Introduction
- The Kurdish question in the 20th century.
- Major stakeholders.
- Kurds and foreign policy.
The Kurdish question emerged at the beginning of the 20th century, but it still remains unresolved. On the one hand, some nations support Kurds in their fight for their self-determination. On the other hand, some countries see these efforts as terrorist activities and a threat to their wellbeing. The primary stakeholders involved in the associated conflicts are Turkey, Syria, Iraq, as well as the USA, Iran, and Russia (“Who are the Kurds,” 2019). This ethnic group is trying to gain its independence or, at least, to get basic rights in the territories where they have lived for centuries. At the same time, these people became the force that has been used by different actors to address certain geopolitical issues.

Historical Background
- Historical territories of Kurds.
- The aftermaths of the First World War.
- The 1920 Treaty of Sevres.
- The 1923 Treaty of Lausanne.
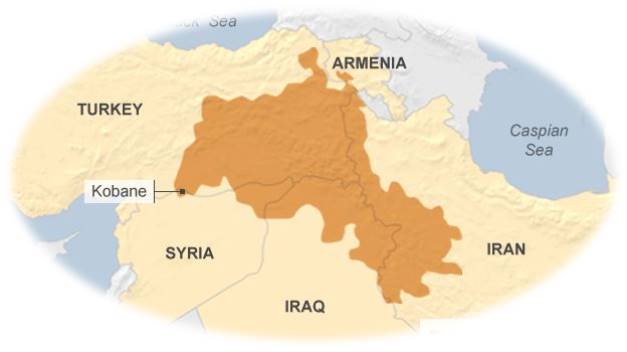
For centuries, Kurds inhabited the Mesopotamian plains that are now a part of such states as Turkey, Armenia, Iran, Iraq, and Syria. This ethnic group had to live under the rule of the Ottoman Empire, but when it ceased to exist after the First World War, Kurds tried to earn their independence (“Who are the Kurds,” 2019). The Big Four countries were rather positive regarding the creation of the Kurdish state, which was mentioned in the 1920 Treaty of Sevres. However, three years later, when the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne was signed, Kurds lost their hopes as they were torn to be ethnic minorities of the countries mentioned above.

Kurds in Turkey
- Turkish Kurds seen as a threat to Turkey.
- Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK).
- Victims and destruction.
- Outcomes of the conflict.
The Turkish government has seen Kurds as rebels who undermine the wellbeing of the country by their uprisings. Kurds’ claims and their fight for independence in the 1920s and 1930s become one of the open wounds in the relations between Turkish officials and Kurds. This ethnic group makes up almost 20% of the Turkish population (“Who are the Kurds,” 2019). However, Turkey does not recognize these people’s right to self-determination, which has led to various massacres and armed conflicts. Kurds’ language and their culture were subject to serious oppression. The Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK) was established by Abdullah Ocalan in 1978, and this force became a uniting element for Kurds living in the Middle East. Since the late 1970s, approximately 40,000 Kurds were killed or displaced within the boundaries of Turkey.

Kurds in Iraq and Syria
- Limited freedoms and rights.
- The Islamic State and Kurds.
- Primary reasons for the conflict.
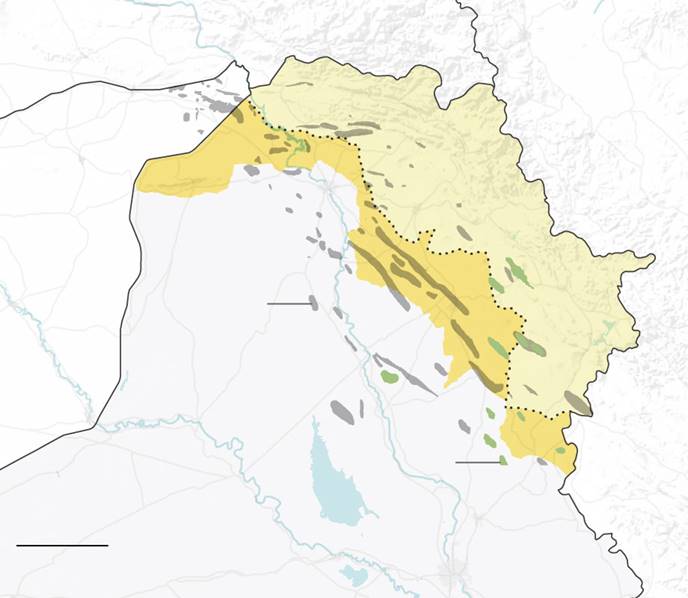
In Iraq and Syria, Kurds enjoyed more rights and were not oppressed with the intensity Turkey displayed. However, this population still had a few rights and freedoms to develop properly. The Islamic State, a jihadist group that emerged after the fall of the Iraqi government in the 2010s (“Who are the Kurds,” 2019). The terrorist group, IS, tried to cease control over the entire territories of Iraq and Syria while Kurds (such forces as People’s Protection Units (YPG)) tried to resist. Apart from the claims for political power in some areas, the IS tried to occupy the territories that are rich in oil and gas (Peçanha, 2017). Kurds try to defend their homes and prevent the complete destruction of cities under the control of IS.
International Relations
- Fight for independence and peace in the Middle East.
- Forces against the IS.
- Iran, Israel, and the USA.
- The USSR and Russia.
The Kurdish question has been associated with the overall peace in the Middle East as this ethnic group remains one of the most oppressed populations in the region, which leads to conflicts. The inability of developed countries, international institutions, and the countries of the area solve the issue has led to numerous deaths and the devastation of vast territories. In the 2010s, Kurds also became one of the primary forces resisting the rise of the IS. Although the input of the Kurds in the fight against the IS can hardly be overestimated, these people are often deceived or neglected. Iran, Israel, and the USA have supported Kurds in Turkey, Iraq, and Syria, while the USSR and modern Russia tended to support the governments of Iraq and Syria. These countries try to solve their geopolitical issues and often use the Kurds and their fight as a tool to achieve their goals.

Conclusion
- The Kurds in the Middle East.
- The Kurds in the international arena.
- Can the Kurdish question be solved?
The Kurds had a chance to create their own state after the fall of the Ottoman Empire, but the major actors in the international arena took this opportunity from them. The ethnic group became divided into territories pertain to different countries. The modern world is as hostile to the Kurds as it was decades ago. The IS is trying to take control over certain territories, while Kurdish groups have contributed greatly to many nations’ efforts to stop the spread of the Islamic State. The involvement of larger countries and their military and financial support have made the conflict lasting and devastating. The Kurdish issue is unlikely to be solved any time soon since the territories this population inhabits are still divided among several larger states.

References
Peçanha, S. (2017). How the Kurdish quest for independence in Iraq backfired. The New York Times.
Who are the Kurds? (2019). BBC.