Abstract
The aim of this experiment was to determine the impact of various types of soil as well as the effect of an energy drink on plant growth. Brassica rapa seeds were grown in Maine potting mix, sand, and a mixture of the two. The impact of the energy drink was determined by comparing plant growth under normal water conditions and a double portion of Redbull drink. The highest growth rates were observed in Maine potting mix and plain water. It was concluded that too much of an energy drink has a harmful effect on plant growth.
Introduction
The healthy growth of plants is determined by the availability of three main requirements: water, nutrients, and light. Additional factors include warmth and air. Water plays a vital role in the germination of plants by activating the hydrolytic enzymes that initiate physiological processes in plants. During growth, water facilitates the transport of nutrients and minerals. Additionally, the intake of water by plants through osmosis provides turgor pressure, which firms up plants thus providing anchorage (Kramer 2012). Light provides the energy that converts water and carbon dioxide into glucose.
Important plant nutrients include minerals such as nitrogen, calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium. These minerals act as co-factors in biological reactions as well as building blocks of macromolecules such as amino acids and nucleic acids (Levetin and McMahon 2011). For these reasons, fertilizer is applied to plants as a common agricultural practice. The type of soil affects plant requirements mainly by influencing water retention, temperature, and the availability of air. Energy drinks such as Redbull contain sugars and vitamins, which are hypothesized to be beneficial to plants.
This experiment aims at determining the impact of different types of soil on the growth and development of plants as well as the effect of irrigating plants Redbull. It was hypothesized that plants would display the best rate of growth when grown in a mixture of sand and Maine soil. It was also hypothesized that irrigating the plant using twice as much Redbull as water would lead to a better growth rate than plain water.
Experimental Procedure
In part A of the experiment, two seeds of Wisconsin Fast Plants (Brassica rapa) were planted in a potting mix containing the Coast of Maine soil, sand, and a mixture of Maine soil and sand. These treatments were labeled as A1, A2, and A3 respectively. The media were moistened as needed after which approximately 4-millimeter depressions were made using two fingers. All seeds were planted at the same depth. The seeds were watered and labeled appropriately. The pots were then thinned to 1 seedling each after three to five days of germination. Wooden stakes and rings were used to hold the plants in place. The rate of growth was determined by measuring the height, the number of leaves, length, and width of the leaves as well as the number of flowers. These growth parameters were taken at three intervals. Between days 13 and 20, the developed flowers were cross-pollinated using a small brush to transfer pollen from the flowers of one plant to another. Extra flower buds and shoots were pruned off until the fruit pods were mature. The plants and pods were allowed to dry for a week after which the seeds were harvested from the pods.
In part B of the experiment, two pots containing the Coast of Maine potting mix were prepared. A similar procedure was used to plant the seeds. Plain water was used to water the plants in the first pot, which acted as the control. The plant in the second pot was irrigated using twice as much Redbull as the amount of water used in the control. The growth of the plants was measured as in part A.
Results
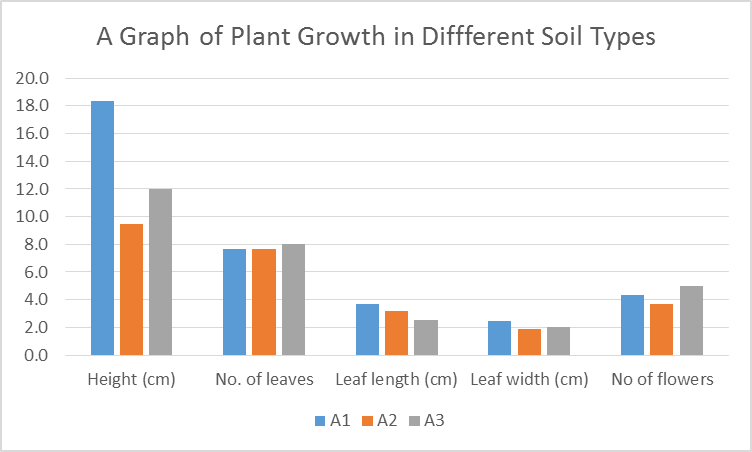
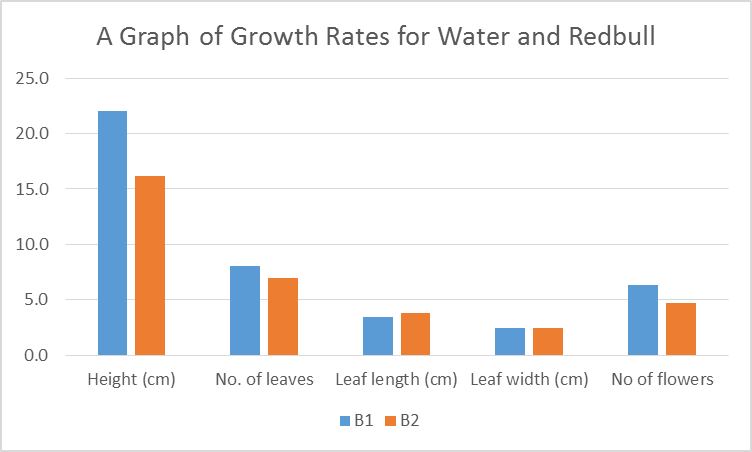
It was observed that the rate of plant growth was higher in the Maine potting mix than sand alone and a mixture of the two types of soil (Figure 1). Conversely, watering the plant with Redbull did not lead to a significant increase in growth rate compared to water alone (Figure 2). An increase in the parameters was noted as the days progressed. A summary of the individual values is indicated in Table 1. The averages of the five parameters are indicated in Figure 1 below.
Table 1: A table of individual values and means of the five growth parameters observed in Brassica rapa grown under varying conditions.
Discussion
The study findings did not support the supposition that a mixture of the two soils would lead to optimum growth. Sand does not contain humus and has poor moisture retention capability hence the observed low growth rate (Noyd et al. 2013). The Maine potting mix is a blend of loamy soil, which contains humus that retains soil moisture and adds soil nutrients thus making it the ideal growth medium.
The findings of this study did not corroborate the hypothesis that using Redbull to water the plant would lead to twice as much growth compared to water. These observations were attributed to the chemical composition of Redbull. Redbull contains chemical ingredients such as caffeine, the amino acid taurine, B vitamins, sugars, and fresh Alpine water. Though energy drinks are beneficial to humans, the presence of caffeine has deleterious effects on plant growth as witnessed by the reduced rate of growth in the plants watered with Redbull. Caffeine causes stunted growth and impairs the overall health of plants (Ferguson 2015). The harmful effects of caffeine are attributed to its capacity to absorb calcium in the soil, which is one of the important plant macronutrients. Consequently, the vascular tissue thins out leading to the poor development of vascular tissue, impaired membrane function, detoxification, and protein synthesis. Caffeine also affects the breakdown of starch to liberate energy. However, certain studies have shown that low concentrations of caffeine are beneficial to plants and lead to improved plant growth (Martin et al. 2013).
The glucose concentrations in Redbull could also have contributed to the reduced growth. High concentrations of glucose impair the uptake and availability of water by plants. It also affects the cell wall structure and delays the maturing of flowering plants (El-Hassanin et al. 2016).
Conclusions
The findings of the study show that Maine potting mix was the best medium for plant growth compared to sand and a mixture of sand and Maine soil. It was also concluded that using plain water on plants was better than a double amount of Redbull.
Works Cited
El-Hassanin, A. S., Samak, M. R., Moustafa, N. S., Khalifa, A. M., and Inas, M. I. 2016. Effect of foliar application with humic acid substances under nitrogen fertilization levels on quality and yields of sugar beet plant. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences 5: 668-680.
Ferguson, S. 2015. Effects of caffeine and vitamin E on Wisconsin Fast Plant. Best Integrated Writing, 2:1-7.
Kramer, P. J. 2012. Water Relations of Plants. Academic Press, New York, USA.
Levetin, E., and McMahon, K. 2011. Plants and Society. McGraw-Hill Education, Colombus, OH.
Martin, C., Zhang, Y., Tonelli, C., and Petroni, K. 2013. Plants, diet, and health. Annual Review of Plant Biology 64: 19-46.
Noyd, R. K., Krueger, J. A., and Hill, K. M. 2013. Biology: Organisms and Adaptations. Cengage Learning, Belmont, CA.