & Khan, R. (2016). Corporate social responsibility (CSR) in banking sector: An empirical study on the Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) Limited. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 18(4), 53-61. Web.
HSBC. (n.d.). Company history. Web.
HSBC Holdings plc. (2017). Strategic report 2016. Web.
Kynaston, D., & Roberts, R. (2015). The lion wakes: A modern history of HSBC. London, United Kingdom: Profile Books.
Trudeau, C., & McLarney, C. (2017). How can banks enhance international connectivity with business customers?: A study of HSBC. IUP Journal of Business Strategy, 14(2), 20-39. Web.