Introduction
Urbanization in most countries has over time resulted in the creation of cities, whose inhabitants set up central locations where trading and business happens and set them apart from the residential areas, where they retire to after a day’s work. The business districts usually have shopping malls and arcades as well as offices, from where various types of goods and services can be accessed.
In order to access these particular areas, individuals have to commute from the residential areas using either public transport or personal means. This daily commute ends up creating lengths of traffic jams as individuals travel to the business districts to either sell or purchase goods and services. This had been the common trend of business until a few years ago when the internet emerged.
In its advent, systems have been developed to help connect the consumers of goods and services with the primary providers, without having them leave their residence. Companies such as eBay and Amazon have enabled producers of commodities to set up warehouses in remote areas and then display their products online for consumers to buy. Customers pay through online payment facilities such as PayPal and the goods are delivered to them. When it comes to provision of services, some careers such as print journalism allow individuals to work from remote areas, and then submit their work over the internet.
These platforms for trading have reduced the need for everybody to travel to one central location in order to access or provide goods and services, ultimately reducing the number of commuters on the roads. This report seeks to provide a concrete explanation of the ways that e-commerce has helped reduce traffic congestion in urban areas, hence making life in such regions easy for inhabitants. The report shall principally focus on the elements of e-commerce in relation to commuter-life in cities. Any other ways in which e-commerce has helped improve city life that are not related to traffic, shall be left out because they will be out of the scope of the current discussion.
Core concepts
E-commerce: How e-commerce works
E-commerce fundamentally works the same way that traditional businesses do, but with the elimination of expansive physical business spaces. This has been affirmed by Krisdiany that “the greatest and the most important benefit of e-commerce is that it enables a business concern or individual to reach the global market” (Krisdiany, 2001, p. 4).
In the simplest form of e-commerce, the merchants of goods and services display their products on a website, outlining the price of each product. The customer, from any part of the world, visits the websites and identifies the product on sale. He then chooses the ones that impress him and adds them to a digital cart. The customer then completes the payment using either a credit card or any other online payment system. The customer then delivers the product to the customer, using whichever shipping method is acceptable.
The rise of e-Commerce
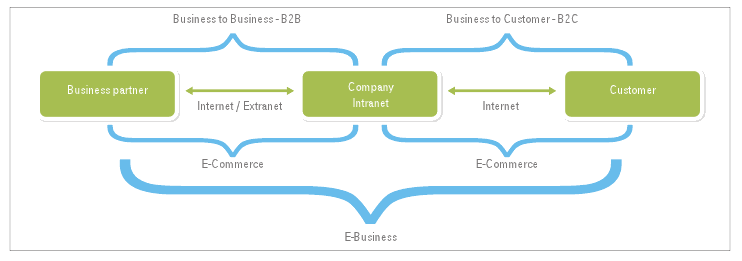
“Electronic commerce is a rapidly growing area enjoying considerable attention in conjunction with the emergence of the Information Superhighway or the building of the National Information Infrastructure (NII)” (Wigand and Benjamin, 1995, para. 1). The growth of e-commerce has been fundamentally been propelled by the increase in popularity of both business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) forms of marketing (Mokhtarian, 2003, p. 3). B2B marketing occurs when a company sells a commodity to another company, which is also interested in selling the product at a profit (Browne, 2001, p. 5).
For instance, manufacturing companies make goods and then distribute them to supermarkets at wholesale prices. The supermarkets then make profits by selling the same products at higher prices, but in retail. B2C marketing is the when a company sells directly to the consumer. For instance, companies dealing with wedding card production might chose to have the customers visit their offices. In this arrangement, the company makes money directly from the consumer. Figure 1 below shows the difference between B2B and B2C E-Commerce.
Reasons for the rising in popularity of e-commerce
There are a number of elements that have made e-commerce attractive to both consumers and producers of goods and services. First, it is the lack of taxation. Selling on online platforms does not subject a company to the kind of taxes they would have been handed had they been selling from a physical location. This has been the reason why companies have embraced the idea, because it eventually leads to increased profits. In addition, e-commerce provides the ability to buy and sell at any time of the day all-year round.
Another factor that has led to the rapid growth of e-commerce is the variety of retailers available on the internet. Customers find it easy to shop online because they can compare the prices and quality of products from different companies by the click of a button. In this regard, international business is not affected by differences in time zones, further maximizing the profitability of a company. An increased penetration of the internet in most countries has also served to make e-commerce more popular. Table 1 below provides a summary of the features that make E-commerce attractive.
Source: own generated
Greatest beneficiaries of e-commerce
Even though almost any company stands to make gains through e-commerce, some have gained more than others have. Online travel is one of the industries that have benefited greatly from the advent of e-commerce. This is because individuals can make hotel, airline and car-rental bookings from any part of the world. By ruling out the need for a physical location of an online travel company’s offices, the providers of the services are able to increase their profits. The makers of consumer electronics and clothes are the other great beneficiaries of e-commerce.
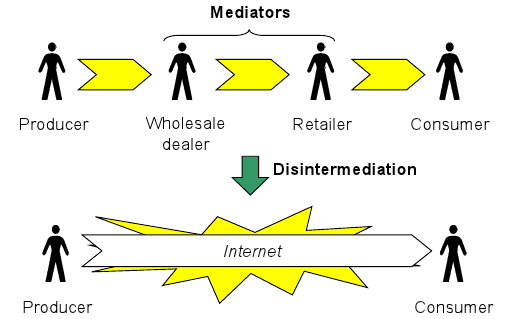
Consumers have learnt that it is much cheaper and convenient to look for electronics and clothing items online. This is because the customers can directly link directly with the company from any part of the world, eliminating the intermediaries that cause the costs to go up as illustrated in Figure 2. By increasing their reach to cover the entire world through online marketing, consumer electronics and cloth manufacturers are able to make more profits.
Traffic congestion
The impact of traffic congestion on financial resource
Traffic congestion is one of the elements that lead to losses for both businesses and their customers. Millions of dollars are lost every single day as consumers make commutes to business districts. Information released by the United States census data indicates that the average American citizen spends at least 50 minutes driving to and from work every day. According to these statistics, an average American commuter is stuck in traffic for average of 34hours every year. This leads to an average cost of $713 dollars per consumer going to extra fuel spent in traffic delays.
The impact of traffic congestion on the health of an individual
Traffic congestion has an effect on an individual’s mental and physical well-being. By sitting in a traffic jam, which they have no control over, individuals end up feeling helpless and stressed. By exposing an individual to such circumstances on a regular basis, they may end up developing stress-related illnesses such as high-blood pressure. As far as physical health of individuals is concerned, sitting in a traffic jam limits the movement of the person by confining him to a particular posture.
The gases inhaled in the period that the drive is stuck in the traffic jams also have a negative impact on his health. According to an article published on the Wall Street Journal,
“New public-health studies and laboratory experiments suggest that, at every stage of life, traffic fumes exact a measurable toll on mental capacity, intelligence and emotional stability,” (Hotz, 2011, para.2).
E-commerce and traffic
One of the elements of traditional business processes that e-commerce has eliminated is the need for customers to travel to physical shops in order to make purchases. E-commerce has also led to a decline of the need for providers of certain services to travel to fixed offices in order to serve customers. Reducing the number of individuals on the roads travelling to one central business district has helped make life in most cities much easier as individuals do not have to subject themselves to the pressure of sitting in traffic jams for hours in order to buy a product or access a service.
Secondly, because a good number of people opt to use e-commerce as opposed to tradition forms of buying and selling, then number of vehicles on the road at any particular moment has gone down, lessening the length of traffic jams. This is further heightened by the fact that most companies that offer e-commerce services transport the goods at night.
Conclusion
This report had set out to explain how e-commerce has served to help make life in cities better by eliminating the stresses associated with traffic jams. To this end, the e-commerce process was clearly evaluated, alongside the advantages that have made it a popular avenue of conducting business. To shape the discussion, the effects of traffic jams on people’s health and financial well-being were explained. Later, a link was drawn between e-commerce and a reduction in traffic on the streets.
It is worth noting that the topic of discussion was a broad one and that in no way was this particular report conclusive. Further research needs to be done on the topic in order to find out if the length of time per week that individuals spend commuting went down after they starting using e-commerce. Such research was beyond the scope of this report. Table 1 below provides a summary of the discussion.
Recommendations
E-commerce alone is not going to reduce the problem of traffic congestion in cities. Companies need to put concerted effort to ensure that they make full use of available technology, in a bid to cut down the need for workers to commute to places of work on a daily basis. For instance, the use of simple technology like Skype can help simulate office set-ups, thus allowing the members of staff to serve from any place around the world. Educating people on a change of attitude is another step that both companies and governments can use to help reduce the problem of congestion arising from commutes to and from markets. Individuals need to be made aware that travelling to business district to buy something ends up wasting both their time and money.
Reference List
Browne, M. (2001). The impact of e-commerce on transport.
Hotz, R. (2011). “The Hidden Toll of Traffic Jams.” Wall Street Journal. Web.
Krisdiany, K. (2011). Green E-Commerce.
Mokhtarian, P. (2003). A conceptual analysis of the transportation impacts of B2C E-Commerce. Web.
Norris, M., West, S. & Gaughan, K. (2003). “E-commerce: Concepts and Technologies.” Harbug.
Sonntag, R. (2004). Whitepaper B2B E-Commerce: Using hidden potential.
Wigand, R. & Benjamin, R. (1995). Electronic Commerce: Effects on Electronic Markets. Journal of Computer Mediated Communication, 1(3), 1-10.