The State of New Jersey Department of Health strongly supports effective observations and efficient strategies to monitor and prevent injuries and violence and to completely curb the resulting impacts in the community. The association strictly addresses the key causes of both intentional and unintentional forms of injuries at specific groups of populations and ages in the community to find the core of the problems and find solutions to them (Ridenour et al., 2019). This includes historic issues like racism and oppression which force some communities to be involved in activities associated with injuries and violence. New Jersey Department of Health identifies injury and violence as a public health problem in New Jersey. It directs its attention to identifying the role played by local health departments in defending and refining general community safety and health through collaborations and support.
New Jersey Department of Health has devised strategies to discourse the origins of injuries and violence across all the ages within the people of New Jersey. The strategies go further to address the exact populations impacted by explicit injuries and acts of violence grounded on gender, age, disability, and race. Moreover, they ensure that proper public health interventions are employed and executed effectively in addressing the various groups of people. The strategies include:
- Training and support to increase the capacity of all local New Jersey-based healthcare departments on how to identify, address and monitor injury and violence-related occurrences with their trends.
- Increase funding of all the local health departments to help them maintain infrastructure and strategies of prevention. Also, to improve their surveillance, analysis of datasets, and enhance leadership positions.
- Implement methods that discourse protective and dangerous factors for different types of violence and injuries.
- Integrate the prevention of injury and violence in other correlated health efforts like maternal and child health.
- Educate and encourage representatives, institutions, and administrations to raise the alertness of injury and violence as a general public health problem.
- Support the development and implementation of surveillance and reporting systems across the state.
- Collaborate with local public health departments, community, and stakeholders through assisting efforts.
Justification
Injury and violence are significant problems in public health because they cause adverse effects on the general health of communities. They cause impacts like premature death, emotional trauma, disability, burdens to healthcare systems, forfeiture of productivity, physical trauma, and deprived mental health. Injury and violence usually comprise homicides, suicides, self-inflicted injuries, and also injuries resulting from undetermined intentions. Healthcare systems receive the entire burden resulting from this problem (Ertl et al., 2019). The predictability of injuries and violence is high; thus, it is easy to prevent and control their occurrence and hence avoid any adverse effect they can cause to an individual.
In New Jersey, injuries and violence are the major causes of death, debility, and indisposition. In 2016, unintentional injuries were rated as the third most cause of mortality and injury in New Jersey; it caused over 3,800 deaths (Wilson, 2017). These deaths are primarily due to unexpected occurrences like vehicle accidents and falls (Curry et al., 2017). Intentional injuries such as suicides and homicides have also impacted New Jersey and have resulted in the death of many. Annually over 700 New Jersey Residents die from committing suicides (Wilson, 2017). Suicides have become a boundless health problem in New Jersey because this number is very anomalous for normal people living well with no underlying issues.
Violence has become a great concern within the young people in New Jersey. Among persons between the age of 15-24, violence is the leading cause of death (Ridenour et al., 2019). Homicides come second in resulting in death between that age bracket. Annually over 400 cases of homicides are reported in new jersey (Wilson, 2017). The victims of homicides are black males who account for more than 80% of the problem (Wilson, 2017). Female-based homicides that account for more than 40% in New Jersey (Wilson et al., 2020) usually result from killings by former intimate partners. Homicide has become a great health concern in the State of New Jersey.
Recently, an overdose that results from unintentional poisoning has bypassed vehicle accidents as the leading cause of deaths and injuries in New Jersey. Males mostly account for the rate since they have been reported to be three times expected to perish than females (Wilson et al., 2020). Motor vehicles come second after an overdose in causing injuries and deaths among New Jersey residents. Annually over 274,000 motor vehicle accidents occur in New Jersey. They result in over 600 deaths (Curry et al., 2017). Young persons and the elderly account for the most crushes while males have generally been classified to be involved mostly in the accidents since they account for over 70% of them (Curry et al., 2017). Deaths resulting from vehicle accidents and overdose have increased rapidly hence this has become a great health problem that needs to addressed with immediate effect in New Jersey.
Injury and violence prevention ensures the well-being and enhanced health of all the members of the community. Effective procedures and methods for preventing injuries include technology and engineering, education and change of behaviors among individuals, law enforcement and legislation, adjustments to the environment, enhancements to the safety of products. To prevent violence the effective procedures, include enhancing skills towards solving problems, amending policies to address social conditions that encourage and lead to violence, and encouraging safe and strong relationships among all groups of people in the community. Strictly employing the above approaches leads to proper living and hence healthy people free from any problems within the society.
Local healthcare organizations and departments are responsible for developing and maintaining conditions that keep people healthy by curbing injuries and violence. Moreover, they are responsible for addressing the effects of violence and injuries in societies they should be assisted in assessing injuries and violence and also in the formation of action plans at all community population levels which include individual and societal levels. This is achieved through prover evaluation and improvement of the programs. Prevention efforts should be diverse and specific towards increasing the protective factors to all possible causes of injuries and violence. In addition, prevention exertions should effectively address and reduce all forms of oppressions whether institutional or structural through increasing of protective factors. Policy development and assurance are entitled to healthcare departments. They must work with other partners in sectors of the education system, law enforcement agencies, workplaces, healthcare systems, transport agencies, and community groups to ensure that they devise the most effective policies regarding violence and injury prevention. In order to effectively discourse and control the origins of injury and violence across the lifetime, local healthcare departments and practitioners must use community resources through proper accessibility plans and engagements.

Implementation of a Violence Surveillance System
- New Jersey Violent Death Reporting System was developed and its maintenance is through an agreement with other centers. It is located in the Center for Health Statistics.
- It has a very rich dataset from medical examinations, death certificates, and police reports.
- Local health departments and community groups use the data from the system to carry out collaborative procedures and interventions in preventing and reducing deaths resulting from violence and injuries.

Awarded Funds from CDC to Aid in Addressing Overdoses
- New Jersey Center for Health statistics has been funded to conduct research and surveillance on the overdose of an opioid.
- It is an initiative that is data-driven and is focused on employing strict policies and programs to curb the abuse, misuse, and overdose of opioids hence help to stop the problem. This program works hand-in-hand with NJVDRS to help staff and local health practitioners gain knowledge.
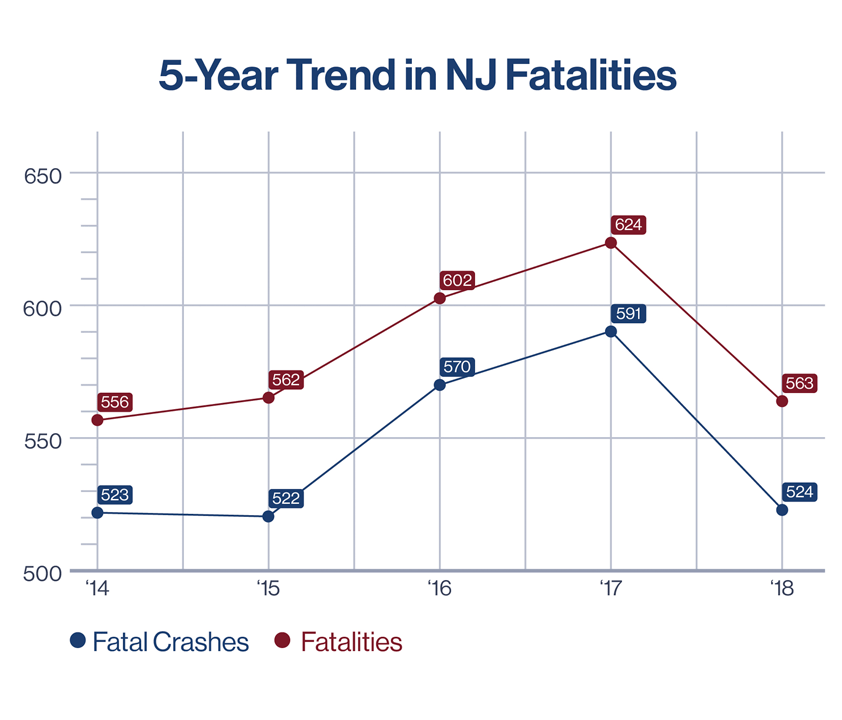
The Trend of Injuries and Deaths Resulting from Motor Vehicle Accidents

Motor vehicle deaths have accounted for injuries and deaths in New Jersey. They were the leading cause of injuries before overdose overtook them.

Accidents commonly affect the young and the elderly in New Jersey. Death resulting from accidents increased from 2015 up to 2017 from when a decrease occurred onwards.
References
Curry, A., Pfeiffer, M., Metzger, K., & Kirk, M. (2017). 56 Catalysing advancements in traffic safety via data linkage: Case example of the new jersey traffic safety outcomes program data warehouse.Injury Prevention, 23. Web.
Ertl, A., Sheats, K. J., Petrosky, E., Betz, C. J., Yuan, K., & Fowler, K. A. (2019). Surveillance for violent deaths—National violent death reporting system, 32 states, 2016.MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 68(9),1-36. Web.
Ridenour, M. L., Hendricks, S., Hartley, D., & Blando, J. D. (2019). New Jersey home health care aides survey results.Home Health Care Management & Practice, 31(3), 172-178. Web.
Wilson, D. (2017). Indigenous populations and the domestic violence death review process. In Domestic Homicides and Death Reviews (pp. 287-316). Web.
Wilson, N., Kariisa, M., Seth, P., Smith IV, H., & Davis, N. L. (2020). Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths—the United States, 2017–2018.Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 69(11), 290-297. Web.