The proximate causes are the immediate or the closest trigger of a phenomenon while the ultimate causes are the real reasons why a given phenomenon took place the way it did. Professor Jared Diamond believed that certain civilizations were able to dominate others economically, militarily, culturally, and politically because of the nature of the environment. He particularly noted that the harsh environmental conditions (extremely cold winters) in Europe forced the Europeans to be very innovative in order to survive in this climate.
As such, they came up with superior approaches of survival in agriculture, and military. The economic and military superiority made it possible for them to have significant influence on other countries politically and culturally. These are the ultimate reasons why they dominate the world (Gault 2010). The proximate reasons were the need to conquer the world through colonialism that made it necessary for them to use their military and economic power to influence cultural and political structure of other countries around the world.
Innovation played a very critical role in advancing the dominant civilization over others. A good example was the military sector. Professor Diamond says that Europe was able to rule the world for over 200 years because of its highly innovative weapons. The only way of subduing the subjects in their colonies was to use superior weapons. Their innovation in the transport sector also helped them in moving their military personnel from one region to another with ease.
I agree with his conclusions that environmental factors played a critical role in making Europeans more innovative than those in sub-Sahara Africa and parts of Asia. These factors made it possible for the continent to dominate the rest of the world (De 2006). The industrialization in the West can be considered an ultimate reason why the civilization spearheaded by Europeans was able to dominate the world. They had to find more raw materials for their companies hence they had to colonize other parts of the world to control these resources. Figure 1 shows the major colonies where these countries obtained raw materials.
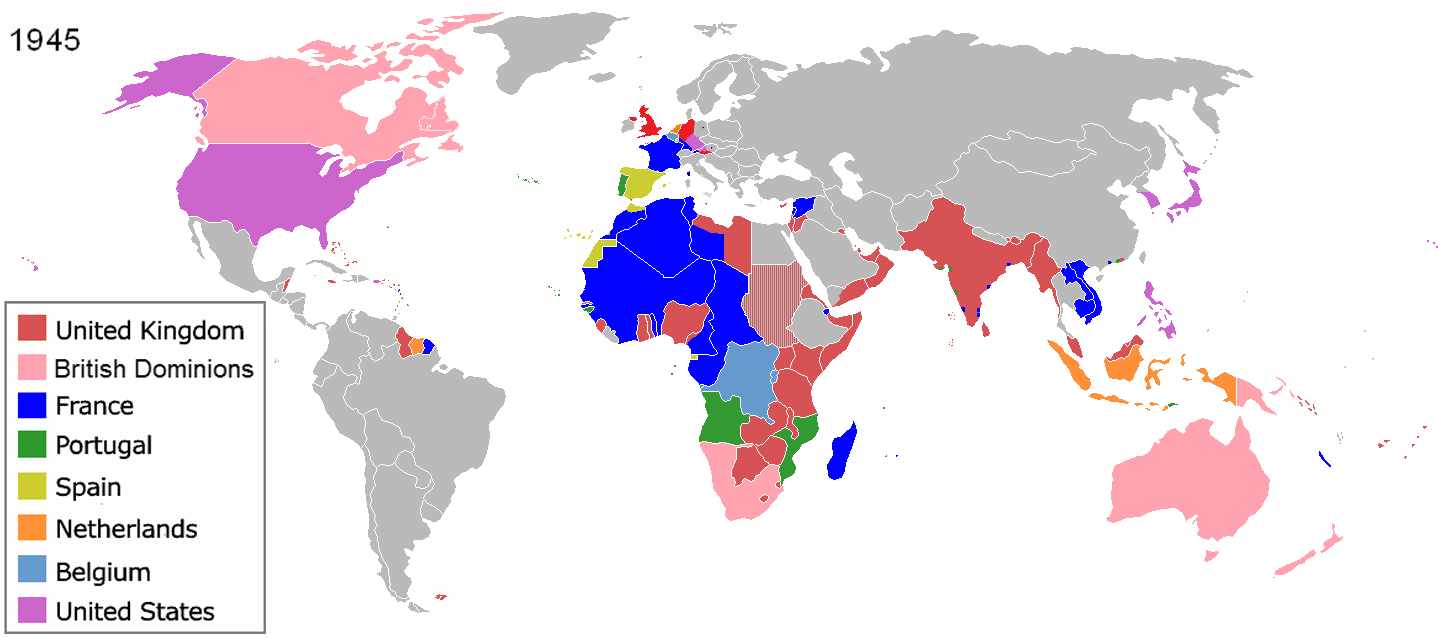
The proximate reason why this European powers’ culture remained influential was their spread of Christianity around the world in places where they colonized. By using religion, they were able to significantly reduce resistance among the communities they colonized. They intertwined their Christian beliefs with economic benefits. Those who believed went through school and were able to speak like the Europeans.
Innovation and Regional Development
Lee Kuan Yew, the founding father of Singapore, argued that Singapore is not as entrepreneurial as Hong Kong. His thought must have been influenced by the fact that Singapore’s rapid development was government-driven instead of being individual investment-driven economy. He felt that in Hong Kong, it was the private sector that was pushing the rapid development of the economy.
The innovative strategies used in Singapore have a number of similarities with those used in the United Arab Emirates. In both cases, the government is playing a central role in enhancing innovation and development. However, the government of the United Arab Emirates has a greater control over the country’s economy than in the case of Singapore. The greatest impediment to improvement of innovativeness in Singapore and UAE is that both countries are yet to fully equip their institutions of higher learning and promote local production of high-tech products such as machines. These countries can solve this problem by trying to invest in the local universities and promoting locally-manufactured products in the local market.
South Korea is a better choice to compare UAE with in terms of innovation because it has already overcome the hurdles and is now competing favorably with developed economies in technology.
According to Michael Porter, for a country to be innovative, it must embrace localized processes when looking for solutions to the environmental problems. Looking for external solutions to solve the local problems cannot yield fruits and it kills innovativeness. Singapore and South Korea have been identified as good examples that can be used by UAE as it tries to move the economy to the next level. In terms of Global Competitiveness Index, the three countries share a common factor in that they are currently experiencing rapid development in this measure. However, Singapore scores much better in this measure and is followed by South Korea (Marklund, Vonortas, & Wessner 2009). UAE comes last when compared to the two.
Global Innovation Index is another measure that can be used to compare United Arab Emirates with Singapore and South Korea. Using this tool, one is able to analyze how a country uses innovation to spur economic growth, productivity, and job creation. UAE, Singapore, and South Korea have been using innovation in transport and communication to spur economic development and create jobs. However, UAE has majorly focused on the transport sector while South Korea has been keen to promote its technology-based industries such as the electronic sector. Singapore on the other hand has a highly diversified economy compared to the other two countries.
The Hofstede cultural dimensions can be used to compare these three countries. Figure 2 may help in understanding this concept further. It is clear that UAE has the highest score in power distance (90) followed by Singapore (74), while South Korea has the lowest (60). UAE also has the highest score in individualism (25), followed by Singapore at 20, while South Korea has the lowest score of 18. When using masculinity as the measure, UAE has the highest score of 50, followed by Singapore at 48 while South Korea has a score of 39.
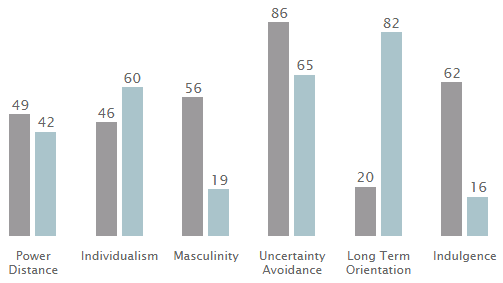
This index shows that uncertainty avoidance is very high in South Korea (85) followed by UAE (80) while Singapore has the least (8). South Korea has the best score (100) in long-term orientation, followed by Singapore (72) while UAE comes last with almost a zero score. In indulgence, Singapore comes first at 46 followed by South Korea at 29 while the score of UAE in this measure is negligible (Link 2014).
The analysis conducted in the section above shows that UAE has not achieved the level of innovativeness that may enable it to achieve economic progress at the required pace. This may have a negative implication on the country’s economy in the future. It is recommended that the government should invest a lot in the field of education, science and technology to promote innovation among the locals. Instead of the government being the leading player in most of the industries, it should allow the private sector to stimulate economic growth by creating an enabling environment.
Organizational-Level Innovation
The Juemirah Group will need to embrace a number of strategies and tactics to become more innovative. Employees-empowerment is one of the most important strategies for this diversified firm. It will involve ensuring that employees have the right skills and expertise in their respective areas that can enable them to come up with new ways of addressing the current or emerging problems, especially in the hospitality industry. They may be taken for regular trainings to enhance their skills.
The Juemirah Group’s human resource manager will be fully responsible for this task. He will ensure that employees are taken for regular trainings or sponsored for further studies if necessary. The main resource needed to achieve this will be money to hire the experts to train the employees regularly. The amount of money required will vary from time to time based on the training needs and environmental factors. Creation of an enabling work-place environment where the top managers can easily interact with the junior employees and share ideas that can help take the Juemirah Group to the next level is also important.
Having an open-door policy will make it possible for ideas to be shared within this company and enhance positive transformation (Cantwell & Molero 2003). This strategy does not need any financial resource to be implemented other than the employees and their managers. It requires the top managers to engage the junior employees when coming up with policies.
Creation of focus-groups within various departments is another tactic that the management of the Juemirah Group should consider. Employees working in the customer-service department, or any other department within the firm, will form a focus group where they can discuss issues affecting their department and come up with the possible solutions. The line managers can be the leaders of each group.
The line managers will be coordinating with the departmental heads so that if resources are needed to implement any innovative strategy then it can be availed. These teams will need regular on-job trainings and necessary equipment that will enable them to coordinate their activities instead of working from an individualistic perspective (Abbing 2010). Talent-search can also help in improving innovation within the Juemirah Group. In this context, the top management will communicate with its employees about a program that seeks to identify talents among the workforce. As such, the employees will be advised to try to come up with innovative ways of addressing common tasks as a way of demonstrating their talents.
The general manager of the Juemirah Group should be fully responsible for this program although he can delegate responsibilities to departmental heads.
Individual-Level Innovation Strategies
Universities play a significant role in enabling the learners to be more innovative than they would have been if they had not gone to these institutions of higher learning (Abbing 2010). Universities empower learners to conduct self-analysis to identify inner capabilities that one never realized he or she had. It provokes critical thoughts among the learners and enables them to have a new perspective towards life in general (Holmquist 2012).
It has a massive impact in terms of enabling the students to understand the challenges in everyday life and how innovation can be used to address these challenges. I believe I am a highly innovative student who often tries to find various ways of addressing academic and social problems. Before joining graduate program, I believed that innovation was only common among the experts in the field of technology hence I did not take it seriously. However, now I strongly believe that I have a role to play in developing unique solutions to the problems that my society faces. I believe that after this program, I will be an innovative individual capable of working with different people in different fields to come up with common solutions within an organizational setting or at the national level.
The metrics that I shall use in measuring my level of innovation will be life and academic skills. I will want to see a difference in the approach I used in the past to address life and academic issues and that which I will use after this program.
List of References
Abbing, E 2010, Brand-Driven Innovation: Strategies for Development and Design, AVA Academia, Lausanne.
Cantwell, J & Molero, Z 2003, Multinational Enterprises, Innovative Strategies and Systems of Innovation, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham.
De, M 2006, Innovation Strategies in Interdependent States: Essays on Smaller Nations, Regions and Cities in a Globalized World, Edward Elgar Pub, Northampton.
Gault, F 2010, Innovation Strategies for a Global Economy: Development, Implementation, Measurement and Management, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham.
Holmquist, L 2012, Grounded Innovation: Strategies for Creating Digital Products, Elsevier Science, Burlington.
Link, A 2014, Public/Private Partnerships: Innovation Strategies And Policy Alternatives, Springer, New York.
Marklund, G, Vonortas, N & Wessner, C 2009, Innovation Imperative: National Innovation Strategies in the Global Economy, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham.