Introduction to the Order Delivery Process (ODP) Concept
The ODP process refers to how the business process flows from one step to another. It flows to the process elements together with their corresponding elements. The ODP process covers the 7Ss, which includes source, stock, store, sell, ship, supply chain planning, and support services (Zhu, Wang & Tang, 2018). The 7Ss help supply goods and services from the factory or organization to its consumers through wholesalers and retailers. The ODP process is very related to transportation management systems. Technology helps many businesses formulate business plans and execute and facilitate the movement of goods and services to customers within the shortest time possible.
The 7Ss covered include stock, which refers to all of the products in the organization that are being sold to generate income. A store is a warehouse where the stock is placed before being dispatched to various customers. Sell is the process or way of passing ownership rights from the owner to the second party, paying consideration to obtain ownership. The ship is the process or logistics involved in the manufacturing company to ensure the stock or products reach their customers within the shortest time possible (Chana, Siripipatthanakul, & Phayaphrom, 2021). Supply chain planning is where the managers in the supply chain organize and plan all logistics and activities that will enable their customers to access their goods and services.
Problem Statement
The ODP process covers all the 7Ss in any organization’s supply chain management. This process gives an organization the ability to reach and attract more customers. It also increases the organization’s visibility in its day-to-day operations of transporting goods and services to its customers. The ODP process also assists in streamlining the shipping process and eases how businesses manage their operations (Barreto, Amaral, & Pereira, 2017).
Despite benefits, there are still many challenges that are brought by ODP processes. The main problem is that many customers need to be more fluent and familiar with the 7Ss or ODP as it is a new idea brought by technology to many people. Due to this problem, the use of ODP processes could be more efficient and effective as to the expectations of many people in many businesses.
Recommendations Along with Resource/Investment Requirements
For the successful implementation of the transportation management system, the business should adopt some scenarios that will effectively and efficiently lead to the success of the performance of the system. The following are the recommendations that the company may adopt for the successful implementation of the system;
- The business’s operations should be ssuccessfulupported in the entire planning process. Before any implementation is done, proper planning is necessary to improve the system’s capabilities for planning loads. Planning involves ensuring all the resources are available to facilitate operations.
- The business should have enough finance for investment and to drive pay. Enough finance makes the company settle its operations, revenue distribution and claims.
- The business should have drivers that can be used to implement the systems efficiently. The drivers may include apps and phones that can facilitate transport management systems’ operations.
- The project manager should be dedicated. Since ODP processes go hand in hand with technology, the project manager must be grounded with information technology knowledge that will assist in information technology project management. The project manager should be well organized and be able to keep people on track and in line with the business project.
- The business should practice in-house development. Business managers should be able to quickly meet the customers’ needs and satisfy them within the shortest time possible. They should be able to cut the cost of the business and increase its revenue-generating activities. The costs incurred by the company should be less than the profit generated by the business (Johns, Duran & West, 2022). Sometimes, implementing the ODP process becomes hectic and costly, but evaluation should ensure that the benefits realized with time should be less than the costs.
Performance Benefits of Transportation Management System (TMS) Implementation
A transportation management system is critical to supply chain management in many businesses. The benefits obtained from its implementations include;
- It helps analyze customer demand and plans how to meet customer demand. This is done by moving goods and services from the production factory to the customers who demand to use them. All the customer expectations and needs are met with the help of a transportation management system.
- It helps improve the services offered to customers and satisfy their needs. This is achieved through real-time updates and non-delays in shipments. Indeed, transportation management enables all the customer needs to be met within the shortest time possible.
- Transportation management systems improve export and import compliance, which minimizes delays in goods and services due to late shipment to attract penalties usually. Compliance helps all the importation and exportation activities to be easily met without any delay of shipping activities that may result in fines.
- Businesses can easily access and track their freight in a single platform locally and globally. All the freight cost incurred by the company is easily tracked and recorded.
Financial Benefits of Implementation of TMS
Return on investments (ROI) is where the business evaluates all of its assets and makes a judgment on the performance of a particular investment compared to other investments. Return on investment is computed by dividing its net profit by its initial investment cost. Return on investments also helps determine the profitability of the business. A positive return on investment implies that the company is making a profit, while a negative return on investment suggests the industry is losing.
The financial drives of return on investment are expressed in four different ways below.
Profitability
This is the way a business measures its profit generated relative to expenses incurred. The investment cost incurred by the firm on visibility, capacity and utilization and salary drive and maintenance totalled $67000 per month. The benefits obtained by the business stand at $120000 per month.
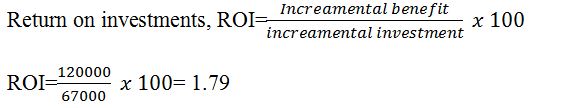
The positive ratio implies that the business makes a profit since the net benefits exceed the investment cost.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement is the financial statement that gives the business all the information regarding its cash inflows and outflows. The cash in hand for the company before implementing the system stands at $102000. This is the cash the business had to facilitate its system implementation. The total cash outflow used in initiating the plan amounted to $71500. This cash flow was mainly meant for the successful initiative of the system. In comparing the cash inflow and cash outflow, the business gains an income of;
Income= cash inflow- cash outflow
Income=$102000-$71500= $30500
The implementation of the system should be done since the cash flow used in the process is less than the cash inflow.
Asset Turnover
Asset efficiency shows how the business generates its revenue from utilizing the assets. Asset turnover is the ratio that shows or measures the business’s efficiency in generating income using support.
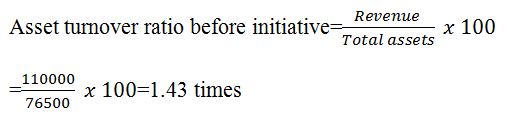
The ratio is above one, implying the firm utilizes its assets to generate revenue.
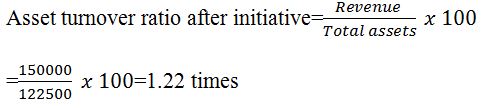
The ratio is smaller than before the system’s initiative, implying that the system being an organizational asset, was efficiently utilized to generate revenue.

The inventory turnover ratio after the initiative is smaller than before the industry due to the efficient system utilization to generate revenue.
Revenue Growth
This shows the rate at which the business grows with the implementation of the system.
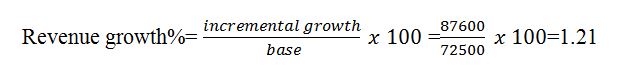
Timeline for Implementation
The process of implementation period depends on the business leadership team, the software to be used, and its integration. The implementation timeline is as shown.
Table 1 – Implementation Timeline
Conclusion
In summary, transportation management systems assist businesses in executorships, business planning, and optimization of the movement of goods physically from producers to consumers via wholesalers and retailers. In planning, supply chain management plays a key role in identifying ways of shipping goods that cost less to improve business profits. In execution, there is an actual time exchange of information from the producer to the consumer via wholesalers and retailers. In the long-term optimization, the ability of the business to measure and track its reports together with its performance is critically done.
References
Barreto, L., Amaral, A., & Pereira, T. (2017). Industry 4.0 implications in logistics: an overview. Procedia Manufacturing, 13, 1245-1252. Web.
Chana, P., Siripipatthanakul, S., & Phayaphrom, B. (2021). Effect of the service marketing mix (7Ps) on patient satisfaction for clinic services in Thailand. International Journal of Business, Marketing, and Communication, 1(2), 1-12. Web.
Johns, B., Duran, O. S., & West, C., (2022). Magic quadrant for transportation management systems. Gartner, Inc. Web.
Zhu, L., Wang, Y., & Tang, T. (2018). Big data analytics in intelligent transportation systems: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 20(1), 383-398. Web.