Introduction
Telehealth is a disruptive technology that affects the process of care provision and broadens the horizons of healthcare in general. The current evidence shows that telemedicine contributes to the development of value-based care and improved patient outcomes (Randazzo, 2018).
Care providers should investigate the phenomenon of telehealth to gain access to cutting-edge technology that could make patients content and create premises for other improvements. Telehealth should be viewed as the future of care provision due to numerous advantages that block off the lack of reliability, such as convenience, innovation, ease of access, and adherence to different health regimens.
Precis
In the article completed by Ellimoottil et al. (2018), health systems implementing telehealth were studied in detail to assess the degrees of technology development and expansion. The authors claimed that there are specific challenges that reduce the willingness to implement telehealth among care providers. The focus of Ellimoottil et al.’s (2018) article is on the discussion of how senior leaders could contribute to the implementation of telehealth.
It was hypothesized that the strategic goals of the facility should respond to the opportunities offered by telehealth. The growing demand for technology creates premises for care providers to seek additional investment opportunities. Ellimoottil et al. (2018) identified that telehealth could be associated with career development opportunities in the case where care providers would adopt an updated workflow and support telehealth champions.
Information identified in Ellimoottil et al.’s (2018) article is relevant because it acknowledges the need for technology in care provision and outlines the positive future of care models that are based on telehealth. Accordingly, technology should be utilized to motivate improvement and educate patients on the benefits of telehealth and other interconnected tools.
Mind Map Discussion
Based on the mind map in the figure below, it may be concluded that there is a decent number of benefits and opportunities linked to telehealth that are mitigated by various concerns. The biggest obstacle to the implementation and improvement of telehealth initiatives is the inability to engage enough individuals.
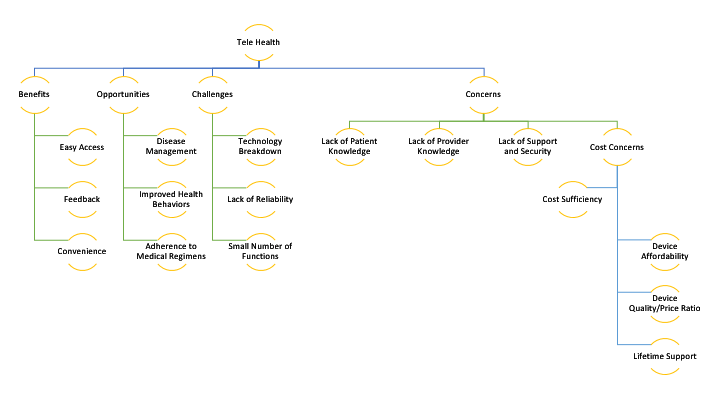
Even if care providers might be aware of potential opportunities linked to health technologies, a high percentage of providers do not possess enough knowledge to complete the expansion (Pendse & Nugent, 2017). It is essential to align telehealth against the strategic vision of the facility and make sure to allocate resources adequately. Therefore, financial support should be seen as one of the essential contributors to the success of telehealth-related initiatives.
Another critical idea that can be synthesized from the mind map is that telehealth initiatives cause too many concerns and, therefore, should be appropriately prioritized. Pilot projects in telehealth should be supported by the government and external investors so that more clinical departments and care receivers would become more interested in new pilots (Fraiche et al., 2017). This also means that telehealth teams should be ready to reply to all kinds of requests from the clients because the latter often do not have enough knowledge to manage health services correctly.
Improvements in the area of telehealth can only be generated under the influence of staff members and clinicians who are carefully engaged in the process of refining digital health systems. Lurie and Carr (2018) suggest that telehealth expansion depends on the existence of technology advocates who are not going to perceive it as a disruption.
On the other hand, patient education plays a critical role in the process of dealing with the challenge of telehealth. The idea is that the majority of patients merely do not recognize the benefits and opportunities linked to telehealth. To resolve this, facility management and staff members should educate patients to improve their experiences (Koru et al., 2016; Randazzo, 2018).
After addressing all the challenges and opportunities, the team would have to evaluate the outcomes of telehealth implementation. However, this poses another challenge for care providers because the process of patient experience enhancement is going to take time. Nonetheless, telehealth investments might be predicted to generate improved patient outcomes, increased returns on investment, and more patients that are contented.
Conclusion
The mind map and a brief literature review on the subject both hint at the fact that the majority of patients and providers have not yet discovered all the opportunities that telehealth might bring to the table. As existing telehealth initiatives are continuously expanded, it may be reasonable to elaborate on brand new agendas and introduce patients to the benefits of telehealth.
Different health departments require various approaches to telehealth implementation, which means that clinical performance could be improved even without a unified approach to telehealth and other healthcare technologies. The future of telehealth depends on the ability of clinicians and patients to recognize the value that technology could bring to healthcare and acknowledge the value of the personal contribution. Patience and humility should be at the forefront of telehealth implementation.
To conclude, the current paper outlined a mind map for telehealth, while mostly focusing on the most significant concerns that avert patients and care providers from fully acknowledging the impact of technology on care provision.
Despite the cost of telehealth implementation, the majority of challenges, such as the lack of functions and a high chance of breakdown, can be quickly outstripped by the convenience of use, constant feedback from patients, and ease of access. From smaller hospitals to large health systems, practically anyone can navigate through the opportunities offered by telehealth and only pick the ones that are going to be beneficial to the organization. Existing care delivery models should be carefully customized to respond to the value of telehealth, as the latter represents one of the shortest pathways to maximized patient experience and workplace efficiency.
References
Ellimoottil, C., An, L., Moyer, M., Sossong, S., & Hollander, J. E. (2018). Challenges and opportunities faced by large health systems implementing telehealth. Health Affairs, 37(12), 1955-1959.
Fraiche, A. M., Eapen, Z. J., & McClellan, M. B. (2017). Moving beyond the walls of the clinic: Opportunities and challenges to the future of telehealth in heart failure. JACC: Heart Failure, 5(4), 297-304.
Koru, G., Alhuwail, D., Topaz, M., Norcio, A. F., & Mills, M. E. (2016). Investigating the challenges and opportunities in home care to facilitate effective information technology adoption. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 17(1), 53-58.
Lurie, N., & Carr, B. G. (2018). The role of telehealth in the medical response to disasters. JAMA Internal Medicine, 178(6), 745-746.
Pendse, S. R., & Nugent, N. R. (2017). Mental health challenges and opportunities in rural communities. The Brown University Child and Adolescent Behavior Letter, 33(6), 1-7.
Randazzo, G. (2018). Challenges and opportunities facing nurse executives in the era of value-based care. Nurse Leader, 16(2), 96-100.