Introduction
Innovation is a key attribute of a successful business, particularly in the technology sector, which allows companies to grow and adapt to changing markets and the global economy. Innovation is characterized by challenging conventional notions, creating new frontiers, and applying meaningful strategy to fulfill consumer needs. Apparently, with the fast rate of technological development, innovation in the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) industry is becoming inevitable. It is the only platform left for players in the industry to leverage competitive advantage (He n.d.).
With the knowledge that modern consumers of products in this sector go for products that are in tandem with the latest technology, ICT companies are becoming more innovative and recruiting skilled manpower to keep up with the competition in the market (“Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.” 2009). One such company is Huawei Technologies, a Chinese telecommunications and consumer electronics conglomerate which transitioned from a primarily regional player to a global corporation that is amongst the top industry leaders. Huawei has developed a strategy of aggressive innovation and business growth to enter new markets by providing high quality, market breaking products at lower prices than its competitors.
2009
The inception of Huawei into the ICT industry can be traced back to 1987 when the company entered the market, amid vast competition from existing players like Samsung. By 2009, Huawei was already experiencing its first breakthroughs in the international market. 2009 was a challenging year not only for the telecommunications market but also for the global economy. Even so, the Huawei’s 2009 report indicates that the company weathered the storm and maintained an upward curve in terms of ROI. For example, the company recorded increased its sales by 19% from the previous year, recording a net profit margin of $2.7 billion.
Huawei’s profitability at this time can be attributed to its relationships with telecom operators as well as the expansion of the business in the global market to 14.1% (“Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.” 2009). In addition, the emergence of the 3G network allowed for Huawei to expand its operations in key areas of network infrastructure, software, professional services, and devices. Furthermore, in 2009, Huawei saw major changes to its organizational structure and internal processes to improve efficiency and service delivery (“Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.” 2009).
Innovations
Just over two decades into its launch, Huawei had already taken its position in the ICT sector through customer-centric innovations. The company invested heavily in its R&D department in order to ensure that the quality of its products in the market was comparable or even surpassed those of giant players like Samsung and Apple. The organization’s efforts had already borne fruits. For example, the company launched the LTE/EPC network, one of its own kind in the world, and which was first operated in Oslo, Norway (Drahokoupil, McCaleb, Pawlicki & Szunomár 2017).
Secondly, Huawei became the first telecom company to launch an end-to-end 100G solution from the routers to transformations systems. With the aid of this network, the 2009 report shows that operators were able to build ultra-broadband networks that provide high quality services to the consumers. For instance, the ultra-broadband network allows consumers to access high-definition videos. Lastly, 2009 saw Huawei step up its production of smartphones by launching Android-powered gadgets such as U8220 and U82230. The smartphones were among the most competitive in the market at the time.
Business Model
A business model refers to the strategy an organization intends to use to create value and make revenue. Like any other organization, Huawei’s business strategy is based on parameters such as key partners, key activities, key resources, customer relationships, customer segments, cost structure, revenue streams, and channels. By 2009, Huawei Technologies had already obtained partners such as developers, integrators, electronic suppliers and universities that assisted in R&D.
The main activities of the organization ranged from businesses such as IP networking and routers, to design, manufacturing, end-to-end delivery and service, and support. The resources owned by Huawei at the time included telecom equipment, R&D institutes, intellectual property, and its workforce.
The customer relationships were majorly based on price, service and support, trust and leadership. Huawei market segment was massive public – no specific target market. The channels for marketing Huawei products include corporate and regional offices, dedicated team of sales, retailers, social networks such as Facebook and Twitter, among others. The main streams of revenue at the time were majorly the sale of devices, network operations, consulting and engineering services, business solutions, and service contract fees.
Organizational Culture
Huawei’s organizational culture was initiated at the very birth of the company in 1987. The organization set out its acceptable values and code of conduct that was to be followed by all stakeholders. Of key interest then, as it remains now, was to create a pool of loyal customers by streamlining its services and products to meet customer needs. By 2009, Huawei’s annual report illustrates the progress the company had made in cultivating its unique culture in the telecom industry.
2019
Recent years have seen Huawei become a household name in many countries, particularly due to its rapid development of consumer devices alongside telecommunications networks. Huawei has increased its business and reputation through the growth of 4G networks in most developed countries and a gradual transition to 5G. Also, it now offers a wide range of smartphone devices, particularly in the low- to mid-range price point, while having many features of flagship devices which appeals to markets of developing countries (Han & Sohn 2016).
However, Huawei has faced some challenges regarding its association with the Chinese government and accusations of patented technology theft from other firms. Overall, the company is in a much better state than 10 years ago and has demonstrated significant innovation on every front.
Innovations
In 2019, Huawei has already become a household name in the telecom industry. The company’s investment in R&D across all its branches around the world. This includes the Y7 smartphone that was launched in 2018, and which has managed to compete with the latest models from companies like Samsung and Apple.
Business Model
Key partners: Since 2009, Huawei has received many partners that are helping the organization to work towards its objectives. These include the Huawei Partner Network, the Ascend, and MediaPad brands, MIT Communications Future Network as well as joint ventures with other telecom companies like Motorola, Siemens, and Telecom Venezuela.
Key activities
Huawei has stepped up its endeavors through diversification of operations and activities. Currently, the company engages in training, design, manufacturing, marketing, and sales, installation and integration of networks as well as training and certification programs.
Key resources
Huawei’s key resources include a pool of more than 170, 000 employees, telecom equipment, 21 research and development institutions, production and deployment process, know-how, intellectual property, Nexus 6P – co-designed and manufactured by Google,
Value propositions
Huawei boasts as one of China’s leading manufacturer of telecom equipment. Other than the normal telecom operations, Huawei also makes devices that are used in cloud computing. In addition, it provides top-notch technology that is used in the telecom industry.
Customer relationships
Through the creation of quality products and valuable technologies, Huawei maintains customer relations by fostering trust through efficient customer service and support that prioritizes customer satisfaction and loyalty. In addition, the company has a dedicated team of sales that ensure maintains the presence of Huawei’s products in the market. Huawei’s co-production with other companies such as Google helps to ensure that the company’s reputation remains intact in the market. The most important aspect of customer relations is arguably the pricing of Huawei’s products. The company has streamlined its products to endure that people of all financial levels can afford Huawei products. This strategy helps the organization to retain its customers.
Customer segments
Huawei’s customer segments include the massive (mobile public), governments, public safety organizations, media and entertainment, finance, and educational institutions.
Cost structure
To become a global player in the telecom industry and to compete effectively with established rivals in the industry, Huawei Technologies is left with no other option but to invest heavily in the venture. Therefore, the current cost structure leans heavily toward large expenditures (see Fig. 1). Some of the areas that cost the company include employees, facilities, manufacturing and distribution, deployment, operations, marketing, taxes, sales and support, machinery, parts, and components as well as data centers and marketing.
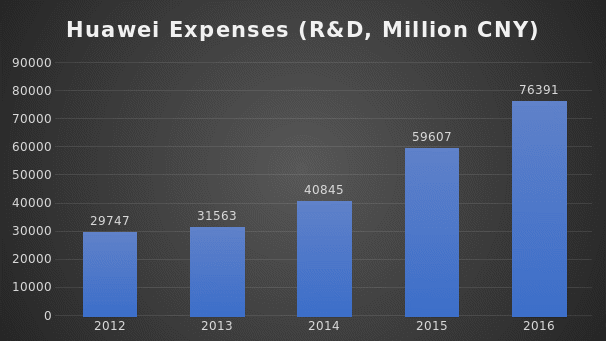
Revenue streams
Huawei gets its ROI from different sources. For example, the sale of devices, network integration services, network operation, engineering, and consulting services, assurance service like public safety and learning services, business solutions and service contract fees. All these revenue sources are responsible for the company’s overall sales and net profit margin.
Channels
The marketing strategy of Huawei products involves different channels of distribution. These include regional and corporate offices scattered in 170 countries, retailers and dedicated salespersons, contact centers, its website, and social networks. The role of all distribution channels is mandated with the role of ensuring that the company’s products are availed in the market at the right time and in the right condition.
Organizational Culture
Organizational culture refers to the beliefs, values, and attitudes that are shared by all stakeholders and which are considered to be the drivers of the organization’s success. In essence, an organizational culture depicts what the organization is known for by the external environment. Huawei’s culture is embedded in what they call the wolf-culture. Wolves are peculiar animals that portray some interesting features that are worth emulation.
For example, the bloodthirsty character of wolves is emulated by all employees in the organization because they are highly sensitive to market dynamics and are ready to respond to any changes that take place. Secondly, wolves are generally resistant to cold. This implies that the employees of Huawei are unmoved by difficulties – they face their challenges head-on irrespective of the degree of difficulty involved.
Additionally, the wolf-culture is embraced because wolves are known to do things in teams. All the members of Huawei are encouraged by the management to consult one another and share opinions that can be helpful to the organization. Extant studies show that team building is a virtue that many organizations in the modern world rely upon to foster innovation and creativity within an organization. Experts attribute this to the fact that people are designed to think differently, and the varied opinions given by different people can be combined to solve the problem or develop a new product.
Another important feature of Huawei’s organizational culture is being customer-oriented. All the ventures the organization engages in are meant to improve customer experience and satisfaction. For example, the innovations mentioned above were intended to improve the quality of services offered in the telecom industry and avail affordable but quality products in the market. In doing so, however, Huawei is keen on the sustainability aspect of its development – especially with regards to the protection of the environment.
To this end, the company had, by 2009, implemented the use of more than 3, 000 alternative energy sources to power its operations around the world. Such a move implies that the organization is concerned about the sustainable development of both the telecom industry and society.
Arguably, members of Huawei know pretty well that integrity is at the embodiment of success in the telecom industry as it is for any other industry. As such, the company ensures that all its stakeholders conduct themselves with the highest ethical standards. Through its customer care service, Huawei ensures that it retains its customers by fulfilling its promises and providing the quality of products they promote through various platforms.
2029
Recently, Huawei has announced that it plans to overtake Samsung as the leading smartphone manufacturer. It plans to continue its aggressive expansion in the market, producing quality phones of all price ranges which would allow it to enter more markets globally as smartphone adoption increases. Furthermore, Huawei continues to invest in telecommunications infrastructure as it will continue to produce more efficient networks past the 5G generation. Other areas of growth include artificial intelligence and nanotechnology which can be adopted into telecommunication networks and devices. Overall, Huawei’s future is focused on rapid innovation and widespread adoption of its devices, ensuring its lead position as a telecommunications conglomerate.
Innovations
Huawei regards innovation as the driver of the telecom industry. This implies that a company that demonstrates the ability to come up with new quality products based on the latest technology are likely to receive more customer satisfaction feedback and therefore increased sales. The company’s design and innovation departments are forecasting that the 5G network is going to be a game changer in the world (Lin 2017).
With a speed of up to 5Gigabyte/s, the 5G network is going to revolutionize operations in the telecom sector and increase the speed of service provision via the internet. In light of this, the company plans to incorporate the network in its products within the next decade. Secondly, Huawei plans to increase the quality of its products as has been the case since its inception 30 years ago (Lin 2017). For example, the Y7 model that was launched early in 2018 has received a lot of reviews from customers who view the product as one of the best smartphones in the market today.
Business Model
Going into the next decade, Huawei’s business model is expected to have transformed to a significant extent. The company is planning to leverage effective leadership and intensify its marketing campaigns to deal with the increasing competition, especially in the smartphone sector. To achieve this, the company will redesign its website and social network advertising platforms in order to tap into the vast online market that has been increased by an increase in internet connectivity. In the same breath, the company plans to revamp its e-commerce platform in all 170 outlets around the world. This will ensure that customers can access, compare, and purchase Huawei products from the comfort of their homes. Such a move will be effective in increasing the company’s market share in the industry.
Customer relations is another segment that the company intends to look into within the next decade. This is a sensitive area because modern employees are concerned with the level and quality of customer care and service they receive. As would be expected, customers tend to buy goods from companies that treat them with respect and decorum. In light of this, Huawei seeks to increase the number of customer centers in every country. According to the organization’s projection, this will aid in helping the company to get primary feedback from real customers, and thus make the necessary rectifications that can guarantee customer satisfaction.
Also, Huawei’s model on key activities is likely to witness major changes by 2029. The company plans to increase the number of products and services offered to its customers. To achieve this, Huawei will be compelled to invest heavily in the R&D sector and acquire more production machinery and qualified manpower. Also, the company will be forced to increase the number of its collaborative research partners such as universities.
This will enable Huawei to upscale its implementation of the 5G network that could see many customers scramble for the company’s products. This will undoubtedly be a game changer. Overall, the company plans to maintain high high-end work ethics and world-class customer service that will see the company pose a threat to its rivals in the industry. Further, this business model will only be achieved if the company revisits its leadership and management structure. People who in leadership positions who are unfunctional must be demoted or retrenched and replaced by other competent leaders who can steer the company’s agenda going into the future.
Organizational Culture
10 years from now, the leadership of Huawei believes that the organization will have made many strides ahead in terms of customer experience and sustainable development. Several plans are in the company’s radar with regards to fostering its organizational culture and coping with any necessary adjustments in the next decade. To begin with, Huawei plans to streamline its customer care services across all the 170 and more countries that it operates. Basically, this would mean paying more attention to feedback and encouraging professional service delivery by all its staff.
According to the management at Huawei, they project that efficient customer service is going to increase the company’s market share and put the company in an even better position to compete effectively with other rivals in the industry. Moreover, the company believes that customer-centric innovations are the drivers of any successful technology. Huawei intends to develop products that will meet the needs and imaginations of customers and make them realize the value for their money.
Secondly, with the increasing effects of climate change, Huawei has been at the forefront in the campaign against global warming. Accordingly, the company plans to expand its safe energy operations by embracing the use of alternative sources of energy. This will help the company to serve as an example and encourage other telecom companies to do the same.
The third aspect that Huawei seeks to foster its organizational culture is teamwork. The management is working on a plan to ensure that all Huawei employees around the world collaborate in working towards the company’s goals. This will be achieved through career development and exchange programs that will be implemented by the company’s leadership within the next 10 years. Such programs will ensure that the organization attains workplace diversity which an important driver of innovation.
Discussion
As global society has entered the era of information and communications technology (ICT) which has experienced agile evolution, Huawei has taken a leap into adapting it as part of the business plan. ICT is inherently transparent and customer-driven, with technology and infrastructure centered on innovative technologies such as the cloud for collaboration. Over the last 10 years, numerous enterprises have undergone a digital transformation, and many more will continue to do so leading up to 2029.
Huawei has greatly benefited from this, offering its technologies and services for a number of purposes in order to implement innovative products, services, and customer support (“New ICT Drives Innovation”). Comparing Huawei’s image, products, business model, and culture over the last decade and predicting its growth to 2029, highlights the necessity of innovation to prosper in the competitive telecommunications sector. Huawei is ultimately able to do so through a competent approach to marketing and developing consumer devices which fill in vital market gaps and push the industry forward.
Table 1. Changes in Huawei (2009-2029): Overview.
As Table 1 shows, Huawei has made an impressive leap in its progress by deciding to focus on and invest in the development of ICT and the related technology. The company has shifted from the unorganized and traditions-driven local firm to a global corporate entity that encourages the active professional, cultural, and technological growth. In retrospect, the shift toward incorporating non-incremental innovations into the context of the firm and creating opportunities for enhancing the corporate growth are the key success factors that have allowed Huawei to gain its current level of popularity. The company has gained significant social and strategic advantages due to the current business model and corporate values deployed in its setting.
Another significant change that was made by the company in order to boost further development concerns the corporate culture and values. Specifically, the introduction of diversity and the active promotion of cross-cultural communication has led to interdisciplinary cooperation and knowledge sharing. The latter, in turn, has created premises for the transfer of the company from a typical company to a corporation that is capable of making a difference in the target market.
Huawei has shown the propensity toward retaining the traditional values of diligence and loyalty, yet it has also become open to other changes, which encompass the ability to meet diverse customers’ needs, the skills of controlling the cultural change and gearing it toward the enhancement of communication with potential customers, and other important alterations. Thus, with each innovative solution proposed to the corporate setting over the past 20 years, the ones that can potentially contribute to further progress have been selected meticulously. With a well thought-out decision-making framework and a set of values aimed at development and meeting customers’ needs, Huawei is likely to remain at the helm of the global IT market in the future.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, it is apparent that Huawei has moved a long way since its entrance into the ICT industry in 1987. The company has managed to take a position in the industry, managing to compete with giants like Samsung and Apple. A mention of Huawei today would leave one imagining the latest smartphone or technological solution that has been fronted by the organization that is headquartered in China.
With Huawei now operating in at least 170 countries, its business strategy and lessons from the past mistakes will enable it to become a force to reckon in the telecom market share. It is in the view of this fact that the organization has rolled out plans to strengthen its R&D sector and focus more on products that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In doing so, the company must remain true to its ideals of maintaining integrity in production and customer care sectors. This implies that while the company seeks to innovate and remain relevant in one of the most competitive industries, the company should not compromise on the quality of its products. The management of the organization must also be streamlined to offer the necessary leadership that is required to strengthen the stature of the company at the global stage.
In a nutshell, the success of Huawei in the ICT sector underscores the role played by technology in making lives better and more fulfilling. The 10 years challenge is an efficient strategy for predicting the pattern of technological achievements of an organization. By looking into the organization’s journey within the last 10 years, it is particularly easy to predict future ventures and developments. For example, having availed into the market the legendary Y7 smartphone, one can only guess that Y8 is in the process of being developed, and could be launched sooner or later this year.
Reference List
Drahokoupil, J, McCaleb, A, Pawlicki, P & Szunomár, A 2017, ‘Huawei in Europe: strategic integration of local capabilities in a global production network’, in J Drahokoupil (ed), Chinese investment in Europe: corporate strategies and labour relations, European Trade Union Institute, New York, NY, pp. 211-229.
Han, EJ & Sohn, SY 2016, ‘Technological convergence in standards for information and communication technologies’, Technological Forecasting and Social Change, vol. 106, pp. 1-10.
He, D N.d., New ICT drives innovation. Web.
‘Huawei’s research and development activity’ 2017, Statista.com. Web.
Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. 2009 annual report. 2009. Web.
Jackson, K 2018, Huawei: leadership, culture and connectivity, SAGE, New Delhi.
Lin, Q 2017, ‘Enabling the effective open innovation in Business Ecosystem: a case study of Chinese catch-up firm Huawei’, PhD Thesis, Aalto University, Helsinki, Finland.