Abstract
There have been changes in the climate of today that has seen reduction of the amount of rainfall we receive. Abu Dhabu, a city in the Emirates where the desert like conditions prevails, has been adversely affected by these changes. Therefore the amount of water used for irrigation has to be regulated.
Modern methods of irrigation such as use of hydroponics have been introduced to reduce the amount of water wasted in irrigation farms. The following is a case study of an experiment done in the University of Peradeniya Sri Lanka to illustrate how hydroponics saves water and energy.
Case study
The use of hydroponics gardening in growing of vegetables, fruits and other plants has been so common in the world today. Many farmers are going into this advanced technology of plant growing because they believe that plants grown hydroponically have better quality than the ones grown under the normal soil planting.
The extensive use of hydroponics systems is also attributed to the many reported problems related to soil. Scientists decided to come up with technology where the use of soil would be reduced or find an alternative for the soil in a bid to curb the many soil related problems (Tavakkoli, Fatehi, Rengasamy, & Mcdonald, 2012).
The human population of the world is also increasing and leading to a subsequent rise in challenges to plant growing and agriculture in general.
The land available for the people to conduct their cultivations has been reducing since more space is occupied by human settlement and construction of infrastructure. The hydroponics gardening system is capable of producing a large volumes of crops in a small portion of land.
With many parts of the earth experiencing a change in climatic conditions, the growing pattern of plants has also been interfered with since the amount of rain and seasons are also changing. This technology of hydroponics in plants growing can adopt the reduced rainfall amounts since it seeks to save water used by the growing plants.
Many scientists believe that this advancement in the technology of plant growing is too superior and reliable than the old methods of planting and irrigation. Despite this huge support for the hydroponics systems, there has been little research done on this field of plant growing to prove the reliability and superiority of this technology.
Due to lack of more research evidences to support the fact that hydroponically grown plants are superior, an experiment was done in the University of Peradeniya. The experiment was to illustrate the comparison of a hydroponically grown plant and a soil-grown plant.
The experiment was done on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in both the hydroponics system and soil growing conditions. The physiological measures used in this research included comparing the shoot and root ratios, rates of photosynthesis, and stomata conductance of the lettuce grown under the two different conditions.
Materials used in the experiment
Vegetable
Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) was used as the experimental crop
Amount of Water
Amount of Energy
The annual difference of water intake between the two methods is 8400/7= 1200 m3. The pumping system used an average of 0.17 kW to pump 1m3 of the hydroponic solution. Therefore, this requires 204kWh of energy for 1200m3 (1200 × 0.17).
Amount of CO2 Emissions
According to Bandara from University of Peradeniya, the experiment shows that an average of 1200 kg of natural gas would be needed annually for 1ha farm of hydroponics.
The following formula is used to calculate the total amount of CO2 emissions.
Total amount of CO2 emission=Total amount of natural gas × hydrogen to carbon ratio × CO2 to carbon ratio
= 1200 × 12/16 × 44/12
=3300 kg
Medium
Coir dust was used in both soil and hydroponics culture in the following sizes:
Hydroponic culture- 50×33×9 cm3
Soil culture- 45×30×5 cm3
Amount of minerals
Hydroponics culture- 6.0mM KNO3, 4.0mM Ca (NO3)2, 1.0mM NH4H2PO4, 2.0mM MgSO4.7H20
Soil culture- 1.075g N, 1.175g P, 0.375g K
Procedure

This experiment was conducted in two different methods and therefore the requirement of the process would also differ at some point. The first bit of the experiment used the conventional method and thus soil culture was considered here.
The other part of this research was the hydroponics systems where there was no use of soil. The following is a brief illustration of the stages followed in each of these two processes (Hanses, 2010; West Virginia University, 2014.
Soil Culture
In this experiment, the soil to be used was first grounded to have a fine texture, and this was done to enhance penetration and proper mixing of nutrients with the soil particles. After this, 10 kg of livestock manure was mixed properly with the fine soil with a view that each plant would acquire 250 g of the manure.
Before the next stage, the test was conducted to establish the concentration of the initial minerals on the soil. It is important to conduct this test before adding the inorganic fertilizers to the soil since the calculation of used mineral nutrients by the plants would be easier.
The seedlings were transferred two weeks after the planted seeds had germinated. They transplanted in seedling trays that measure 45×30×5 cm3 where they are applied with nutrients.
Hydroponic Culture
In this case, polystyrene boxes were used to hold the medium which was coir dust. Each box measured 50cm by 33cm by 9 cm where four plants were expected from each of them.
The nutrient solution was then prepared as per the stated amount of mineral required in this experiment. This hydroponics solution was then passed through the grown plants to enable them absorb the nutrients.
Random measurements of the parameters stated in this experiment were done when the plants had reached 30, 37, and 45 years. Four plants were picked randomly from both the hydroponics and soil culture for these measurements to be taken. Also, the number of leaves in the plants taken for the study was recorded.
Results
Root lengths, dry weights and root: shoot ratios
The root lengths of the plants grown in the hydroponics were slightly higher than the lengths of the soil grown plants. These plants also had their roots being more resistant to growth as the initial lengths of their roots were close to that after the experiment.
The hydroponically grown plants recorded higher shoot dry weights as compared to those from the soil which had high root dry weights. This is one of the best ways of determining the quality of the harvest one should expect after the plants have grown to maturity. The following is a set of data collected in this experiment.
Mean root lengths, root dry weights, shoot dry weights and shoot: root ratios of hydroponically grown plants and soil grown plants
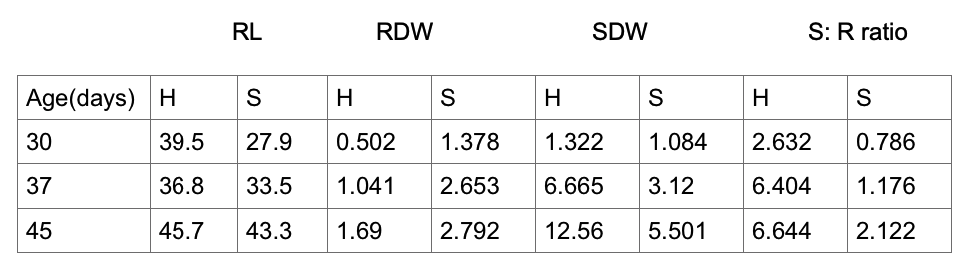
Key; RL– mean root length, RDW– mean root dry weight, SDW– mean shoot dry weight, S: R ratio– mean shoot: root ratio, H– hydroponically grown plants, S– soil grown plant
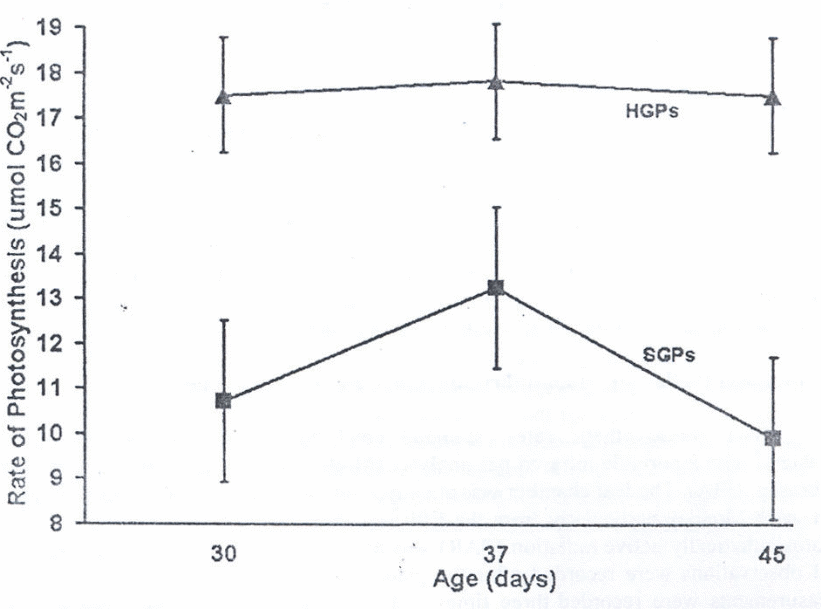
Net Photosynthetic Rates
The hydroponically grown plants recorded higher net photosynthetic rates when compared to what the soil-grown plants had in this case. There are various factors associated with the rate of photosynthesis exemplified by the plants’ efficiency of using the solar energy and the leaves’ stomatal conductance of carbon (IV) oxide.
Therefore, studying the net photosynthetic rate is also very important when analyzing the solar-energy consumption.
Transpiration Rates
Furthermore, it is the plants grown in the hydroponics system that recorded a higher rate than those plants grown in the soil-based method. This shows that the plants on the hydroponics setup absorbed more moisture from the solution (Bandara, 2008).
Hydroponics in Agriculture
This is a technology of growing plants by using solutions of mineral nutrients without the necessity of using soil as a medium. This idea was brought up when scientists found out that soil is not mandatory for plant growth through their researches.
Over the years, soil has been used because it provides the growing plants with support. In this soil, most of the mineral nutrients are also stored.
Further studies also showed that water played a major role during the absorption of these minerals because the mineral nutrients are absorbed by the plants in the form of inorganic ions dissolved in water. The important minerals are diluted in water as the plants are grown in a medium containing the solution.
The medium is where the plant would be anchored while growing. The media used in hydroponics include coconut husks, gravel, mineral wool, and expanded clay pebbles.
This advanced technology in plant growing can be used by indoor gardeners and also those who prefer growing their fruits and vegetables in the outside environment. This is possible because hydroponics can use both the natural light and the artificial ones when growing.
There are various hydroponics system plans to be used in different parts of the world in growing of vegetables, fruits and other plants. These different setups have the same idea of hydroponics growing but the difference comes in the type of medium used in the growing and the state of the nutrient solution.
This technique is categorized into two main areas depending on the media used in the categorization. The 2 categories are the solution culture and the medium culture. The solution culture is that plan where there are no solid media used in the growing process of the plants under the hydroponics technology.
Examples of hydroponics solution culture are the static solution culture, the continuous flow solution culture and the aeroponics. On the other hand, the medium culture is a hydroponics technique in which there is a medium used in growing the plant.
The plants are supported by the media while the solution containing the mineral nutrients is passed through so that growing plants can absorb them. Names are attached to these type of setups according to the medium used like the sand culture and rock wood culture.
In terms of the state in which the nutrient solution is having, the hydroponics systems are also classified into two major areas. This is the Still Solution Hydroponics and the Re-circulating Solution Hydroponics.
The former method is one where the mineral nutrients solution is static while the latter has the hydroponics solution in constant circulation. Electronic pumping machines are used to maintain the circulation of the solution in cases where the system is operating at a larger scale.
The Working Mechanism
The way in which the hydroponics systems work is quite simple. It entails passing of mineral nutrients from the nutrient solution to the plant roots through capillary action. To elaborate on the working mechanism it’s preferable to discuss the media used in this technology and the different techniques used in hydroponics.
Hydroponic Media
The following is an illustration of each of the mostly used media in growing the hydroponics:
Expanded Clay
This medium is something close to marbles which is highly porous. Clay is made into round balls and then heated at high temperatures of around 1200 degrees Celsius. This is done to make the clay highly porous and also to avoid compacting after a period of time.
It is this quality that makes it the most preferred medium by the gardeners. Apart from that, expanded clay is widely used due to its low prices. This makes it more profitable for commercial gardening due to the reduced cost of operations.
The expanded clay has a neutral pH making the gardeners sure that the plants will acquire the exact nutrients from the hydroponics solution. This medium is re-usable since it can be cleaned after being used and sterilized making it economical.
Perlite and Vermiculate
This medium is also a mineral in its state. One unique factor about this type of media is that it is overheated and in extreme cases also expanded. This makes it adapt very well in dry conditions and desert like environments. Although perlite contains more air than vermiculite, it holds little water.
Coco Peat
This is what we get from the leftover of the outer shell of a coconut after the fibers have been removed. The coir provides a very conducive environment for the growing of plant roots. This is so because of the ability of the coco peat to exchange cations at a high rate.
With this modification, this medium of hydroponics growth can store nutrients that are not used by the plant. This would mean that no mineral nutrients would be wasted since the excess would be used in the future since they are stored.
Coco peat also has a type of fungi called trichodema which dominates in it and it is useful to the plant roots. This fungus offers protection to the roots and also enhances the growth of the roots by boosting the speed of growth. Therefore, coir is one of the best media to use in this advanced technology of growing plants.
Gravel
For this kind of medium, any size of gravel is applicable. Even the type of gravel used in aquariums can be used in this case. One important condition to maintain is the constant circulation of water all through the medium. This circulation can be made efficient by use of electric pumps in the system.
A lot of advantages come along with the use of this medium. For instance, this medium is relatively cheap thus giving commercial gardeners a better way to cut down on their cost of production.
This medium is also good when boosting the quality of the fruits or vegetables being planted because it maintains a good drainage system.
Therefore, the water will be saved while as the plants get adequate water for growth. One major precaution when using gravel as the medium is maintaining the water circulation since the plant roots are prone to dry with no constant water flowing.
Polystyrene Packing Peanuts
Though this medium may be cheap and economical to use, there are restrictions that come along with using it. For example, this medium of hydroponics growth is only used in enclosed systems such as closed tubes. It is also very light in weight that the types of plants grown on it are specific. Another major disadvantage of the polystyrene packing peanuts is that the plants might take in some styrene from the medium. Eventually, this is passed to the consumers of the plant and thus set a serious health risk to them.
Techniques of Hydroponic Systems
There is a variety of hydroponics systems used to grow different types of plants. The different techniques have unique specifications that make them suitable for the growth of specific vegetables or fruits.
Despite their classification, all the techniques used in hydroponics systems are aimed at providing nutrients, water, and adequate air to the plants. The following are some of the hydroponics setups used majorly in growing vegetables in different environments.
Still Solution Hydroponics (static)

This is one of the easiest hydroponics techniques to start and develop. In this case, a person would require a container or tank where the nutrient solution is placed. The plant is put into a pot or vessel which would be immersed in a container with the hydroponics solution.
It is important to note that it is only the bottom of the vessel that is immersed in the solution. From this point, the plant in the vessel will be able to absorb the mineral nutrients up through the process of capillary action. The amount of water used must also be taken care of as the plant would need good aeration.
Therefore, the water in the vessel should be at a lower level to allow space for aeration of the plant. When setting up this hydroponics system, good quality and adequate water must be in the container to avoid adding up of water which would alter the aeration of the plant.
When starting the process, the salt concentration of the water should also be low. This is necessary because after a short period of crop’s growth, the fertilizer salts would have been concentrated in the solution.
The still solution hydroponics system has the advantage of being economical in establishing and maintaining it. For example, the type of hydroponics technology does not require electricity or pumping machines.
The Re-Circulating Solution Hydroponics
This is a hydroponics system where the nutrient solution is kept flowing through the roots of the plant grown constantly. It is exactly the opposite of how the static solution hydroponics system operates.
This technology requires a lot of investment in terms of resources and the care that the plants would be offered when growing. This is performed by either developing a pumping mechanism or creating a sloping landscape to enhance the flow of water.

One advantage of this technology is that it allows adjustments on the process while it is in progress. For example, the temperature and concentration of nutrients can be varied according to the type of plant growing and the level that it has grown in this case.
The Substrate Culture
This is a type of hydroponics system where there is a medium used by the plant when growing. In these cases, the basic medium applied excludes soil and applies a substrate that does not contain nutrients. The most preferred substrates include coconut coir, rock wool, vermiculite, and expanded clay.
These materials are used to provide physical support but not for supplying nutrients components to the crop. The medium chosen should be able to last for a long time so as the growth duration of the plant can fit in the active period of the substrate.
Apart from this, the right medium should be able to hold an adequate amount of water. This ensures that the plant receives sufficient water required for maximum growth rate. This is also the same in the air capacity of the substrate as there must be good aeration conditions for the plant to thrive.
Some substrates such as saw dust and composted pine bark are not advisable to use in hydroponics gardening. In the first place, these media are not good to use because they are not consistent in the quality they provide.
This creates problems from the gardeners due to the type of quality that their vegetables or fruits can have after all the hydroponics processes.
These substrates are also not recommended because the rate at which they decompose is high. This makes such substrates not to stay for a long time in comparison to the duration that the plant would take to grow.
This technique helps in reducing the amount of water wasted while irrigating the crops. Also, it assists the plant to get proper aeration enhancing proper growth, few disease infection, and shorter period of growth.
Once a medium is used, it is vital to replace it when planting another time even though this is an optional measure. This is performed majorly to ensure that the vegetable or fruits grown are good quality.
Moreover, replacing the substrates helps in avoiding passage of diseases to the growing plants. This again proves that hydroponics gardening is bound to produce higher quality.
An irrigation scheme is created, and the hydroponics solution is pumped through the plants as the flowing solution is collected in tanks. From this point, the collected solution is pumped back to the dripping points.
Nutrition Film Technique (NFT)
In this type of hydroponics system, there are shallow gullies constructed in a sloping manner during the first step. The plants are then planted along the gullies, and nutrient solution is flown down across the plants.
Down the gullies, the nutrient solution is collected in the set collection tanks from where the solution is pumped back. The flowing of the hydroponics solution stream down the gully is also important in making sure the solution is always aerated.
For the collection tanks down the gullies, it is preferred that one has many smaller tanks instead of a huge tank. This is important because it ensures that the farm has some supplies of the solution, even if there is a breakdown in one of the tanks.
Another advantage of breaking the collection tank into smaller ones is that it avoids spread of diseases, in case there is an outbreak in the garden.
Analysis and Discussion
Comparing the conventional and the hydroponics systems of irrigation
Over the years, the methods of irrigation have changed from the simple systems to advanced levels of irrigating plants. These advancements in the irrigation sector are connected to the changes we experience in the world’s climate and vegetation today.
Different parts of the world are getting drier due to climatic changes and thus the need to conserve the water for irrigation and also make maximum use of it by engaging efficient methods.
Sri Lanka and many countries in the Middle East are affected adversely by these changing conditions that explain their wide participation in hydroponics and other modern irrigation systems.
While illustrating the differences between the traditional methods of irrigation and the use of hydroponics, the following factors are looked at in relation to the two methods;
Harvest Quality
According to this experiment, the crops grown in hydroponics condition are expected to have bigger fruits and leaves while their roots are smaller. On the other hand, the plants irrigated in the conventional way are expected to exhibit smaller fruits and bigger roots.
This is according to the comparison done of the dried weights of the roots and shoots. Therefore, it is apparent that the harvest expected in hydroponics has higher quality than other systems.
The hydroponics systems of gardening do not require use chemicals such as pesticides and herbicides that are usually expensive. This method also ensures there is recycling of the nutrients, and thus it makes it economical.
For the traditional irrigation methods, one would need chemicals to maintain the plants, and the nutrients are also not recycled thus the harvest would not produce high profit as it is the case in these modern irrigation systems.
The growth of the hydroponics can be done all year round since they do not depend on the seasons of the climate. In most of the cases, the plants are grown within modified environments to benefit the farmer by increasing the harvests of a year.
The traditional ways of irrigation rely on the different seasons of the year and therefore will not be possible in some seasons.
Another importance attached to the use of hydroponics is that the rate of growth of plants grown hydroponically is two times faster than that of plants grown in the conventional ways. Amount of yield also multiplies by two in this method of irrigation.
This shows that given the same space, the hydroponics system produces double of what the soil based irrigation system provides.
Water Usage and Saving
In the conventional methods of irrigation, there were be no views of controlling the use of water and avoiding its wastage. It is in these traditional irrigation methods that the water would be directed to the plants in the field without considering the evaporation rates and sipping of water into the ground.
The hydroponics technology has ensured that the irrigation water is saved and used maximally in the growth of plant and thus ensuring highest produces.
For instance, the transpiration rate of the plants grown hydroponically was higher than that of plants reared on the soil in this experiment. This shows that the plants grown on soil did not absorb enough water which implies poor usage.
In the old irrigation systems, there were large operations for the scheme to provide enough water for irrigation. In the hydroponics system, the big structures are not necessary as it requires a tank of recyclable nutrient solution that is cheap and simple to operate as well as maintain. In the experiment, the average annual usage of water in the hydroponic irrigation is estimated to be 8400 cm3 per hectare which is half the amount in traditional irrigation method.
Energy Consumption and CO2 Emission
The farms under irrigation in UAE require irrigation systems which require a lot of energy. In this experiment the method of hydroponic irrigation used was the static solution method.
In cases where the farm need big pumping machines to pump back the nutrition solution, slightly more energy might be needed to run the system.
In this experiment, this factor is noted by the net photosynthetic rates which are affected by the efficiency of the plant in using the solar energy. The plants grown in a hydroponics system had a higher net photosynthetic rate than the soil grown ones.
This is a clear illustration that the hydroponics system enhances the consumption of the natural solar energy.
CO2 gas emission in farms using hydroponics is also quite low. The experiment shows that approximately 3300kg of CO2 would be emitted within one year in farms having hydroponically grown plants.
Conclusion
Generally, the use hydroponics system has been important to the economy and the agricultural sector due to the income retrieved from exportations and other sales made locally. This modern technology of irrigation has indeed improved the quality of harvest got from the schemes.
With hydroponics, the plants are not affected by fungi since there is proper management of the water and thus the crop would not be water-logged. The harvest quality from plants grown hydroponically is also good as the size of fruits is bigger.
This advanced irrigation method has also been proven very useful in saving the water consumed by the plants. In this method of irrigation, the farmers recycle the water they use in the process rather than wasting it to leaching and dampness on the fields.
The energy consumption and emission of carbon (IV) oxide are also handled by this farming technology. The farmer will attain a reduced consumption of energy in the farm in case he/she has adopted any of the techniques of hydroponics systems that do not involve a lot of pumping activities.
In this light, the CO2 emission would also be reduced since the usage of machines in the farm would be limited. Therefore, the use of hydroponics saves water, energy and emission of CO2.
Recommendations and Concerns
Similar to many countries in the Middle East and the surroundings of Sub-Saharan deserts, UAE is experiencing a big challenge of managing the limited water available. This has forced the UAE government to adopt policies that would help to provide adequate water for the people and the irrigation scheme.
The economy is also one crucial factor that this government has to put into consideration as the prices of resources rise alongside the population size. When all these considerations put together, adopting the hydroponics technology is a good idea.
Therefore, this study recommends the implementation of this technology in irrigation projects aimed at being efficient and economical.
Future Work
In Abu Dhabi, the planting of palm trees is one activity that many stakeholders of the Emirates economy take seriously. In the Emirates of Abu Dhabi, the climatic condition that has many desert-like characteristics is good for palm tree planting.
Palm trees make up a big percentage of fruit plants in Abu Dhabi and therefore putting in place this economical irrigation method in its plantation would save the government in this business city a lot of resources in terms of water and energy.
Hydroponics has proven to be so efficient in irrigation and provision of quality agricultural products for national and international consumption. Moreover, the technology also saves water, energy, and the environment making it a good tool to be used in enhancing sustainable practices in agriculture.
Therefore, if investments are made on this area, there are high chances of developing the production of food through this modern technique. This will lead to adequate supply of food for people through cheap and qualified standards of growth.
References
Bandara, D. (2008). Comparison of the Carbon Partioning and Photosynthetic Efficiency of Lettuce. University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka , 2-9.
Estrella, L. H. (2014). An improved, low-cost, hydroponics system for growing Arabidopsis and other plant species under aseptic conditions. BMC Plant. Web.
Goldenberg, J., & Reid, W. (1999). Goldenberg, J., & Reid, W. (1999). Promoting development while limiting greenhouse gas emissions: Trends & baselines. New York:UNDP , 8-15.
Goudie, S., & Farraj, A. (1999). Coastal Change in Ras Al Khaimah (United Arab Emirates):. A cartographic analysis. The Geographical Journal , 12-25.
Hanses, S. (2010). The results of an experimental indoor hydroponics Cannabis growing study, using the ‘Screen of Green’ (ScrOG) method-Yield, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and DNA analysis. Web.
LifeEssay Biology. (2014). What are the advantages and disadvantages of hydroponics farming? Web.
Lone, M. I. (2008). Phytoremediation of heavy metal polluted soils and water: Progresses and perspectives. Retrieved from J Zhejiang University Science B. Web.
Mathew, T. (1987). Society for Soil and Water Conservation. Simple methods of localized water conservation. Areeplachy, Kerala, India , 34-42.
Olivia’s solution. (2014). Advantages & Disadvantages of Hydroponics! Retrieved from Olivia’s solution. Web.
Parks, S., & Murray, C. (2011). Leafy Asian vegetables. Department of Industry and Investment , 3-20.
Putnam, D. H., & Robinson, P. H. (2013). Does Hydroponics Forage Production Make Sense? Alfalfa & Forage News. Web.
Tavakkoli, E., Fatehi, F., Rengasamy, P., & Mcdonald, G. (2012). A comparison of hydroponics and soil-based screening methods to identify salt tolerance in the field in barley. Journal of Experimental Botany, 63(10), 3853-3867.
Tinker, P. B. (1997). Solute Movement in the Soil-Root System. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publishers.
Wang, A. (2005). Synthesis and properties of clay-based superabsorbent composite. European Polymer Journal , 1570-1595.
West Virginia University. (2014). BPC profiles: Mountain State Hydroponics. Retrieved from Davis College of Agriculture, Natural Resources and Design. Web.
Zhao, Y. (2009). Study on precision water-saving irrigation automatic control system by plant physiology. Industrial Electronics and Applications. ICIEA 2009. 345-370.
Zhenmin, Z. (2009). Influence of irrigation water-saving on groundwater table in the downstream irrigation districts of yellow river. Natural Computation, 305-412.