The data exercise entails collecting and analyzing interest rate data for Estonia. The analysis is carried out for a period of nine years that is, between 2002 and 2011. Interest rate in a country shows the average rate charged on money borrowed. In most countries the interest rate is regulated by the central bank. The bank sets the base lending rate and provides a margin which commercial banks can charge customers for money borrowed.
The lending and borrowing rates are different in Estonia. The borrowing interest rate will be analyzed since it has a number of significant impacts on the economy. First, it is a vital tool used by the central bank of Estonia to control the amount of money supply in the country.
When the money supply in the economy is high, the central bank can reduce the amount of money in circulation by increasing the interest rate. This is possible since when interest rates are high, investors would choose to invest the money at hand thus, reducing the amount of money in circulation. Thus, there is an inverse relationship between interest rate and money supply as shown in the graph below.
Graph of interest rate and money supply
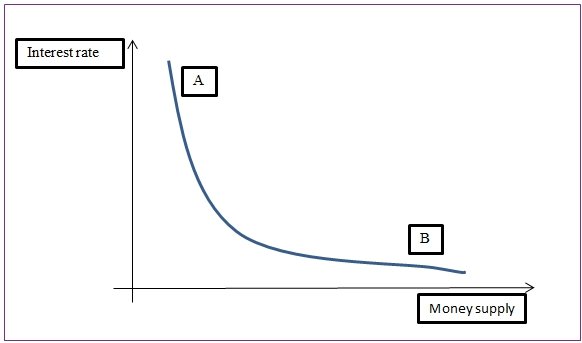
Also, interest rate is used by various central banks as a monetary tool to control inflation. Thus, changes in the interest rate can be an indication of money supply and the state of inflation in a country. At a high interest rate, the money supply is not responsive to changes in interest rates. The paper will analyze inflation adjusted interest rate (that is, the real interest rate) for Estonia.
Data
The table below summarizes the real interest rate for Estonia for the past nine years.
Analyzing the data
For the past nine years, the interest rate has been erratic and in some years negative. The interest rate declined from 1.41% in 2003 to 1.15% in 2004. This could have an impact of increasing the money supply in the economy since investors would prefer to hold money instead of investing. Also, it will have an impact of increasing money supply in the economy since people will be encouraged to take loans at lower interest rates.
Such initiatives may be taken by the central bank of Estonia to stimulate economic growth. Further, such reduction in interest rates creates an inflationary pressure since consumers will be holding plenty of cash that chase fewer goods. Such inflationary pressure caused by an increase in supply in the economy can only be offset by a subsequent production of more commodities so that there is plenty in the market. This will result in real economic growth.
The interest rates were negative between 2005 and 2007 and the absolute values of the negative were increasing over the three years. The negative interest rates imply that the banks were paying the borrowers some money. Thus, it will appear like the banks will compensate the borrowers for the privilege of taking loans.
The negative interest rates are not prudent behavior and quite detrimental to the economy. It slows down economic growth since money is not used for productive activities in the economy. Also, there will be a rapid decline in the profits for the banks. This too will contribute to slow economic growth.
The move is also likely to create high inflation and might affect exchange rates and balance of payment. The negative interest rates also affect the mortgage business. The mortgage is a vital element of the economy. There will be a drastic decline in the income from the mortgage business. Besides, the demand for mortgage is likely to exceed the supply of mortgage thus creating serious shortages that would result in increases in the price of housing.
To finance the negative interest rates, first, banks would often make use of the banks’ reserves. Thus, there is possibility that the minimum cash reserves that should be maintained by the bank will reduce. This in turn reduces the possibility of future lending. Besides, such initiatives would have serious impact on the liquidity of the bank. Secondly, the banks can also finance such negative interest rates from revenues that arise from charging customers exorbitantly.
This is not feasible since revenues earned by commercial banks are closely monitored and regulated to avoid exploiting consumers. Negative interest rates are often used by governments to penalize savings. The intention of the government is to increase the amount of money in circulation. The government intends to encourage spending and not savings. However, it yields no growth effect as envisioned by the government due to the multiplier effect.
Between 2008 and 2009, there was an increase in the interest rate from 2.98 to 10.89. This was expected since the economy was on a negative growth path. Besides, there were slow economic growth and high inflation rate. An increase in the interest rate has an effect of encouraging savings and reducing spending.
Besides, it reduces borrowing. This resulted in a decrease in money supply in Estonia. A decline in money supply reduces the inflation rate. The increase in interest rate from the negative path restored the economy back to the right track of growth and normalcy. This is necessary for economic growth.
In late 2009, the country experienced the global financial crisis. Key players in the economy suffered losses. Commercial banks were worst hit since they had recorded reduction in profitability during the period since the country had negative interest rates.
The money market and the capital market were equally affected. The crisis led to a serious decline in money supply in the economy. Similarly, the banks did not have sufficient liquidity to lend so as to sustain the key banking functions such as lending. The central bank mediated in a number of ways.
First was by reduction of the cash reserve ratio. The second was by reducing the interest rate. Reduction of interest discourages savings and encourages borrowing. The net effect is an increase in money supply in the economy. Also, the money borrowed will be invested in productive activities thus creating more jobs and output.
Also, the increase in money circulation in the economy boosts the confidence of the public in the financial institutions. Thus, the actions by the government to reduce interest rates are likely to have an effect of stimulating the economic growth. The speed of growth will depend on a multiplier. From the above discussions, it is clear that the interest rate is vital in an economy. The graph below shows the trend of interest rate for the nine years.