Executive Summary
The case study reviews the internationalization process of the Chinese company Huawei. In particular, it analyzes the past experience of the enterprise in terms of expanding into the US market and sheds light on the company’s strategic decisions regarding its attempt to re-enter this market. It is recommended that the company form strategic alliances with domestic leaders to pursue several tactical goals. In addition, emphasis should be placed on the importance of diversifying the company’s product portfolio. However, most importantly, the company is advised to allocate resources toward the development of innovations to be able to enhance the quality of its manufactured goods.
Company Background
Huawei is a transnational Chinese company with headquarters in Shenzhen, China. At present, this company is the largest manufacturer of telecommunications equipment in the world. The company is engaged in the creation of telecommunications networks, the provision of a variety of related services, and the production of equipment in both the domestic and foreign markets. The company employs more than 140,000 employees (Huawei, 2016).
It is important to note that 46% of all Huawei employees are engaged in research and development (R&D) (Liu & Zheng, 2013). The research centers of Huawei are located in many countries around the world. In addition, the enterprise has partnered with 28 innovative institutions that are leaders in global technology development. Due to this cooperation, Huawei has received more than 31,000 patents over the past year alone (Liu & Zheng, 2013). In addition, the company makes a significant contribution to the development of global industry.
Huawei individualizes its products to the needs of various consumer groups in order to remain competitive. The company manufactures unique products and offers technological know-how along with cheaper services for customers through multimillion-dollar contracts with local mobile operators (Liu & Zheng, 2013). It is also crucial to note that for many years, the cost of foreign transactions has been exceeding costs in the domestic market.
Despite such an impressive executive summary, it is essential to stress the fact that attaining market share in the US has been rather challenging for Huawei. Indeed, the company found itself in several controversies, after which its image was undermined strongly. In the aftermath, Huawei was accused of copying rival technologies and was forced to cease distribution (Shaolong, 2016). In addition, the US government has banned several operations initiated by the company. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the challenges and barriers that the company may face when attempting to expand into the US market again.
Country Background
One important fact to consider is that the American telecommunications market is quite influential, occupying the second place in volume only after the Chinese market. However, many companies face a number of country-level difficulties that do not allow them to enter the market of American industry. In particular, telecommunications networking and commodity manufacturing are typically controlled and supervised by public authorities.
This control also includes overseeing sales. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is the main body in this regard in the United States, and a 1934 legislative act regulates the flow of investment into the country from foreign states and enterprises (Tao & Chunbo, 2014). These measures are aimed at protecting national interests and US citizens as well as maintaining state security. The described levers of state control enable federal authorities to revoke licenses for violations of the law.
In addition, they can prohibit the signing of contracts and deny the transfer of information. However, most importantly, in the United States, ownership of more than 20% (or 25% under certain conditions) of the communications technology industry by international companies is prohibited. This ban has been applied at the legislative level, and any foreign investment exceeding this margin is blocked.
Entry Strategy
Given the company’s past experiences, Huawei should pursue a global development strategy in the US market. Superior organization should be the central point of the strategy. To be more precise, emphasis should be placed on the effective coordination of organizational units with business solutions agreed on centrally. In order for this approach to be effective, it is necessary that the company follow several strategies.
First, it is crucial to develop a commodity presented in the home market and then enter the US market with a product portfolio that is adapted to the local needs (Tao & Chunbo, 2014). Second, since the American market is developed, it is necessary to offer business solutions aimed at reducing the costs of local operators.
Third, development and refinement of Huawei products should occur through collaboration with scientific and research centers and the subsequent creation of joint ventures (Liu & Zheng, 2013). Fourth, it is important for the company to compete with global players. Thus, the competitive advantage of the company will be the production of a high-tech product at a moderate price, wherein the costs of production will be lower than that of world leaders.
However, the prices for such products are falling. According to experts, prices will continue to fall by 10% on average, which may negatively affect the organization’s ability to provide software and enhance network quality and bandwidth. In order to remain competitive, the company will need to modernize its products and take into account the rapid development of the industry, as this leads to the fact consumers are faced with an increasing range and choice (Shaolong, 2016).
The company needs to expand the infrastructure of key markets, manufacture technologically sophisticated solutions, and achieve product diversification. The current strategy of Huawei has been focused on the creation of a mobile broadband network operating on gigabit traffic (Shaolong, 2016). Nevertheless, experts recommend developing an optical network that will be more operational but less expensive to maintain. Also, it will be important for the company to build an infrastructure in the US market in order to centralize data and data points.
Interestingly, electrical components are the main raw material in the production processes for Huawei (Tao & Chunbo, 2014). Given the nature of the industry and the low possibility of new entrants, Huawei should acquire higher-quality (and more expensive) raw materials from reliable suppliers. Consequently, the diversification of raw materials will be insignificant, and it will be possible to shift suppliers as necessary while reducing their power.
Marketing and R&D Strategies
Importantly, the company should customize the marketing mix. Huawei should employ price skimming so that management can recover costs. In addition, a particular emphasis should be placed on the company’s positioning strategy due to its previous negative experience in the country. Positioning should be aimed at addressing customer needs and reaching its main target groups (Wild & Wild, 2015).
In addition, product attributes, benefits, and offerings should be refined in accordance with US consumer requirements. As for promotion and advertising, each of these measures should be targeted at producing a positive client response. The target audience can be reached through broadcast media, and the heaviest advertising should be employed in major areas so as to attract the attention of the general public.
At present, the company has already decentralized R&D. In particular, in the United States, the company has a research center for the development of innovations (Huawei, 2016). In it, Huawei employees have access to the latest developments and can exchange them at a level still unavailable in China. In terms of expatriates, these workers share the latest methods and information on production technology with their Chinese colleagues. Therefore, the company’s innovative system works in such a way that employees from different countries transfer developments and complement each other’s expertise in order to strengthen the company’s position and achieve competitiveness.
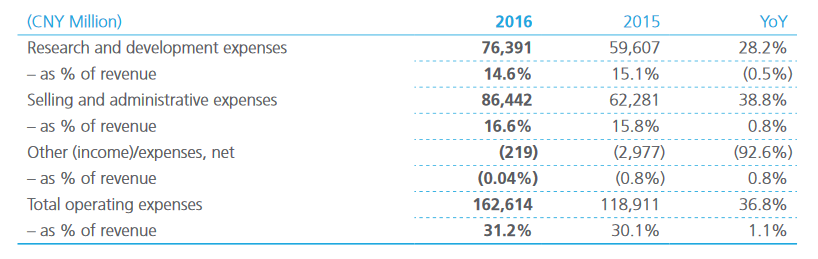
However, in the past financial year, the resources allocated to R&D have decreased by 0.5% in relation to the increased revenue, as evidenced in Chart 1 (see Exhibit below). Interestingly, Chinese researchers who return to China from the US R&D center modernize the production there. Thus, the existing knowledge cycle allows for the transfer of new technologies and developments to all branches of Huawei. Consequently, as a result of further internationalization, the company will be able to continue to acquire new technologies and modernize the existing arsenal of developments for the creation of new assets and their further distribution (Wild & Wild, 2015).
Opportunities and Challenges
One of the greatest challenges that Huawei currently faces is linked to the company’s reputation in the US market, which was undermined after the occurrence of intellectual property infringement. In addition, the greatest threat to the company’s internationalization is the US government, which has rather rigid conditions governing the activities of foreign firms (Tao & Chunbo, 2014). In this regard, Huawei needs to cooperate with national companies in order to gain the trust of the government and collaborate with US-based innovation development centers to avoid the possibility of violations.
The low risk of new competitors is one of the opportunities for internationalization. The company produces inexpensive but high-quality commodities, which will intensify competition in the market among existing leaders. Thus, the company will need to raise the interest of American manufacturers and form contracts with the main players in the market (Tao & Chunbo, 2014).
Moreover, Huawei needs to build trust and expand the workforce by attracting American employees in order to take into account the cultural characteristics of management (Wild & Wild, 2015). In general, the main opportunity for the company in relation to the US market is the creation of next-generation devices and services. They will be more effective from the buyers’ point of view and will be more accommodating to legislative regulations.
Evaluation and Conclusion
Overall, it can be concluded that Huawei should continue to adhere to its strategy of building global collaborations. In order to avoid direct competition, it is strategically important for the company to cooperate with world industry leaders to benefit from existing competitive advantages (Liu & Zheng, 2013). With the help of strategic alliances, Huawei will be able to achieve relatively cheap production. In addition, the company will be able to develop innovative processes to improve commodities.
In general, the global strategy of Huawei should strive to change the focus of activities toward the creation of services correlated with world technological standards and the expansion of infrastructure (Wild & Wild, 2015). In addition, the production of more sophisticated technological solutions and the diversification of products will allow the company to achieve greater competitiveness in new markets.
References
Huawei. (2016). Huawei Investment & Holding Co., Ltd. 2016 annual report. Web.
Liu, X., & Zheng, X. (2013). From technological imitators to technological leaders: Evidence from Huawei case study. International Journal of Technology, Policy and Management, 13(1), 1-14.
Shaolong, Y. (2016). The Huawei way. New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Tao, T., & Chunbo, W. (2014). The Huawei story. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Wild, J., & Wild, K. (2015). International business (8th ed.). New York, NY: Pearson.
Exhibit