Strategies
Blue Ocean Strategy for strategic planning:
- Focuses on the development of new markets;
- Introduces new solutions or products;
- Makes any potential competitors irrelevant;
- Focuses on unavailable markets or not yet exploited;
- Pursues low costs and differentiation simultaneously.
The Red Ocean Strategy:
- Existing markets;
- Uses traditional strategies;
- Characterised by fierce competition;
- Many competitors;
- Choose between low cost or differentiation.
Red Ocean:
- Market defined by industry structures;
- Boundaries are fixed;
- Focus on zero-sum game.
Blue Ocean:
- Market exists in manager’s mind;
- Creates new boundaries;
- New opportunities.



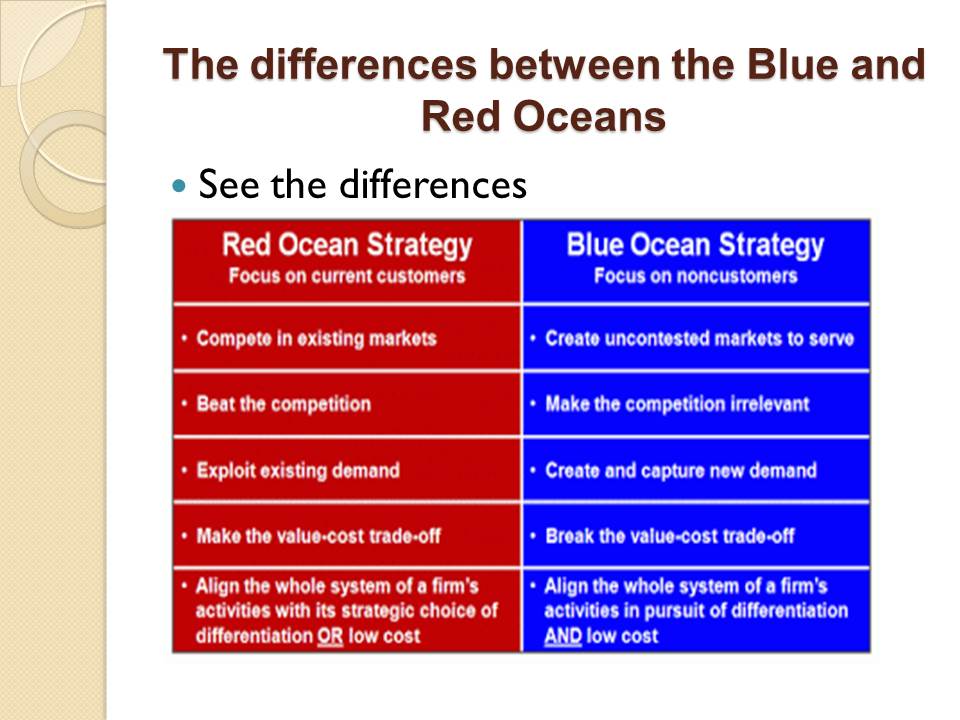
The differences between the Blue and Red Oceans
See the differences
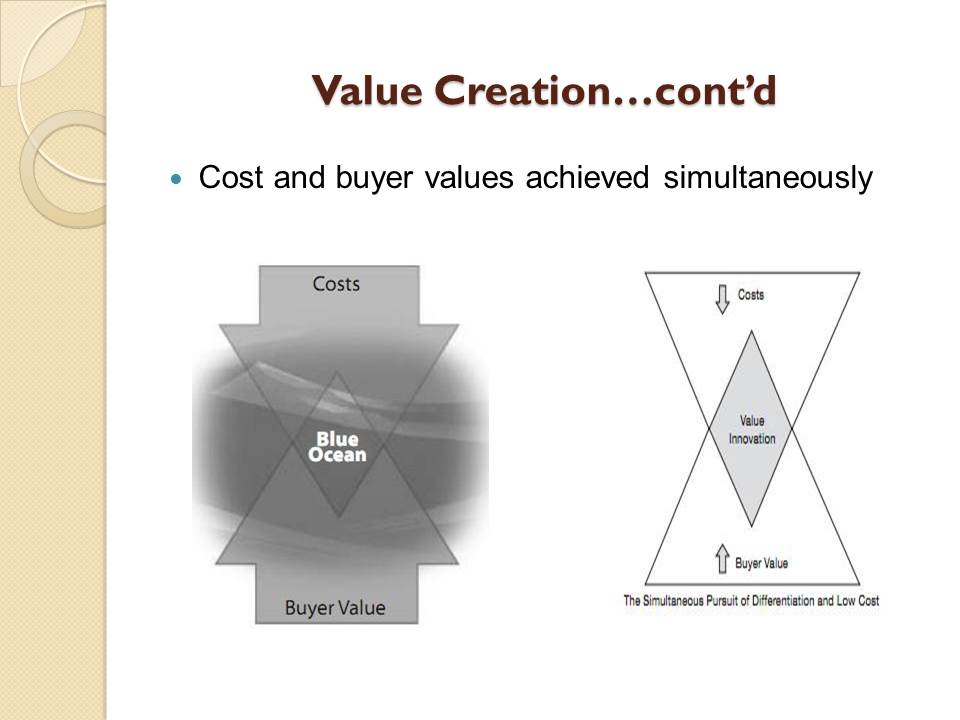
Value Creation with the Blue Ocean
- Value creation is the cornerstone of the Blue Ocean
- Creates value in products and services
- Value creation strategy
- Involve customers through surveys
- Customers are proactive in the process
- Company facilitates value creation
- Cost and buyer values achieved simultaneously
Customer Value
- Interactive – customer and products;
- Relativistic – comparative, situational and personal;
- Judgment of performance or outcome:
- attitude, affect, valence, evaluation, opinion, satisfaction, behavioral tendency and choice
- Consumption or use experience
Key dimensions of customer value created by products or service:
- Economic value:
- A price factor.
- Functional value:
- Solution.
- Emotional value:
- Customer experiences.
- Symbolic value:
- Meaning.



IKEA Application of the Blue Ocean Strategy
IKEA
“We constantly ask: Is there a better way? That’s how the IKEA home furnishings offer remains unique and how we try to make everyday life better for the many people” (IKEA, 2015).
The Blue Ocean strategy captured here
A better way focuses on products or costs.
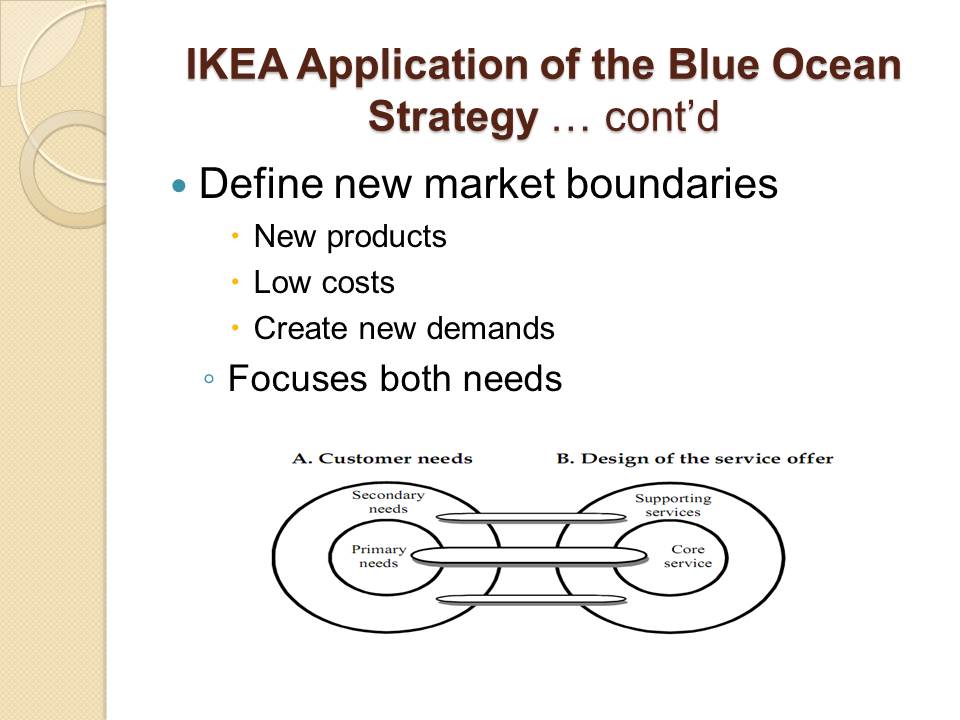
Define new market boundaries
- New products;
- Low costs;
- Create new demands.
Focuses both needs.
Never miss the big picture
- Listen to customers;
- Develop new values;
- Motivate employees;
- Develop the right strategy.
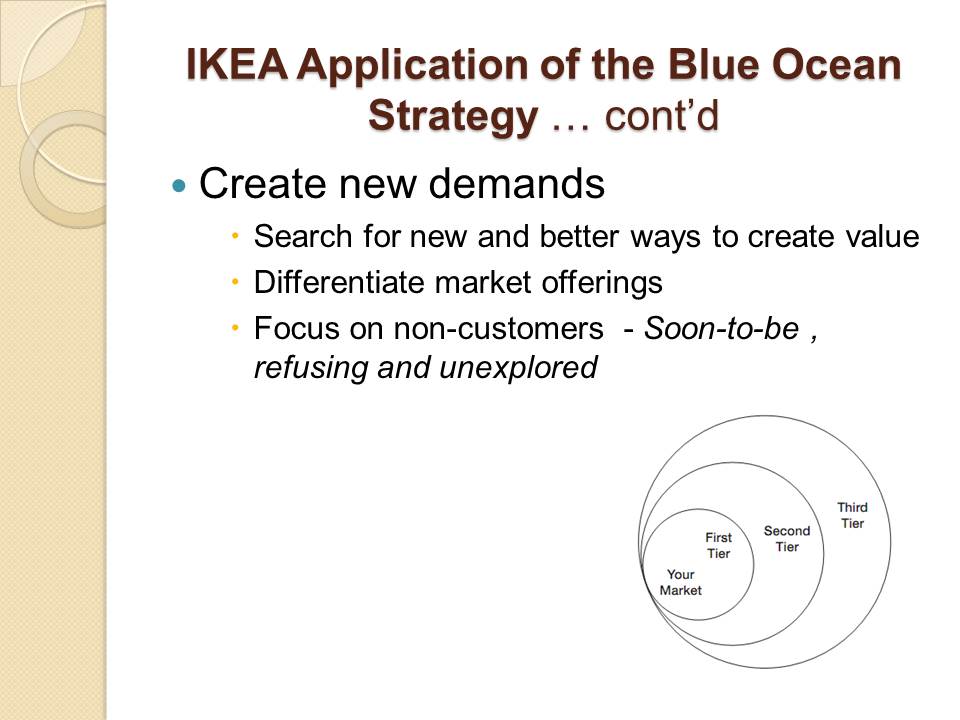
Create new demands
- Search for new and better ways to create value;
- Differentiate market offerings;
- Focus on non-customers – Soon-to-be , refusing and unexplored.
- Use the right strategic sequence
- Product and service design support the strategy.
The right design:
- Buyer utility;
- Price;
- Cost;
- Adoption.
Customer needs guide the design processes.
Overcome internal challenges:
- Recruit the right employees;
- Motivated employees;
- Get the right support systems.
Successful strategy execution is only possible when there are no challenges – that is, the right resources are vital in the strategy.
Engage all employees to execute the strategy.




Conclusion
- The Blue Ocean strategy offers new markets for companies;
- Red Ocean provides existing markets;
- IKEA’s success is attributed to the Blue Ocean;
- For the strategy, create new solutions and define new markets;
- Use low cost and differentiation simultaneously.

References
Bendapudi, N., & Leone, R. (2003). Psychological implications of customer participation on co-production. Journal of Marketing, (67), 14-28.
IKEA. (2015). The IKEA Concept. Web.
Kim, W. C., & Mauborgne, R. (2004). Blue Ocean Strategy. Harvard Business Review .
Kim, W. C., & Mauborgne, R. (2005). Blue Ocean Strategy: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition Irrelevant. United States: Harvard Business School Press.
Rintamaki, T., Kuusela, H., & Mitronen, L. (2007). Identifying competitive customer value propositions in retailing. Managing Servie Quality, 6(17), 621-34.
Wiggins, R., & Ruefli, W. (2002). Sustained competitive advantage: temporal dynamics and the incidence and persistence of superior economic performance. Organization Science, (13), 82-105.