Abstract
In this paper, the researcher wanted to explore factors of innovation development in Dubai schools and how effective they are in promoting creativity and innovation among learners. The researcher used both primary and secondary data sources. Primary data was obtained from sampled participants in four schools in Dubai. Secondary data was obtained from books, journal articles, and reliable online sources. The findings show that students’ limited interaction with the business environment, overemphasis on exams, and limited interest shown by parents and teachers are the major hindrance in creating an enabling environment for innovation to flourish. The study recommends that there should be a multi-stakeholder approach to address current problems.
Introduction
In the current globalized society, education is considered a perfect tool that empowers children to face the world and various forces in their socio-economic and political lives. Schools are under pressure to offer students more than the simple theoretical concepts of dealing with forces in life. Schools have to ensure that they produce highly creative individuals who perfectly understand the forces in their environment and are capable of coming up with unique ways of addressing them.
According to Cankar, Tomi, and Cankar (2013), the world is currently grappling with completely new issues such as global warming, climate change, cyber threat, and cybersecurity, global trade and globalization, radicalization and violent extremism, and communitarianism among other complex social issues that never existed in the past. To address these problems, society often turns to schools to find solutions.
Institutions of learning are considered the epitome of knowledge centers where research is highly valued. However, some stakeholders have warned that most of the local learning institutions in the United Arab Emirates are completely out of touch with the realities. The system is so focused on exams that very little attention is given to the need to promote creativity and innovation. Rogers (2016) defines innovation, in the context of schools and school management behavior, as the ability and willingness to use and promote creativity in an organizational setting.
According to Zhao (2012), the education system in Dubai is a step ahead of that in other emirates within the country. This is partly attributed to the massive development of Dubai city as a major global tourist destination and a business hub. The city is home to the world’s tallest building and the largest man-made island. These new forces in the environment have forced the stakeholders in this emirate to rethink the education system. It has become evident that it is critically important to have an education system that supports creativity and innovation in line with the current environmental forces and the changing trends.
Students must learn to think creatively to address the current issues they face and other issues affecting society. Rogers (2016) says that for students to be innovative, they need an environment that supports innovation. They need the material and emotional support that will allow them to think creatively to come up with ways of addressing the forces within the environment. Some institutions have tried to create systems and structures to enable their learners to think creatively and to come up with ways addressing problems they face in their environment.
These are some of the issues that the stakeholders must consider when trying to motivate creativity and innovation among learners. In this paper, the researcher seeks to explore factors of innovation development in Dubai Schools and how effective they are in promoting creativity and innovation among learners.
Research Objectives
The research outcome in this project may play a significant role in informing the policies which stakeholders in the education sectors embrace when redefining the curriculum used in this country. The importance of this study makes it necessary to come up with clear objectives that should be achieved by the end of the project. The following are the research objectives for this study:
- To explore different factors of innovation development in Dubai schools and how effective they are;
- To determine how innovative students in Dubai schools are in addressing the social issues they face at school;
- To come up with recommendations on how to improve creativity and innovation in Dubai schools.
Research Questions
The process of collecting data may sometimes be confusing as one may encounter numerous pieces of information, some of which may not be entirely relevant to the study. As such, Zhao (2012) advises that a researcher should come up with clearly defined research questions that would help in the process of collecting the needed data from various sources. The following are the research questions that were used in this study.
- What are the different factors of innovation development in Dubai, and how effective are they?
- How innovative are students in Dubai schools when it comes to addressing various issues that affect them?
- What can be done to help promote creativity and innovation in Dubai schools?
Theory and Hypotheses
Background
Innovation is increasingly becoming a major key to solving the socio-political and economic problems that the United Arab Emirates face in the twenty-first century going forward. According to Andersson and Djeflat (2013), for a long time, the United Arab Emirates relied heavily on oil and gas to support its economy. However, with the oil reserves expected to dry up in the near future, there have been attempts to find creative ways of diversifying the economy.
The stakeholders have turned to innovative ideas to promote tourism and trade in the local economy. The efforts put in place have borne fruits, and currently, the city of Dubai is a top tourists’ destination and a global business hub. Although the efforts put in place by the government and stakeholders to transform the economy of Dubai has been impressive, Andersson and Djeflat (2013) say that it is worrying that most of the experts involved in these projects came from other countries.
The designers and other experts who put up Burj Khalifa, the tallest building on earth, were foreigners. The local stakeholders also had to seek the services of these foreigners when designing and constructing the Palm Island, which currently holds the record as the largest man-made island in the world. The government has invested heavily in the field of education. However, the fact that the country has to rely on foreign experts is a sign that the education sector, in its current form, is not capable of meeting the local demands in a globalizing society.
Creativity and innovation is a virtue that people learn. It is apparent that the learning institutions in the country have not inculcated the culture of innovativeness among the learners. More emphasis is still placed on passing examinations instead of having creative ways of solving problems in society. Excellence in the education sector is still placed on exams instead of looking at the holistic growth and development of the learners.
Rogers (2016) says that to secure our future, we have to fix the education system. We have to empower the future generation in a way that will enable them to address the emerging socio-economic and political problems from a different perspective compared with the current generation. That is why this research is very critical. It will help in ensuring that the future leaders and workers in this country are capable of understanding the changing trends and patterns and can define creative solutions for such emerging issues.
Literature Review
According to Oxford Business Group (2014), the education sector in Dubai has undergone massive changes over the recent past as stakeholders try to ensure that the institutions can produce graduates who can manage the emerging forces in the environment. The government of Dubai has invested heavily in the education sector, especially in terms of infrastructure and human resources.
New schools have been built, and the old ones renovated to ensure that they meet the international standards as the city becomes a center of attention globally in terms of tourism and trade. The stakeholders have also made a concerted effort to ensure that these schools have the right number of teachers who are qualified and capable of meeting the emerging needs in the education sector. Andersson and Djeflat (2013) say that the government has even hired some international teachers to ensure that the local schools have the required number of staff capable of meeting the needs of students in the best way possible.
However, Blatchford (2014) says that the level of creativity among the local students is not as high as many would expect based on the massive investments that have been made in this sector. Learners are still focused on passing their exams just as it was in the past. It means that as the government-engineered massive infrastructural and human resource development in the education sector, the vision and mission remained the same. Little was done to ensure that focus in the education sector was redefined to be in line with the emerging environmental forces.
Innovation Management and Practices and Impact in Schools
According to Alon, Jones, and McIntyre (2013), creativity and innovation must be inculcated in people from a very early to empower them in their future lives. It is a concept that people learn and must be embraced early enough. Trying to promote creativity and innovation in institutions of higher learning is important. However, it is more important to ensure that culture is promoted among learners from the early stages of education.
Rogers (2016) says that high school students should be empowered by making them creative in solving the problems they face. In high schools, these learners already understand some of the real challenges in life. They understand poverty and its dangers, and factors that may lead to it. They also understand the concept of success. At high school, learners understand some of the real challenges in life. They reason rationally and can be trusted to offer solutions to some of the problems at home or school.
As such, they are the best group of learners who should start embracing creativity in addressing socio-economic and political problems. Their focus should be moved from passing exams to understanding of the real life challenges and how they can be addressed. Blatchford (2014) says that high school students are capable of come up with innovative solutions to some of the problems they face in life.
In a study that was conducted by Audretsch, Link, and Walshok (2015), for students to be creative, they need to understand the forces in the labor market and the environment in which they are expected to work after graduation. They need to be in touch with the realities in the society beyond what they read in books. They have to understand the real problems for which innovative ideas are needed. When they are allowed to interact with the realities in the labor market, they get to understand to understand the reason why they are in classrooms.
They get to appreciate that their focus should be to use the knowledge learnt in class to address the real life problems. Such students get to appreciate that the only way of being ahead of the rest is to come up with unique ways of solving the environmental issues. When such an environment is created for the learners, they become innovative because they know it is the only way of being successful in life.
Case Study: Benchmarking
Phillips Exeter Academy in New Hampshire, the United States, is one of the high schools that have adopted a very unique mode of education. According to Tan and Perleth (2015), the learning system in this school is based the application of Harkness education. This form of education involves learners sitting in large groups and discussing ideas with minimal teacher intervention. This mode of teaching fully empowers learners and relegates the role of a teacher to that of a guide.
The student-centered approach used in this school highly encourages innovation among the learners. During the round-table discussions, students are encouraged to come up with innovative ideas of solving the social problems they face at home or at school. Each student will propose the idea and the group members will discuss it and develop it into a practical action plan in case it is viable.
Phillips Exeter Academy also uses Socratic Method of education where learners engage in cooperative argumentative dialogues where questions are answered and answers are given from various perspectives as a way promoting critical thinking. It is a concept meant to empower learners to embrace peer reviews and development as they try to address real life problems. The school was selected because it epitomizes creativity and innovation in a school setting.
The institution is also keen on promoting co-curriculum activities to help learners identify their special talents that may help them in their later lives. Some of the alumni of this school have become United States’ presidents such as Franklin Pierce, top government administrators such as Robert Lincoln, top entrepreneurs such as Mark Zuckerberg, Ulysses Grant Jr., and Jay Rockefeller, and other top celebrities such as David Rockefeller, China Forbes, and Drew Pearson.
It is a clear demonstration that students from this institution understand the forces in the society and can come up with practical ways of solving them. The creativity and innovativeness that Mark Zuckerberg learnt from this institution helped him come up with Facebook to ease social communication, an invention that has made him become one of the top 10 billionaires in the world.
Students in Phillips Exeter Academy are highly motivated and self-driven towards creativity and innovation. The administration and the system in the school make it possible for the students to understand real life challenges in the country. They understand that the best way of dealing with the emerging issues in the society is to be creative and innovative. The institution has not come up with specific awards for the students.
However, students who excel in sports, science and art fairs, academics, and other activities are often recognized and in some cases given financial incentives (Tan & Perleth 2015). The moral incentive, especially in the form of praise encouragements by the teachers and administrators for those who demonstrate unique levels of creativity also motivates the students to be innovative. To ensure that innovation is sustainable at this institution, the administration has created a culture where every student is expected to come up with a unique and practical solution to a real life problem. The culture keeps the students constantly focused on creative thinking.
Theoretical Concepts
It is important to look at some of the theories related to creativity and innovation that can help inform the policy makers who are trying to redefine the education system. One of the major theories relevant to this study is the Humanistic Theory of Creativity. According to Tan and Perleth (2015), this theory- as put forth by Maslow, Rogers, and Fromm- holds that every human being desires to achieve self-actualization. Self-actualization is a state where one feels that he or she has achieved what was expected and can now focus on other issues in life. Self-actualization should not be confused by wealth accumulation (Andersson & Djeflat 2013).
In the context of learners in high school, self-actualization can be achieved when the learners feel that they have registered excellence in their academics and can now use their knowledge to address complex problems in the society. Self-actualization creates a sense of satisfaction and confidence among learners. It makes them feel that they have unique capabilities that can be used to find unique solutions to the current or future problems. Blatchford (2014) says that teachers and parents must play a major role in inculcating the confidence among the learners and make them feel that they have the capacity to address socio-economic and political problems in the society even at that tender age.
The Psychoanalytical Theory of Creativity is another important concept that should be used to motivate creativity and innovation among high school learners (Cooke 2012). This theory, which is often associated with Sigmund Freud, holds that people tend to be creative in reaction to difficult circumstances that they cannot avoid (Tan & Perleth 2015). A clear example is the issue of exams. Most students often fear exams. It is an emotional torture that they have to suppress because the system of education is anchored on examination. However, they have come up with creative ways of addressing the difficult situations in the name of exams.
Some students make very short notes to help the cram the concepts specifically to pass the exams. After the exams, they rarely remember the concepts. Others have come up with very creative ways of cheating, such as writing down major formulas and concepts in highly concealed places that examiners cannot detect. Such creative efforts that these students often take to pass the exams should be transformed into solving real life problems. Policy change is needed in the education sector to ensure that learners worry about solving real life problems in the business or social environment, not in the exams. They should start worrying about coming up with practical means of achieving success in the society instead of excelling in theoretical concepts in exams.
Hypotheses
The review of literature conducted above help in shedding light about the issue under investigation. It helps in understanding the weaknesses in the current education system and what can be done to ensure that creativity and innovation can be promoted. The following is the hypothesis that has been developed based on the reviewed literature.
- H1o. Linking education systems and activities with labor market/ business environment will not promote creativity, innovation, and enterprise.
- H1a. Linking education systems and activities with labor market/ business environment will promote creativity, innovation, and enterprise.
Methods
Data Sources
In this study, data was collected from various sources to help find the link between education system and the business environment. The study used both primary and secondary data sources. A comprehensive literature review was conducted from secondary data sources such as books, journal articles, and reliable online sources. Primary data was collected from a sampled population of respondents.
Research Design
According to Cooke (2012), when defining the research design, one must understand the objective of the study. The primary objective in this study is to explore different factors of innovation development in Dubai schools and determine how effective they are. To achieve this objective, both qualitative and quantitative research will be relevant in this study. Quantitative research method will help in determining the magnitude of the impact of innovation and the level of efforts that stakeholders have put in place to promote it. On the other hand, qualitative method will facilitate a descriptive analysis of the relevant factors.
Looking at various phenomena and case studies will help in explaining why and how creativity and innovativeness can be promoted in Dubai Schools. The mixed method will ensure that the research not only answers the questions of why and how in the study but also provide the magnitude of the impact of various forces on innovation.
Sample and Data Sources
Data needed for this study can be collected from students, teachers, and experts in the field of education. It is easy to reach these people within the city of Dubai. However, one of the main constraints in this study was the limited time available for the project. As such, it was necessary to come up with a manageable sample population from whom data was collected. The researcher had three different categories of people who were included in the study.
They were head teachers, students, and education experts. As such, stratified sampling method was necessary to ensure that respondents from each of the stratum mentioned above were identified. In each stratum, researcher used simple random sampling to identify specific participants for the study. The researcher avoided any form of bias when identifying the participants and when collecting data from them. Four private schools within Dubai were selected to take part in the study. The researcher identified 7 students from each of the four schools in grades 10-12 to take part in the data collection process. The head teachers and selected employees in these schools were also part of the data collection process. The following are the schools selected to participate in this project:
- Dubai International School.
- Al Mawakeb School.
- Al Ittihad private School.
- The International School of Choueifat.
Procedure
The researcher identified a number of schools that were appropriate for the study. A letter was written and then physically delivered to the administrators of these private schools to seek permission for the research to be conducted in their institution. Approval was given from the four schools named above. The researcher then selected seven students from each of the schools who were surveyed. In each school, one student was selected to take part in a face-to-face interview with the researcher.
Head teachers in the seven schools were also interviewed. The researcher also identified some employees, especially the teachers in these institutions, to get their views about the issue under investigation. After collecting data from these four institutions, the researcher identified three experts who were also interviewed within Dubai. The use of questionnaire helped in collecting data from the head teachers and the experts. The primary data that was collected was analyzed using both qualitative and quantitative methods.
Measurement
In this study, the variables were defined to help in understanding the measurements. Innovativeness in Dubai schools was the dependent variables affected by the independent variables. On the other hand, infrastructure, leadership, teaching approach, and exposure of the learners to the market forces were the independent variables.
Analysis and Results
Descriptive Statistics
In the methodology section, it was explained that descriptive statistics was one of the major methods used in the analysis of the data collected from the participants. One of the major issues that the researcher wanted to determine was the different factors of innovation development in Dubai and how effective they are. The following question was posted to the participants.
What are the different factors of innovation development in Dubai and how effective are they?
The following graph shows the data that was obtained after analyzing the response obtained from the participants in the study:
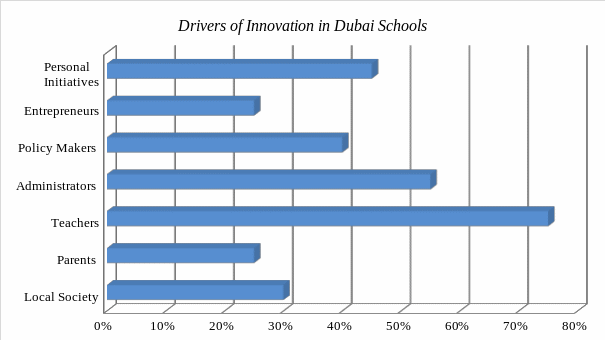
As shown in the figure above, the local community, parents, teachers, administrators, policy makers, experts, and personal initiatives are the key drivers of innovation in Dubai schools. It is clear that 75% of the respondents felt that teachers are very effective in promoting change because they spend a lot of time with learners at school and have significant influence on them. The data also shows that 55% of the respondents felt that administrators and policy makers were other significantly important drivers. Those interviewed also admitted that personal initiatives among the learners can also promote creativity and innovation among learners. The next question below wanted to determine what can be done to promote creativity and innovation in Dubai schools.
What can be done to help promote creativity and innovation in Dubai schools?
To answer this question in relation to the above question, the researcher identified forces that limit innovation in Dubai schools so that they can be eliminated. The figure below shows the response obtained from the participants.
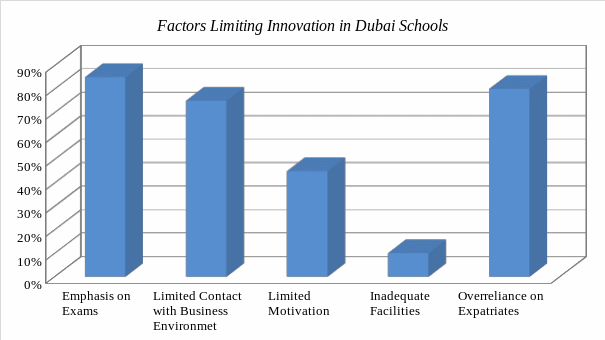
A number of factors were identified as major hindrances to creativity and innovation in Dubai schools. Emphasis on exams, limited contact with the business environment at, limited motivation, inadequate facilities, and overreliance on expatriates were some of the factors identified as major hindrances to creativity and innovation. The data shows that 85% of the participants blamed overemphasis on exams, 75% blamed overreliance on expatriates, while 70% blamed limited contact that students have with the business environment. Eliminating these factors can help promote a culture of innovation in these schools.
Other Types of Analysis
The researcher also used qualitative analysis to help provide a detailed explanation to the descriptive data analyzed above. The following is one of the questions the researcher posed to the respondents.
How innovative are students in Dubai schools when it comes to addressing various issues that affect them?
Most of the respondents felt that students in Dubai schools are not innovative when it comes to addressing issues that affect them both at school and out of school. When asked to explain why, they stated that most of them are only focused on passing their exams at the expense of finding creative ways of solving social problems. The results obtained show that the four schools lack cooperation with the external environment (government organizations, companies, and entrepreneurs).
These institutions rarely invite external stakeholders such as top government experts and accomplished entrepreneurs to help the learners think creatively. The stakeholders should find ways of addressing to promote creativity and innovativeness in Dubai schools. The question below focused on determining how learners can be involved in solving societal problems as a way of motivating them to be innovative.
How can students in Dubai schools be involved in solving socio-economic and political problems in the country?
The graph below shows the suggestions of the respondents, indicating the most preferred ways of doing so.
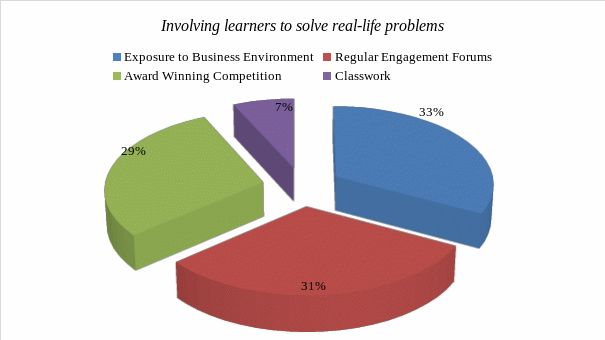
As shown in the above figure, a number of respondents (33%) having regular engagement forums where students meet industry experts and entrepreneurs was considered one of the most effective ways of involving students in solving real life problems. Another 31% felt that exposing the learners to the business environment helps them understand the real-life forces that they must be ready to deal with. Award winning competition was also believed to be a good motivation for students. Some of the respondents (7%) also noted that lessons learnt in class should not be ignored.
Discussion
The analysis of primary data above shows that the level of innovation in Dubai schools is below the expectations of participants who were interviewed. One of the issues that they brought out was that schools lack cooperation with external forces. The stakeholders in the education system have failed to make learners realize that the concepts they learn in school are expected to help them address real life problems. In fact, one of the entrepreneurs interviewed stated that some of the college graduates are unable to apply the concepts learnt in classroom in real world situations. It forces the employers to spend resources training the new employees who are fresh from college to enable them understand how to deal with real life challenges at work.
In the analysis of primary data, a number of factors were identified to be the factors that limit creativity and innovation in Dubai schools. One of the top factors is overemphasis on exams. Students are so keen on passing their exams that they pay less attention to realities in the socio-economic and political contexts. The stakeholders such as parents, teachers, administrators, and entrepreneurs have also failed to motivate students to be innovative.
The fact that the entrepreneurs can easily hire expatriates to do skilled work such as designing unique structures eliminates the pressure to have local talents who can undertake such tasks. The culture of innovation should be created among learners so that they can embrace creativity as a way of addressing issues that they face in their school and after school life.
Theoretical Implications
This study has a significant contribution to the theoretical concepts proposed by other scholars. It has demonstrated how Humanistic Theory of Creativity can be used in the context of promoting creativity and innovation in the school context. The theory has been used extensively to explain how creativity can be promoted in an organizational setting. However, the outcome of this study now shows that the theory can also be relevant in making the learners be creative. The study also shows how the Psychoanalytical Theory of Creativity can be used to make learners feel the pressure of the socio-economic and political forces so that they can be part of the solution to some of the major problems in the society.
Managerial Implications/Recommendations
The need to promote creativity and innovativeness in Dubai schools is obvious. However, the stakeholders have been unclear on the best approach that should be taken to address the issue. The administrators and those in top managerial positions in the country will find this document very important as they try to come up with policies that can help promote innovation in these schools. This study provides clear recommendations on what the stakeholders should do to promote creativity and innovation in these schools. The following are the major recommendations that are made in this study:
- Schools should do Memorandum of Understanding between government organizations and companies where they can use their innovation centers to run and test some ideas and activities;
- Brainstorming hours should be created where students are asked to find ways through which they can solve real-life problems;
- Schools in Dubai should come up with science fair and business fair where students are encouraged to come up with ad showcase innovative ideas of solving socio-economic or political problems;
- School administrators should use benchmarking as a way of embracing best practices within their institutions.
Limitation and Future Research
It is important to note that there were a number of limitations in this study. Time constraint was the biggest challenge. The process of reviewing literatures, collecting and analyzing primary data, and developing a report is time consuming. The researcher had to plan well and do everything within the limited period. Inaccuracy of information gotten from the various sources was another issue. Some of the headmasters were not truthful when answering the questions because they were keen on protecting the image of their school. Other respondents did not take this study seriously and provided answers just for the sake of completing the interview.
Insufficiency in the number of respondents was also an issue. The time available for the study forced the researcher to use a small sample size. The researcher had planned to collect data from entrepreneurs. However, the limited time that was available made it impossible to interview them. As such, data was not collected from this important group of participants.
Conclusion
Globalization is creating an environment where countries have to compete in various fronts to achieve the desired success. Currently, Dubai is competing with cities such as Paris and Cape Town to attract global tourists. This city is also competing with other regional cities to become a dominant business hub. Creativity and innovation is critical in achieving success in such a competitive environment. It is important to inculcate the culture of creativity and innovation among learners at very early stage of their development to prepare them for the competitive nature of the environment in the world after school.
The paper has identified a number of drivers of innovation that Dubai schools should embrace and hindrances that should be dealt with to ensure that the schools become innovative. The stakeholders in the education sector should consider the following recommendations:
- Learners should always be exposed to the business environment and be allowed to interact with experts and entrepreneurs to promote innovation among them.
- Award winning competitions should be organized regularly in schools where learners are encouraged to use their knowledge to try to solve specific socio-economic or political issues in the society.
Reference List
Alon, I, Jones, V & McIntyre, J 2013, Innovation in business education in emerging markets, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Andersson, T & Djeflat, A 2013, The real issues of the Middle East and the Arab Spring: addressing research, innovation and entrepreneurship, Springer, New York.
Audretsch, B, Link, A & Walshok, M 2015, The Oxford handbook of local competitiveness, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Blatchford, R 2014, The restless school, John Catt Educational Ltd, Woodbridge.
Cankar, F, Tomi, D & Cankar, S 2013, Factors of the innovation development in school, Knowledge Management & Innovation, vol. 19, no. 21, pp. 1245-1251.
Cooke, P 2012, Complex adaptive innovation systems: relatedness and transversality in the evolving region, Taylor & Francis, New York.
Oxford Business Group, 2014, Report: Abu Dhabi 2014, Oxford Business Group, Oxford.
Rogers, D 2016, The digital transformation playbook: rethink your business for the digital age, Columbia Business School Publishing, New York.
Tan, A & Perleth, C 2015, Creativity, culture, and development, Springer, London.
Zhao, Y 2012, World class learners: educating creative and entrepreneurial students, Corwin Press, Thousand Oaks.