Introduction
Rising inflation leads to increased cost of living, reduced purchasing power, and reduced economic growth, and it can also lead to increased government debt. High inflation also causes market interest rates to increase. This is because when the cost of goods and services rises, the demand for money also increases. Inflation is also a critical factor in determining the yield curves for treasury securities, which are used to calculate the cost of borrowing money.
The Impact of Rising Inflation in 2022-2023
In 2022-2023, rising inflation caused market interest rates to increase. Banks and other financial institutions responded to the inflation by increasing the deposit interest rate to incentivize customers to keep their money with them. Higher inflation reduces the purchasing power of money, meaning customers need to earn a higher return on their deposits to maintain the same level of purchasing power (Mgammal and Mahfoudh 10).
The increased interest rate also serves as a hedge against rising prices. As deposit interest rates go up, so do borrowing costs for individuals and businesses. Companies are more reluctant to take out loans, limiting their ability to invest in new projects and expand their businesses, which restricts overall economic growth (Mgammal and Mahfoudh 10). Higher interest rates discourage consumers from taking loans, reducing their spending power and economic activity.
The rising inflation made lenders charge higher interest rates to compensate for the additional risk associated with lending. The higher interest rate is also an attempt to increase their profits as the cost of goods and services continues to rise. The elevation in interest rates meant borrowers had to pay more for their loans. Thus, the occurrence strained their budgets, as they had to pay more for the same amount of money. Furthermore, consumers had to reduce spending as their purchasing power was reduced.
The rising inflation caused investors to become more hesitant to invest in the market. The above further reduced the amount of money available to lenders, causing interest rates to increase even further (Mgammal and Mahfoudh 10). This hurt the economy as demand for goods and services declined.
Rising inflation had a significant impact on yield curves for treasury securities in the USA, Euro Area, and the United Kingdom. As inflation rises, the yields on treasury securities increase, thus pushing the curve up (Mgammal and Mahfoudh 8). Thus, the investors will demand higher returns on their investments to compensate for the higher cost of living.
Causes of Rising Inflation
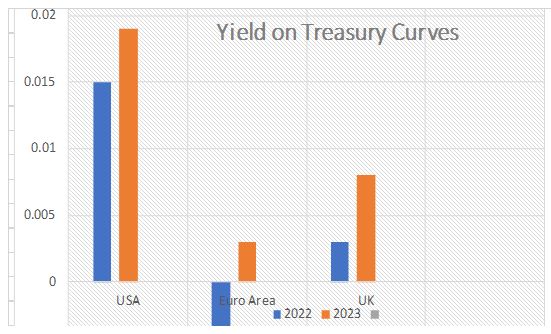
The rise in inflation was caused by several factors, including increasing demand for goods and services, rising energy prices, and increasing wages. As a result, the yield curves for treasury securities in the three countries significantly increased. According to Graph 1 below, in the USA, the yield on 10-year treasury securities rose from 1.5% in January 2022 to 1.9% in December 2023 (Furman 80). In the Euro Area, the same security rose from -0.7% in January 2022 to 0.3% in December 2023 (Furman 81). The bond yield security in the United Kingdom increased from 0.3% in January 2022 to 0.8% in December 2023. (Furman 81). The increase in the yield curves shows rising inflation’s effect on the cost of borrowing money.
Conclusion
Therefore, inflation led to an upsurge in market interest rates, particularly deposit rates. This hurts the economy, as businesses and consumers become less willing to take out loans, leading to reduced economic growth. The high inflation in 2022-2023 significantly affected market interest rates, making it more expensive for borrowers to take out loans. As the yields on treasury securities increase, borrowing money will also increase, making it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This could lead to a decrease in consumer spending and investment, which could harm the economy as a whole.
Works Cited
Furman, Jason. “Why Did (Almost) No One See the Inflation Coming?” Intereconomics, vol. 57, no. 2, 2022, pp. 79–86. Web.
Mgammal, Mahfoudh Hussein. “The Effects of Inflation, Interest Rates and Exchange Rates on Stock Prices: Comparative Study Among Two GCC Countries.” International Journal of Finance and Accounting, vol. 1, no. 6, 2012, pp. 604-621. Web.