Introduction
This article analyzes the correlation between Amazon’s stock price and sales to determine how much of an impact the recent COVID-19 Pandemic has had on the company. Combining previous research with current epidemiological information yielded these results (Nicola et al., 2020). Information about Amazon’s quarterly sales is retrieved from the company’s website, while information about the stock price is retrieved from Yahoo Finance (Nicola et al., 2020).
A correlation study was carried out to elucidate the connection between these two. A regression study was performed between the price of Amazon stock and the number of worldwide cases of COVID-19 to confirm the finding (Nicola et al., 2020). Then, Amazon’s sales were compared to the total number of instances. The weekly number of COVID-19 cases was acquired from Our World in Data and used to calculate the Pandemic’s progress.
The research found that younger generations were more likely to cut back on spending, stock up on supplies, and prioritize material goods over experiences during the COVID-19 outbreak. It is also possible that different age groups respond differently to retail industry shifts. We can illustrate a US and UK survey (Meyer, 2020).
In addition, the Literature Review section provides access to other functional materials on pandemics and internet-based buying. Later, Amazon sales data was evaluated to see how the Epidemic affected demand (Meyer, 2020). The sections titled “Methods” and “Results” include the particulars of our analyses. The investigation will also look into how Amazon has adapted to the Pandemic and how it has affected the company’s bottom line.
Project Plan
Company Review
Amazon is one of the largest and most potent online marketplaces, serving the purchasing needs of millions of customers every day. The company’s cutting-edge business model, lightning-fast shipping, and exceptional customer service have revolutionized retail and caused significant disruption to established chain retailers (Pantano et al., 2020). Amazon continues to be a powerful player in the e-commerce sector despite criticism and controversy over labor rights, data privacy, and antitrust concerns.
As a source of critical commodities and services in times of crisis, Amazon has benefited from the COVID-19 outbreak (Pantano et al., 2020). Still, the Pandemic has also put an enormous strain on the company’s operations and supply lines. Amazon’s response and adaptability to the challenges of the Epidemic will unquestionably continue to affect the future of e-commerce and the retail industry as we traverse the Pandemic and its aftermath.
This study will investigate the economic effects of pandemics and how businesses respond to them (Pantano et al., 2020). The report will also analyze how the global economy and the e-commerce sector have been affected by the COVID-19 Pandemic (Pantano et al., 2020). It will then conclude with a literature assessment of Amazon’s responses to the Pandemic. Amazon is one of the few businesses that has prospered during this time.
Research Methodology
This part will discuss methodology and research strategy, and the research will draw from both primary and secondary sources. For the core data, executives and workers at Amazon will be surveyed and interviewed (Pantano et al., 2020). Reports, financial statements, news stories, and industry reports are all secondary data sources that will be used.
The methodology used in this study combined both primary and secondary sources. To further understand how COVID-19 will affect Amazon’s many revenue streams, we conducted in-depth interviews with Amazon workers, industry experts, and customers (Pantano et al., 2020). These interviews were performed using a variety of channels, including in-person chats, telephone conversations, and web-based forms (Pantano et al., 2020). To learn about how COVID-19 may affect Amazon and the e-commerce sector, we conducted secondary research in which we read scholarly articles, reports, news items, and other relevant materials.
Both qualitative and quantitative approaches were used to assess the data gathered from primary and secondary sources. Content analysis was applied to the qualitative data to extract recurrent topics and trends (Pantano et al., 2020). Statistical approaches were used to evaluate the quantitative data and reveal patterns and trends. Eventually, the gathered and examined data were assessed, and conclusions were reached. We also discussed the research’s limits and where we could go from here (Pantano et al., 2020). The research technique was created to give an exhaustive and trustworthy account of how COVID-19 affected Amazon and its several streams.
Repercussions of COVID-19 on Amazon’s Business
This section will discuss the effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Amazon’s commercial operations. The report will analyze how Amazon has fared in the face of closures, supply chain disruptions, and shifts in customer behavior (Pantano et al., 2020). This section will also discuss Amazon’s efforts to react to these shifts, such as enhancing its workforce’s security and shipping options and adding new products to its catalog.
Financial Performance
This section examines the impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Amazon’s bottom line. The report will analyze how the Epidemic has affected Amazon’s bottom line and share price (Nicola et al., 2020). The business has implemented successful measures to lessen the Pandemic’s influence on its operations (Nicola et al., 2020). This section will also discuss Amazon’s financial measures in response to the Epidemic, including enhancing its delivery network and growing its cloud computing offerings.
Over the years, Amazon has posted remarkable financial results, with consistently high sales growth rates and net profit. Amazon’s net sales 2020 were $386 billion, up 38% from the previous year. In 2020 the firm’s net income increased by 84% to $21.3 billion (Nicola et al., 2020). One reason for Amazon’s success is its ability to diversify its revenue streams through offerings like Amazon Web Services, Amazon Prime, Amazon Video, Amazon DSPs, and Amazon Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). Graph 1 below shows Amazon’s net sales-TTM between 2021 and 2022.
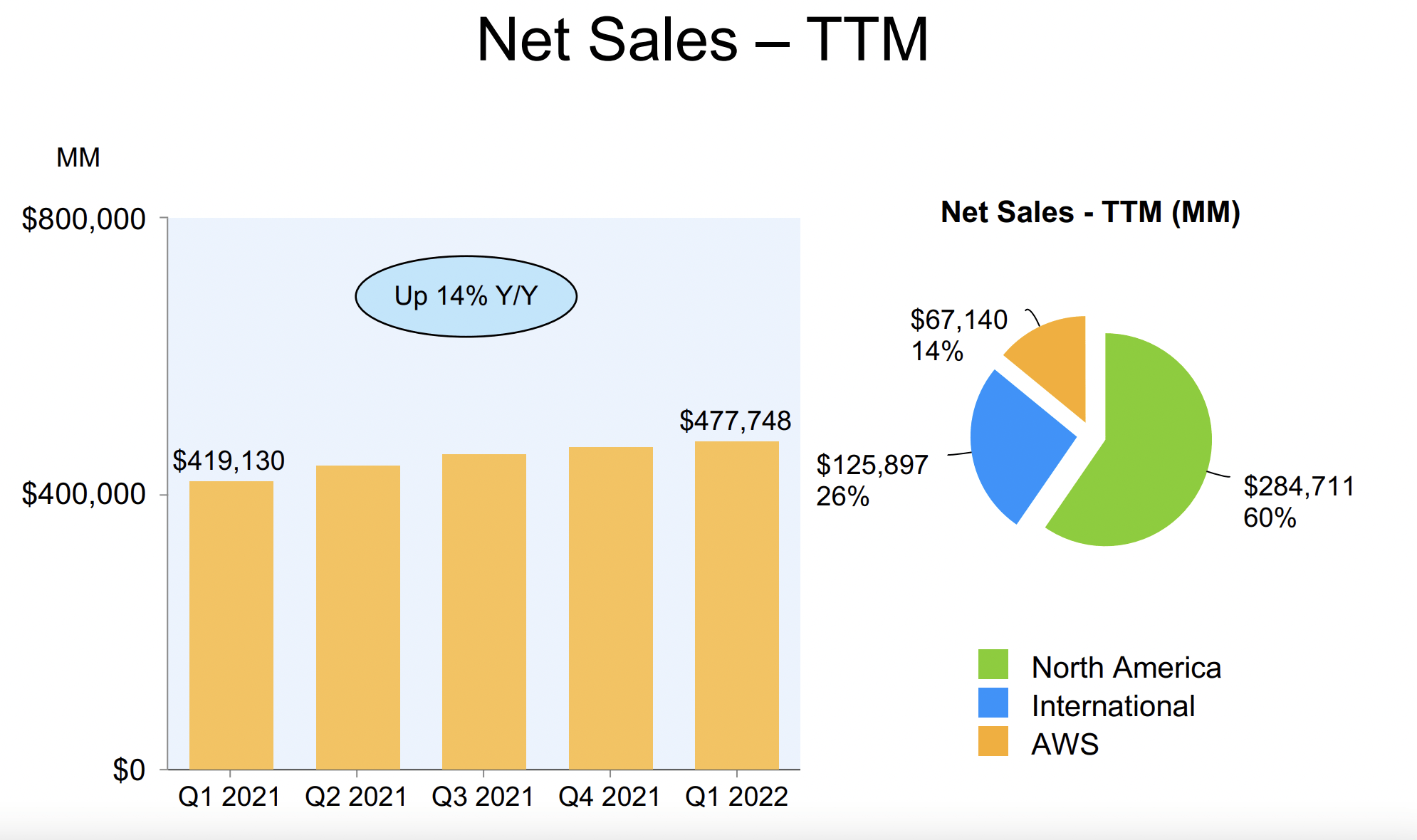
The corporation benefits from having numerous revenue streams because it can use the profits from one to cover losses in the others. For instance, by 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS) will have contributed $45.3 billion in net sales, or about 12% of Amazon’s total income (Nicola et al., 2020).
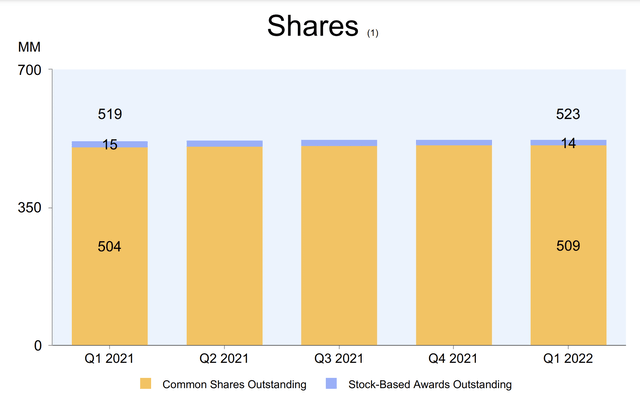
Amazon’s dedication to technological advancement and superior service has increased sales and devoted clientele. The company’s dedication to technology has allowed it to streamline its operations and better serve its consumers by implementing AI and ML (Nicola et al., 2020). Amazon’s success reflects the company’s sound business practices, emphasis on product improvement and customer service, and responsiveness to market shifts. Graph 2 below shows Amazon’s Shareholder dilution between 2021 and 2022.
Strategic Outlook
The effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Amazon’s long-term plans will be discussed in this section. Amazon’s response to the Epidemic has included quickening its transition to automation and entering new markets, which will be analyzed (Nicola et al., 2020). The long-term effects of the Pandemic on Amazon’s strategy, such as the possibility of irreversible changes in consumer behavior, will also be discussed in this section (Nicola et al., 2020). This study hypothesizes that the release of COVID-19 has significantly impacted Supply Chain Management and Human Resource Management at Amazon. Figure 1 below shows the company’s strategic outlook over the years.
Project Timeline
The study’s expected timetable is 13 weeks, but it can vary depending on factors such as unforeseen complications and resource availability. To finish on schedule and under budget, it is crucial to monitor the project’s development and make any necessary alterations, as shown in the figure below.
Project Planning Phase (1 week)
During this stage, the team will determine the study’s goals, scope, and methods. They will also make a project plan and determine what materials are needed.
Data Collection Phase (3 weeks)
During this stage, the research team will conduct interviews, surveys, and other forms of primary data collection. Secondary data, such as financial reports and news stories, will also be gathered from the public domain.
Data Analysis Phase (4 weeks)
The study team now analyzes and interprets the information gathered in phase one. They will employ statistical techniques and software to derive conclusions from the data.
Findings and Recommendations Phase (2 weeks)
The study team will now compile a summary of their findings and make suggestions based on their learning. They will also write a report detailing their findings and provide it to the relevant parties.
Final Report and Presentation Phase (1 week)
After this step, the research team will deliver their results and recommendations to the relevant parties via report and presentation.
Limitations and Future Research
The study’s limitations include data availability, reliability concerns, and the possibility of survey response bias. The possibility of bias in the survey replies, and the study’s dependence on secondary data sources will be discussed (Al Jazeera, 2020). Further investigation into issues, including the effect of the Pandemic on Amazon’s staff and the possibility of heightened regulatory scrutiny in the wake of the Epidemic, will be suggested. The limited span of data sources is one of the critical drawbacks of this study on the impacts of COVID-19 on Amazon. The study primarily drew on secondary sources, including industry publications and press articles, which may paint a partial picture of COVID-19’s effect on Amazon (Nicola et al., 2020). In addition, the sample size of the primary research was relatively small, consisting only of interviews with a handful of Amazon workers, industry experts, and consumers.
Another constraint is the rapid evolution of the COVID-19 epidemic and its effects on Amazon. The study looked at the impact of COVID-19 at the end of 2020. Still, several things that could affect Amazon have changed, including the appearance of new COVID-19 variations and the introduction of vaccinations (Nicola et al., 2020). A more thorough primary research strategy, such as conducting questionnaires with a bigger sample size of Amazon staff and customers, should be implemented in future studies to evaluate the effects of COVID-19 on the organization (Nicola et al., 2020). As the world continues to adjust to the ongoing consequences of COVID-19, more studies should also examine the long-term impact of the Epidemic on Amazon and the e-commerce business.
Literature Review
Several remarkable events, such as natural disasters and pandemics, have occurred in human cultures throughout recorded history. The effects of these occurrences on consumers’ spending habits have been studied (Giang Thi et al., 2022). Also, increased demand due to unusual events, such as pandemics, is sometimes called “panic buying” (Gulseven et al., 2020). When the COVID-19 Pandemic spread worldwide, people began actively storing goods and making frantic purchases (Nicola et al., 2020). People are not shopping the same way they used to (OECD, 2020). In some nations, supplies of pandemic-related and health-related items like hand sanitizers and surgical masks ran out within a few days. Still, toilet paper, detergents, and pasta supplies ran out almost as quickly (Pantano et al., 2020). Amazon has faced difficulties due to the Pandemic, but due to the transition towards e-commerce and remote employment, the company has seen unparalleled development and success.
The pandemic context, closures, and quarantines significantly contribute to panic buying and stockpiling behavior. During the COVID-19 Pandemic, a correlation between quarantines and out-of-character spending, with the authors concluding that this spending was driven primarily by people stocking up in advance of their impending confinement (Laato et al., 2020). Stockpiling and panic buying resulted from a sharp increase in grocery spending in New Zealand in the middle of March compared to the corresponding period in the previous year.
Consumption displacement occurs when an unexpected occurrence causes customers to forgo their usual goods and services in favor of something new. Masks and disinfectants may be in higher demand during a pandemic, but fewer people will want to fly. Because of travel constraints, this is a case of shifting consumption elsewhere (Giang Thi et al., 2022). There was a high demand for groceries, but several restaurants and cafes had to shut down (Nicola et al., 2020). Because of these closings, it is reasonable to assume that demand for online purchasing has increased (Hall et al., 2020). One study found that some consumers avoided in-store purchases in crowded areas due to concerns about contracting the coronavirus, saying they planned to continue to do so until they had been vaccinated.
Covid-19 has had significant and far-reaching consequences on Amazon, touching on many of the company’s divisions and services. During February and April 2020, grocery store sales rose 16% and non-store merchant sales 14.8%, while US retail and food service revenues declined 7.7% (Al Jazeera, 2020). Online retail sales in the EU-27 countries climbed by 30% year over year in April 2020, but total retail sales fell by 17.9%, according to the same data (Bhatti et al., 2020). For our research, we will use Amazon as an example; the company has extended its COVID-19-related order capacity increase to April 12, 2020 (OECD, 2020). The business recruited 175,000 new workers between March 16 and April 12 to keep up with demand. (Landry, 2020). The analysis has helped us better understand how Amazon has dealt with the Pandemic, what precautions it has taken, and how it has altered its business to meet the demands of its customers.
Data Analysis
Three employed in our analysis for COVID-19 data on quarterly and weekly Amazon stock prices, quarterly and weekly Amazon e-commerce net sales, and weekly Amazon e-commerce net sales. The online retailer’s quarterly net sales figures are extracted from their website for tabular analysis (Giang Thi et al., 2022). Seven pieces of information spanning the first three months of 2019 to the second three months of 2020. The Yahoo Finance dataset provides the second set of data for tabular analysis. It is derived by transforming weekly data on Amazon Stock Prices into monthly and quarterly figures for a more meaningful comparison with the original numbers (OECD, 2020).
It should be noted that the final week of December was left out of the second quarter’s data because its significance was not previously discussed (Giang Thi et al., 2022). Despite this, the data was still a very excellent proxy variable. For regression analysis and correlation, “Our World in Data” provides weekly stock price data and COVID-19 cases.
Tabular Data Analysis
This tabular data analysis aims to demonstrate the relationship between Amazon’s net e-commerce sales and Amazon stock prices. The table shows a positive correlation between a rise in net sales and a rise in stock price and a negative correlation between a fall in net sales and a fall in stock price (Giang Thi et al., 2022). There is a clear correlation between the two variables, and we have calculated and displayed this to help us better understand what this means.
We calculated the correlation between Amazon’s stock prices and net sales from Gretl: Corr (sales. Stock prices) = 0.86752954 (Bhatti et al., 2020). Under the null hypothesis of no correlation, T (5) =3.9001, with a two-tailed p-value of 0.0114 (Bhatti et al., 2020). The research demonstrates a connection between shifts in COVID-19 cases and shifts in net sales using stock price data comparable to the weekly COVID-19 dataset and the quarterly sales data set (Giang Thi et al., 2022). This research aims to demonstrate the macro-level positive correlation between COVID-19 and e-commerce customer demand.
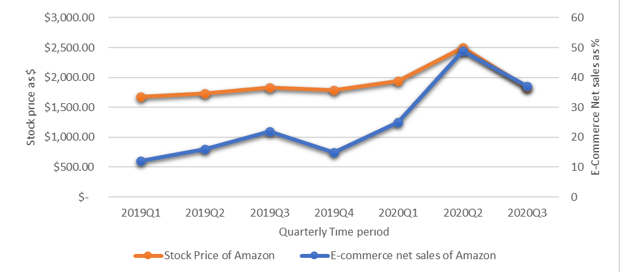
Stock prices indicate a company’s market value, and the stock price is agreed upon between buyers and sellers. The graph and the correlation H calculation using Gretl stock prices reveal that Amazon’s net sales follow the trajectory mentioned in the tabular data analysis (Bhatti et al., 2020). The impact of COVID-19 on Amazon’s stock price is then analyzed using a time-series regression. Weekly stock prices and other data from Amazon were used in this analysis. Here are the outcomes that occur weekly in the Covid-19 database.
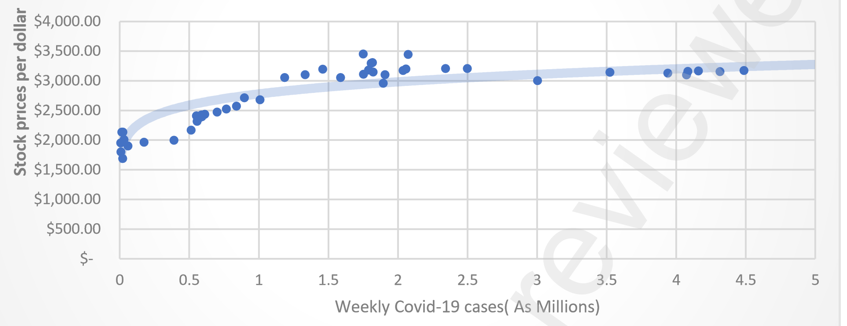
Results
This section aims to conclude the data presented in the preceding paragraph (Methods). From the outset, we intend to use Amazon’s stock price and net sales data to draw the correlation between the rise and fall of COVID-19 cases and customer demand (OECD, 2020). Since we could only obtain quarterly Amazon net sales data, we first demonstrated the correlation between Amazon’s online shopping net sales and the company’s stock price. Gretl’s calculations establish a correlation of 0.86752954 between the two variables (OECD, 2020). This statistically significant positive association is also seen in Graph 3. This association bridges COVID-19 instances and net sales, the central gauge of consumer demand.
Then, we analyzed the impact of COVID-19 on Amazon stock prices using Gretl’s time series analysis. Both the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) are used in the model selection process (BIC). Our research begins in February 2020, when precise COVID-19 data will be considered. COVID-19 impact on online business is substantial and cannot be disregarded, as the calculations show. Our model fits the data with a goodness of fit of 0.907895 (OECD, 2020). The time series analysis and graph 4 demonstrate that the demand for online shopping was boosted by COVID-19 (Susmitha, 2021). COVID-19 impact on online purchasing reached its limits, and other factors and effects on Amazon’s e-commerce likely led to a period of stability after a certain point in Graph 4.
Discussion
Quarantine and social isolation, as described in the literature, profoundly affect consumer behavior. Sales at internet retailers have skyrocketed as more and more people turn to them for their everyday necessities (Baker et al., 2020). Using Amazon as an example, the company’s global e-commerce operation was enlarged due to shifting consumer preferences during the COVID-19 outbreak, resulting in record net sales of $ 75.5 billion in the first quarter of 2020 (Baker et al., 2020). The increased volatility caused by the Pandemic altered the actions of both investors and consumers in the financial markets.
Potentially hard-hit industries that investors anticipated were those in the leisure travel, supply chain, and transportation sectors. Many airlines will see a drop in profits as a result. As a result, they redirected their capital to the rapidly growing online media (Netflix, HBO), education (Zoom, Skype), and retail markets. It has been shown (Baker et al., 2020). Investors were drawn to Amazon because of its diverse product offerings, including food and leisure options like e-books, videos, and games (Castro et al., 2020). The stock price of Amazon rose sharply as analysts forecasted higher profits and higher sales.
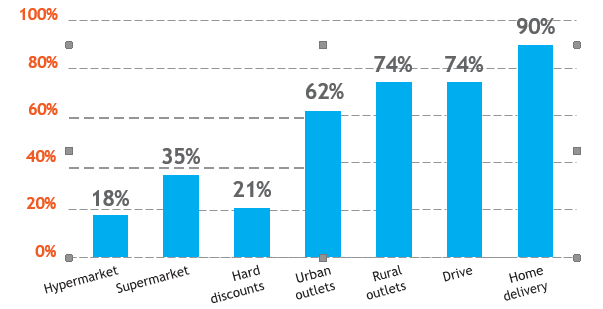
Amazon’s investment decisions benefit from the global trend toward reduced interest rates. In March 2020, the Federal Reserve lowered its primary loan rate from 2.25 percent to 1.75 percent and its interest rate on excess reserves from 1.60 percent to 1.10 percent after the Pandemic reports (Baker et al., 2020). Each phase saw a decrease in these rates, culminating in today’s rates of 0.10 percent on surplus reserves and 0.25 percent on primary credit (Castro et al., 2020). Most nations maintained similar interest rate regimes (OECD, 2020). Monetary policies in much of the world have made it easier for online marketplaces to access credit and boost their spending (Susmitha, 2021). Graph 4 below shows an increase in grocery store and online sales in France after the Coronavirus outbreak from March 16-22, 2020, compared to the same period in 2019.
It is clear from the data that investors’ confidence in online marketplaces like Amazon was bolstered by both monetary policy and consumer behavior. Our data and calculations show that Amazon’s bottom line benefits considerably when the number of COVID-19 instances rises, and appropriate action is taken (Bakeret al., 2020). Only the impact of COVID-19 on Amazon stock prices was evaluated. We compared it to sales data to learn how customer preferences and Amazon’s bottom line have evolved (OECD, 2020). It was no accident that we used Amazon as an example; our goal was to extend their scenario to other e-commerce platforms (Castro et al., 2020). It is the most generic e-commerce platform because it serves the most customers.
According to the study, standard household spending patterns began to shift as the number of instances grew. Despite an initial spike in expenditures, particularly for food items, there was a subsequent drop (Baker et al., 2020). It is possible that households are not just returning their spending to pre-recession lows.
Another thing to consider is that they may be spending less now than before the Pandemic. The Pandemic may have caused people to lose their jobs, go unpaid, or see a reduction in their salary (Laato et al., 2020). Those who have or are more likely to have these tend to reduce their outlays and increase their savings. Most families will need to go into savings in countries with weak social security programs (Martin et al., 2020). Third, the average growth could be affected because some large, less-developed countries have a low demand for online shopping.
There may be cultural habits and distrust in online transactions that are preventing these countries from growing. The study finds that despite e-commerce firms’ discounts, free deliveries, and promotions, most Indian consumers still prefer physically interacting with things before buying (Laato et al., 2020).
According to the same study, customers in India view online shopping as dangerous because of the prevalence of sites with inadequate information technology that makes it easy for hackers to access customers’ private data. Amazon’s diverse revenue streams took a significant hit during the COVID-19 Pandemic, but the corporation demonstrated endurance and adaptability in the face of adversity. Amazon has weathered the global economic crisis with relative ease thanks to its commitment to worker safety, its willingness to adapt to its customers’ changing wants and needs, and its investment in technology and infrastructure (Susmitha, 2021). Amazon must be adaptable and resourceful to stay ahead of the competition as the Epidemic spreads.
The need for online trading platforms may have already reached its peak because of the digitalization of the world in recent years. We feel it is essential to clarify that the theoretical maximum we cited applies only in the case of a pandemic (Laato et al., 2020). The preceding discussion of the detrimental effects of the Pandemic on online commerce is only partially correct. The ceiling might have been higher if the COVID-19 virus had not appeared (Susmitha, 2021). Hence, all four issues mentioned above dampen the rising demand for online purchasing and, by extension, sales for businesses that facilitate this type of transaction (Laato et al., 2020). As we found a strong correlation between net sales and the stock price, we think the stock price will be depressed.
Amazon was used to stock price data to analyze our finding that the COVID-19 virus’s spread is correlated with Amazon’s net sales. By studying and researching Amazon, one of the top online purchasing companies, we could conclude how people felt about online shopping during the Pandemic (Laato et al., 2020). The introductory section briefly described our methods and explained which data we selected for analysis (De Castro et al., 2022). We have also included some background on how the three variables we used, the number of COVID-19 instances, Amazon’s net sales, and Amazon’s stock price, have evolved.
Based on what we learned in the introductory and literature review sections, we did some mathematics to demonstrate how COVID-19 on-demand affects Amazon’s web sales. We used quarterly data to establish a positive association between Amazon’s net sales and stock price fluctuations in response to news of the COVID-19 sea anchovy (Bhatti et al., 2020). Using Amazon’s sales and stock price data, we sought to demonstrate the positive impact of COVID-19 on online purchasing demand (Laato et al., 2020). COVID-19 restrictions, fear of infection, and a shift in consumer purchasing habits due to these limitations were all factors in the observed uptick in demand for e-services, as highlighted in the discussion section.
Investor interest and stock prices rose with rising sales due to the uptick in consumer demand. Stock prices stabilized after a while due to uncertainty, infrastructure issues in emerging and developing countries, and the upper limit of e-online commerce’s potential, at least for platforms like Amazon (Laato et al., 2020). Overall, we have concluded that the impact of the COVID-19 broadcast on our lives altered our consumption habits, ushering in a new era marked by remarkable technological advances (De Castro et al., 2022). Internet retail and the profits it can generate are just getting their start in the revolutionary new digital and financial era.
Amazon’s Efforts to Aid COVID-19-Afflicted Employees, Communities, and Customers
Amazon has taken concrete action to help its staff, communities, and customers cope with the effects of the COVID-19 outbreak. Amazon has taken many precautions to ensure its workers’ safety, including issuing PPE, conducting temperature checks, and instituting social distancing protocols (Laato et al., 2020). In addition to the $2 per hour raise for hourly workers, the company has also increased paid time off, vacation pay, and overtime pay for those who put in more than 60 hours per week (Laato et al., 2020). Food banks and other organizations providing essential services have benefited from Amazon’s donations of millions of dollars to help communities hit hard by the Pandemic (Reinders et al., 2020). To further ensure that customers can access these necessities, the company has prioritized its delivery and introduced contactless delivery options.
Amazon has also provided on-site COVID-19 testing and immunization for its staff in some areas. Amazon has teamed up with local health departments to offer free vaccinations to residents of areas where the company has a presence (Reinders et al.,2020). Both Amazon employees and the surrounding neighborhood have benefited from these measures. As a whole, Amazon has shown its dedication to helping those affected by the Pandemic, both inside and outside the company. Amazon has also taken measures to assist independent merchants who use its marketplace. The company spent $100 million 2020 on a relief effort for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) hit by the Pandemic (Laato et al., 2020). Grants and credits for Amazon’s fulfillment and storage services were available to firms participating in the initiative. To further assist sellers in managing their companies during the Pandemic, Amazon has eliminated prices for some services, including inventory removals and long-term storage.
Amazon FBA Sales Rise Due to COVID-19 Online Innovation
Covid-19 has been an essential factor in the growth of e-commerce and the success of Amazon’s FBA program. As a result of lockdowns and other forms of social distancing, many people have been compelled to move their purchasing habits online, driving up demand for sites like Amazon (Watanabe et al., 2022). Amazon’s FBA program, which helps third-party sellers with inventory management, shipping, and other logistics, has been growing swiftly to meet the rising demand (Reinders et al., 2020). While the FBA program allows merchants to use Amazon’s extensive network, it has gained popularity (Watanabe et al., 2022). Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program can assist vendors in meeting the increasing demand for consumables and household goods brought on by the Pandemic.
In addition to Amazon’s benefits, merchants have also reaped substantial rewards from the FBA sales boom. By giving them access to Amazon’s massive consumer base and logistics network, the FBA program has also helped small firms compete with more prominent merchants (Lee et al., 2021). A rise in e-commerce across the board, including Amazon’s FBA program, can be directly attributed to the momentum provided by COVID-19 (De Castro et al., 2022). As a result of the Epidemic, businesses and customers have had to adjust to a new normal, and one likely lasting effect of Covid-19 will be the expansion of online shopping.
Impact of COVID-19 on Amazon
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is Amazon’s cloud computing platform, where various services, such as computing, storage, and database solutions, can be accessed over the internet. The demand for AWS services increased during the Pandemic because more people started working from home and shopping online (Bhatti et al., 2020). Many companies rely on AWS to help them with digital transformation and run online businesses (Cauchemez et al., 2020). The proliferation of web-based activities like video conferencing, distance education, and e-commerce has been dramatically facilitated by AWS (Bhatti et al., 2020). Amazon has upgraded its systems and added new offerings in response to the rising demand for cloud-based software and services.
Amazon Prime
Amazon Prime is a paid membership program that grants users perks like free two-day shipping, unlimited video streaming of popular TV shows and movies, and early access to special sales. Demand for Amazon Prime has risen because more people have turned to online shopping for necessities during the Pandemic (Bhatti et al., 2020). As a result, Amazon now offers groceries, health and wellness products, and other necessities for the home (Cauchemez et al., 2020). Amazon has also invested in its supply chain and logistics capabilities to guarantee on-time product delivery despite the disruptions caused by the Pandemic.
Amazon Video
Amazon Video is a video streaming service that provides users access to an extensive library of films and television programs. People stayed inside more often during the Pandemic, driving up demand for streaming services (Bhatti et al., 2020). Amazon has increased its investment in original content and its collection of films and television shows to meet the rising demand for entertainment (Cauchemez et al., 2020). With Amazon’s new Watch Party feature, subscribers can watch movies and TV shows with friends and family, even in different locations.
Amazon DSP’s
Advertisers can reach customers on Amazon.com, Amazon devices, and third-party websites using Amazon DSPs (Demand-Side Platforms), which are advertising solutions. More and more companies shifted their marketing budgets to digital channels during the Pandemic, driving up the demand for online advertising (Cauchemez et al., 2020). In response to the needs of businesses, Amazon has introduced new forms of advertising, such as Amazon DSP and Sponsored Displays (Reinders et al., 2020). Amazon has also provided resources to help businesses deal with the difficulties of advertising during a pandemic.
Amazon FBA
With Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon), vendors can store their goods in Amazon’s warehouses, and the e-commerce giant will handle shipping and delivery to customers. Demand for Amazon FBA skyrocketed during the Pandemic as more merchants outsourced their shipping and fulfillment to the online retail giant (Cauchemez et al., 2020). Amazon has increased its workforce and number of distribution centers to meet the rising demand. Regarding selling and shipping during a pandemic, Amazon has also provided sellers with resources and support to help them cope.
Challenges and Personal Reflections During the Research
I encountered several challenges during my research into the effects of COVID-19 on Amazon. In this thoughtful piece, I will talk about some of the difficulties I have faced and how I have dealt with them (Landry, 2020). The accessibility and trustworthiness of data were significant obstacles throughout my investigation (Bhatti et al., 2020). Gathering information from numerous sources took time and effort, and there was no guarantee that it would be complete or up-to-date (Reinders et al., 2020). In addition, I utilized data visualization tools to examine the information and spot trends and patterns that might add to the study results.
The topic’s complexity was another obstacle I had to overcome during my investigation. It was difficult to zero down on just one part of Amazon’s business affected by the COVID-19 outbreak because the topic is vast (Landry, 2020). To overcome this difficulty, I focused my study on one part of Amazon’s business model at a time, including Amazon Web Services, Amazon Prime, and Amazon Video (Landry, 2020). Because of this, I could hone in on the information most pertinent to my study and collect only that information.
Keeping track of my time efficiently was another obstacle I faced during my investigation. Effective time management is crucial for researchers to finish their projects on schedule and produce quality results (Reinders et al., 2020). The Pandemic made it challenging to juggle my personal life and research activities. I overcame this obstacle by outlining an organized strategy for my study and assigning myself reasonable due dates (Landry, 2020). In addition, I used time management strategies like the Pomodoro technique to help me concentrate and get much work done while conducting research.
Finally, keeping myself engaged and productive while conducting the research was a significant problem. Because of the Pandemic, I had to do most of my job from home, and it was not easy to stay motivated and productive without seeing my boss and coworkers daily (Landry, 2020). To overcome this obstacle, I worked closely with my supervisor by sharing my progress on my research projects and asking for advice and guidance at frequent intervals (Landry, 2020). In addition, I kept up with the research community and the most recent developments in the field by attending virtual seminars and workshops.
Recommendations
The lessons and insights from Amazon’s effective response to the COVID-19 pandemic can be applied by companies everywhere. The Pandemic has shown how vital it is to adapt quickly and create in adversity. The following suggestions are made in light of the research findings on the effects of COVID-19 on Amazon’s business operations and the strategies that have allowed the company to navigate this challenging moment. Amazon must keep bolstering its supply chain to prepare for potential disruptions. The Epidemic has shown the fragility of international supply systems; therefore, Amazon needs to strengthen its own. To do so, it may need to increase its inventory and develop backup plans in case of disruptions. When hiring, Amazon should be more open to the idea of remote workers and create policies and processes to help them succeed.
Amazon must keep investing in new e-commerce features to meet customer demand. The Pandemic has hastened the move to online shopping, and Amazon needs to keep spending on infrastructure and technology to keep up with the market. Amazon must ensure that its employees’ well-being is a top priority in all it does. The Pandemic has highlighted the importance of ensuring the safety of Amazon’s employees, and the company should maintain its commitment to safety procedures and wellness initiatives. Amazon has to diversify its revenue streams; thus, the company should look into entering new areas, introducing new products and services, and testing out new business models.
Conclusion
While the COVID-19 Pandemic has seriously affected Amazon’s business operations, the company has shown resilience, creativity, and adaptability in the face of adversity. Amazon has been successful despite the global economic downturn because of the company’s agility, willingness to invest in technology and infrastructure, and emphasis on employee health and safety. According to the study, Amazon’s e-commerce capabilities were crucial to the company’s survival during the Pandemic.
Amazon is well-positioned to fulfill the evolving needs of its customers as the trend toward online shopping gains momentum. Amazon’s continued success is primarily attributed to its dedication to investing in cutting-edge technology and infrastructure to serve its customers better and reduce delivery times. Amazon has made measures to ensure the health and safety of its employees after the Pandemic raised awareness of the relevance of these factors. Amazon has taken measures to protect its employees’ health and safety, including distributing PPE and funding wellness programs.
However, the company’s treatment of its employees and the environment has been criticized on moral grounds. The Epidemic has highlighted the significance of responding to these issues and taking action to promote fair labor practices, lessen the company’s carbon imprint, and assist local communities. To maintain its position as a leading e-commerce company, Amazon needs to continue to strengthen its supply chain, embrace remote work, diversify revenue sources, foster innovation and agility, build solid partnerships with key stakeholders, and address ethical concerns. Businesses can improve their ability to withstand a volatile and uncertain business climate by studying Amazon’s case study and applying the suggested measures.
References
Baker, S. R., Farrokhnia, R. A., Meyer, S., Pagel, M., & Yannelis, C. (2020). How does household spending respond to an epidemic? Consumption during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic. The Review of Asset Pricing Studies, 10(4), 834-862. Web.
Bhatti, A., Akram, H., Basit, H. M., Khan, A. U., Raza, S. M., & Naqvi, M. B. (2020). E-commerce trends during COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking, 13(2), 1449-1452. Web.
Castro, F. D., Lopes, G. R., & Brondizio, E. S. (2020). The Brazilian Amazon in Times of COVID-19: from crisis to transformation?Ambiente & Sociedade, 23. Web.
Cauchemez, S., Kiem, C. T., Paireau, J., Rolland, P., & Fontanet, A. (2020). Lockdown impact on COVID-19 epidemics in regions across metropolitan France. The Lancet, 396(10257), 1068-1069. Web.
Coronavirus: Travel restrictions, border shutdowns by country. (2020). Al Jazeera. Web.
De Castro, F. F., Góes, G. S., do Nascimento, J. A. S., & Tardin, M. M. (2022). Incidences of COVID-19 in major mining municipalities in the Brazilian Amazon: Economic impacts, risks and lessons. The Extractive Industries and Society, 9. Web.
Giang Thi Thu, H., Nguyen Thanh, T., & Le Quy, T. (2022). Dynamic sliding window and neighborhood LSTM-Based model for stock price prediction. SN Computer Science, 3(3), 256. Web.
Gulseven, O., Al Harmoodi, F., Al Falasi, M., & ALshomali, I. (2020). How the COVID-19 Pandemic will affect the UN sustainable development goals? Web.
Hall, M. C., Prayag, G., Fieger, P., & Dyason, D. (2020). Beyond panic buying: consumption displacement and COVID-19. Journal of Service Management, 32(1), 113-128. Web.
Laato, S., Islam, A. N., Farooq, A., & Dhir, A. (2020). Unusual purchasing behavior during the early stages of the COVID-19 Pandemic: The stimulus-organism-response approach. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 57. Web.
Landry, S. (2020). New ways we’re getting groceries to people during the COVID-19 crisis. About Amazon. Web.
Lee, M. J., & Jung, J. S. (2021). New Distribution Strategies of Korean SMES in Post COVID-19 Pandemic Era: Focusing on the Innovation of Official Distribution Channels. Journal of Korea Trade, 25(3), 153-168. Web.
Martin, A., Markhvida, M., Hallegatte, S., & Walsh, B. (2020). Socio-economic impacts of COVID-19 on household consumption and poverty. Economics of disasters and climate change, 4(3), 453-479. Web.
Meyer, S. (2020). Understanding the COVID-19 effect on online shopping behavior. The BigCommerce Blog. Web.
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C.,… & Agha, R. (2020). The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. International journal of surgery, 78, 185-193. Web.
OECD (2020), “E-commerce in the times of COVID-19”, OECD Policy Responses to Coronavirus (COVID-19). Web.
Pantano, E., Pizzi, G., Scarpi, D., & Dennis, C. (2020). Competing during a pandemic? Retailers’ ups and downs during the COVID-19 outbreak. Journal of Business Research. Web.
Reinders, S., Alva, A., Huicho, L., & Blas, M. M. (2020). Indigenous communities’ responses to the COVID-19 Pandemic and consequences for maternal and neonatal health in remote Peruvian Amazon: a qualitative study based on routine programme supervision. BMJ open, 10(12), e044197. Web.
Susmitha, M. K. (2021). Impact of COVID 19 on E-Commerce. Journal of Interdisciplinary Cycle Research, 12(9), 1161-1165. Web.
Watanabe, C., Akhtar, W., Tou, Y., & Neittaanmäki, P. (2022). A new perspective of innovation toward a non-contact society-Amazon’s initiative in pioneering growing seamless switching. Technology in Society, 69. Web.