Introduction
Nurses are subject to great emotional and physical stress. Hence, dissatisfaction with life and depression may arise, which will affect the quality of nurses’ work. The business challenges addressed are productivity numbers and rising costs. This issue was chosen due to the fact that emotional burnout in nurses is a severe form of chronic fatigue syndrome and is one of the most common problems faced by many medical staff. The consequences, if the problem is not solved, are a significant reduction in the productivity of nurses and a deterioration in the results of patient treatment. The problem is actually occurring in any medical institutions and departments, regardless of their size; it can be specified as a nursing burnout syndrome (Montanari et al., 2018). The abnormal and unwanted condition that is happening is an excessive workload on nurses. Nurses overwork many shifts and suffer from the uneven nurse-patient ratio every day. Constant overwork and constant work in conditions of limited time lead to emotional burnout among nurses. A standard should appear that will regulate the work of nurses in such a way as to allow them to reduce overwork.
Background: Current State
This initiative aligns with the vision of the organization as it is interested in improving the effectiveness of nurses. It is important to the mission of the organization in many tangible ways such as improving the patient outcome or patient satisfaction. Specific conditions that indicate a problem and need for reducing workload of nurses is significant enhancement in burnout among medical staff.
Target State: SMART Goal
SMART Goal is paying attention to mental health problems among nurses, in particular, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of emotional burnout. Current and target state are the size of the workload for nurses; thus, the gap to be addressed is the reduction of nurse-patient ratio.
Analysis
Conditions of insufficient nursing staff are preventing the desired future state from being reached. They exist because of the discrepancy between the workload and remuneration of medical workers (Connors et al., 2019). The root causes of the gap are insufficient funding of the healthcare sector. The cause-and-effect analysis presented in the form of fishbone diagram can be seen in Figure 1.
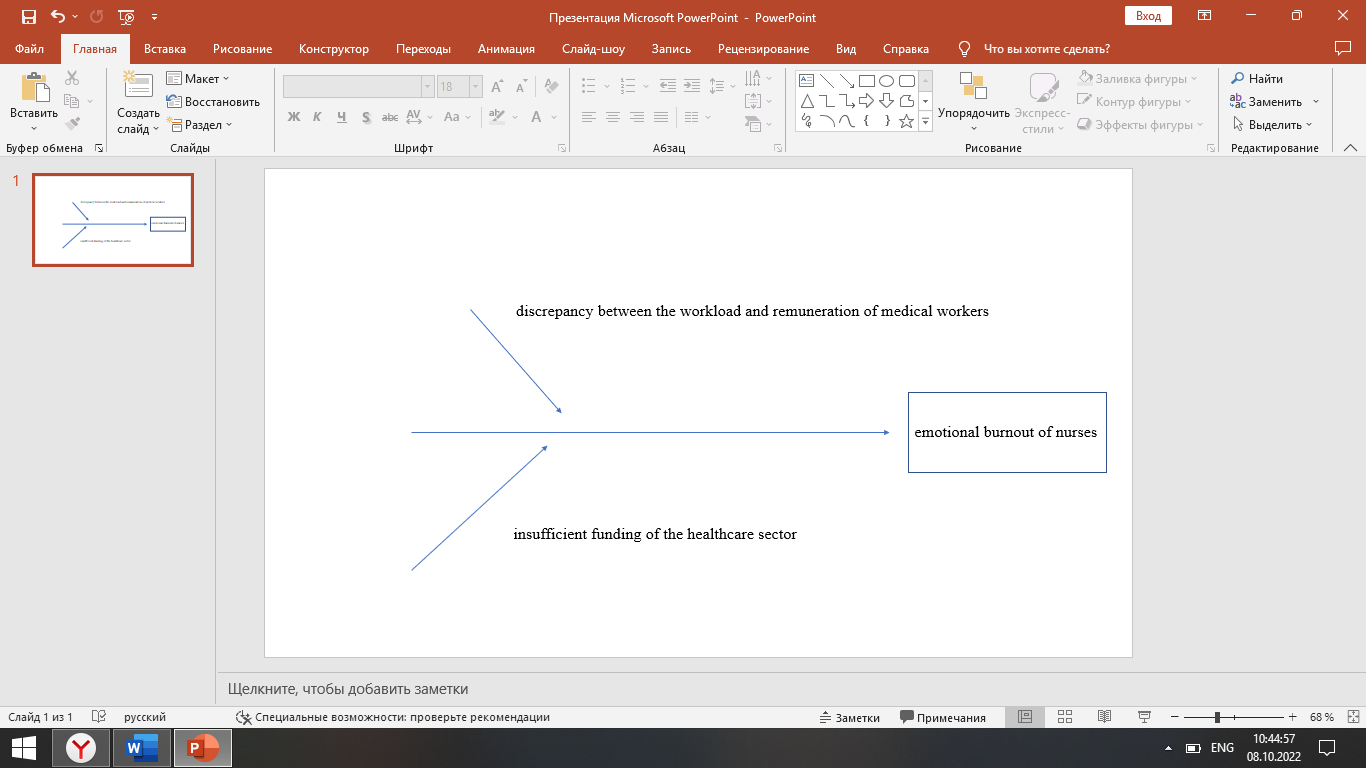
Figure 1.
Cause Analysis Summary
Root Cause
Hypothesis
Countermeasures/Experiments
To test and validate the recommended hypothesis listed in above, surveys will be conducted among patients and nurses to assess their satisfaction level. The main actions and outcomes of implementing plan are to find and hire employees (Grigorescu et al., 2020). The main barriers expected are lack of funding and resistance to change among employees. They can be addressed by participating in government programs for additional financial assistance and conducting master classes for employees. The financial and managemental support and monetary and personnel resources will be needed. To assess the success of the changes, a questionnaire will be used among patients and nurses according to their level of satisfaction.
Completion Plan
Confirmed State
Metrics post-implementation should be to increase the satisfaction of both patients and nurses themselves. The proposed countermeasures will help to reach future state and goals due to the reduced likelihood of emotional burnout among nurses. Performance will be improving over time in the data as the hired nurses and manager will gain more experience and improve their performance (Grigorescu et al., 2020). New problems created were caused by the difficulty of adapting new staff. They had a negative impact on the problem making it worse in the short-term perspective.
Follow-up
The required standard work includes hiring specialists, and training includes working with a manager and adapting new employees.
Lessons Learned
The changes planning went well, however, the implementation of these changes can be improved. In the process, the importance of management and finding an approach to each employee has been learnt (Montanari et al., 2018). It would be possible to organize the process of adaptation of new employees differently, paying more attention to it.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Project Budget
Environmental
Utilities
Equipment
Personnel 17
Events 17
Total Project Costs (from each table): $22, 750
Cost Benefit Analysis
The advantages of this method are, first of all, savings on finding new employees and motivating them to work in the long term (Rodríguez-García et al., 2020). Moreover, cost benefits consist in savings on attracting new customers due to an increase in the number of loyal patients as a result of increased patient satisfaction.
Income Acquired Per Evaluation/Assessment
Total Income of first year: $445, 000
Benefit for the 1st year: $445, 000 − $20,500 = $424,500
Conclusion
First of all, the potential benefits and savings that may result from the project implementation will be to improve the quality of life of nurses. Moreover, the introduction of means to combat emotional burnout among nurses significantly reduces health care costs of constantly searching for new employees (Hindman, 2019). An increase in the number of medical personnel will have a positive impact on population health and considerations of diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI), as it will allow more patients to be treated. Other positive effects of this project are increased reimbursement, increased staff morale and institution liability associated with the preservation and care of emotional and physical resources of the medical center.
References
Connors, C. A., Dukhanin, V., & Wu, A. W. (2019). Peer support for nurses as second victims: Resilience, burnout, and job satisfaction. Journal Indexing and Metrics, 25(1), 727– 728.
Grigorescu, S., Cazan, A. M., Rogozea, L., & Grigorescu, D. O. (2020). Original targeted therapy for the management of the burnout syndrome in nurses: An innovative approach and a new opportunity in the context of predictive, preventive and personalized medicine. EPMA Journal, 11(2), 161– 176.
Hindman, A. (2019). Utilizing scribes to improve patient-centered care and efficiency and reduce burnout. Oncology Issues, 34(4), 46– 50.
Montanari, K. M., Bowe, C. L., & Chesak, C. S. (2018). Mindfulness: Assessing the feasibility of a pilot intervention to reduce stress and burnout. Journal Indexing and Metrics, 37(2), 3288– 3299.
Rodríguez-García, M. C., Márquez-Hernández, V., Belmonte-García, T., Gutiérrez-Puertas, L., & Granados-Gámez, G. (2020). How magnet hospital status affects nurses, patients, and organizations: A systematic review. American Journal of Nursing, 120(7), 28– 38.