Introduction
Improving the quality of care provided to patients is the goal that all healthcare organizations aim to reach. The development of the concept of Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) allowed facilities to reconsider the way where they are going and the manner in which short-term objectives are achieved. When considering CQI, it is recommended for healthcare professionals to answer such questions as “how are we doing?” “can this be done better and more efficiently” and “can this be done faster?”
Continuous improvement starts with the establishment of a culture of quality enhancement for the patient, the general practice, and the population as a whole. The principle was created based on the fact that despite the highest quality of care, processes and systems in any facility cannot reach perfection. It is necessary to integrate an evolutionary refining process for detecting mistakes or deviations and implement corrective actions (Fernandez & Merrill, 2014). Thus, developing a CQI system that will benefit a healthcare organization is essential for developing strategies enabling team members to assess and improve the delivery of healthcare services. In the current analysis, a proposal for recommended CQI steps to benefit a nursing facility will be provided.
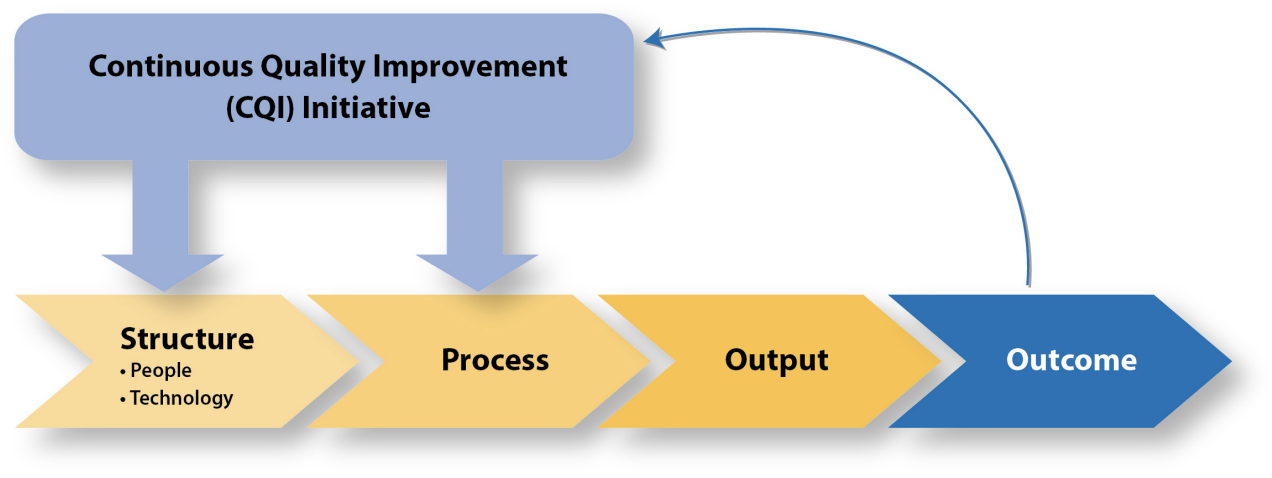
The framework for CQI usually considers three components, such as structure, process, and outcomes (see Figure 1). The structure is associated with the range of human, technological, financial, and other assets for carrying out everyday tasks in a facility (The National Learning Consortium, 2013). CQI in nursing is necessary for examining the characteristics (for example, quality, adequacy, location, and other) of the assets involved in the process of caring for patients.
The process is linked to a variety of activities, tasks, and workflows targeted at achieving desired outcomes. It is notable that despite the fact that most CQI strategies in current research literature focus on clinical procedures, the process also applies to administrative contexts (da Costa, Greco, Bohomol, Arreguy-Sena, & Andrade, 2014). For example, the use of Electronic Health Records (HER) can be used for reaching the goals of both administrative and clinical processes of a nursing facility. The outcome is the component of CQI that indicates the final
“result of care as well as the change in the current and future health status due to the consequences of health care interventions” (The National Learning Consortium, 2013, p. 3). Desired changes represent the efficiency and the cost of caring for patients or a return on investment in the implemented interventions.
Structuring a CQI Plan
The structure of a CQU plan serves as a roadmap for the effort of quality management in a nursing facility. The first step in structuring such a plan is associated with the definition of an organizational mission and scope of practice. This is necessary for engaging all professionals involved in the process, such as nurses, nursing managers, facility directors, Information Technology specialists, and other players. Once the priorities of a plan have been identified, it is necessary to determine the performance measures needed for putting the plan into action. For measuring specific elements of care, indicators are reselected for assessing performance within a focus area. Within a nursing facility, it is proposed to integrate the set of following indicators:
- Patient satisfaction with nursing care, pain management, the information provided to them, and overall care;
- Pressure ulcers rates;
- Patient falls;
- Rates of infections
- Nurses satisfaction with their work;
- Staffing ratios;
- Total hours of nursing care per one patient.
The range of indicators presented in the list above is considered nursing-sensitive and has a direct influence on the stages involved in CQI: structure, process, and outcomes (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2011). Structural indicators are linked to the supply of nurses, their skill levels, education, and other characteristics that influence the quality of care provided to patients. Process indicators (such as satisfaction) measure the assessment of the effectiveness of implemented interventions. Outcome indicators (such as pressure ulcers) measure the quality of nursing care.
After establishing a system of measuring quality indicators on a continuous basis, it is recommended to implement data collection and analysis planning. This step is linked to the collection, tracking, interpretation, analysis, and acting upon the data of an organization. It enables organizations to identify and implement opportunities for improving the current systems of care delivery in order to implement changes as soon as necessary. Organizational management is expected to define the frequency within which data will be collected and analyzed. For example, quarterly evaluations can allow facilities to quickly identify performance measures that should be improved for addressing outcomes.
The identification of improvement opportunities is the next step in the CQI program. The first sub-step of the stage implies the review of performance data for identifying whether the needs are met according to the desired level of quality; this is necessary for defining a performance plan (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2011). The second sub-step involves the interpreting of data to assign meaning to measurements and determine their significance and implications. Both analysis and interpretation are crucial parts of CQI in a nursing setting because of the possibility to compare current and previous indicators for determining the areas that have been improved and those that require additional attention.
Implementing a CQI Plan
At the stage of structuring and preparation, roles and responsibilities are clearly defined while objectives are established. It is expected that the staff within an organization understands the vision and the mission of the plan and is accountable for tasks assigned to them. The implementation of a CQI project will include the process of continuous process monitoring and incorporates the following steps:
- A quality improvement issue is identified with the help of different sources such as administrative indicators of quality, patient complaints, or clinical quality and safety;
- An issue that has the largest impact on the outcomes of a program is evaluated based on patient demographics, the use of resources, and the cost of care (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2011). To address it, quality indicators are selected for determining the data that would be appropriate for measurement;
- Data is collected and reviewed for outcomes;
- Objectives for improvement are established;
- A specific plan of work is developed, modified, and implemented as necessary;
- Barriers to improvement are identified;
- Continuous monitoring practices are put into place for making decisions regarding the next steps;
- Regular modification of practices are conducted to remove any barriers to practice;
- New thresholds are created with the maintenance of positive practices and processes.
The step-by-step plan above reveals that successful CQI implementation requires constant monitoring, analysis, the identification of limitations, the integration of solutions, and their assessment. The cyclical process of continuous quality improvement allows healthcare organizations to integrate positive procedures and evaluate their effectiveness as soon as possible. Because of this, a CQI plan should be reviewed on a regular basis for each critical step involved in it. Nursing facilities that meet the established thresholds can identify priority improvement areas outside the identified objectives.
Noting resource allocation is detrimental since it represents one of the key barriers to the success of CQI plans. Staffing, fiscal resources, front-end investment, time, and other variables are necessary for implementing the CQI model within a healthcare facility (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2011). The improvement of quality at such organizations requires a range of resources from the workforce to Information Technologies, all of which require financial reimbursement in order to work effectively. The shift to models of pay for quality has the potential of enhancing CQI programs and influence positive transformation at healthcare facilities. Thus, it is recommended for nursing organizations to follow the current developments in payment models to align themselves with the most meaningful and effective programs.
Conclusion
The implementation of CQI programs at nursing facilities requires careful planning and the identification of areas, which require the most improvement. The proposed plan integrated a range of steps that any nursing organization can follow to establish the culture of quality improvement and addressing the barriers that limit the quality of care provided to patients. Based on the needs of a facility, performance indicators are identified to aid in quality improvement and the continuous assessment of results. As quality improvement has been associated with both patient and employee satisfaction, creating a positive environment within a nursing facility will be imperative to ensuring the success of organizations.
References
da Costa, F., Greco, R., Bohomol, E., Arreguy-Sena, C., & Andrade, V. (2014). The nursing staff’s opinion about the continuous quality improvement program of a university hospital. Einstein, 12(2), 211-216.
Fernandez, V., & Merrill, D. (2014). Quality assessment and improvement and patient safety in the pain clinic. In H. Benzon, J. R. Rathmell, C. L. Wu, D. Turk, C.E. Argoff & R. W. Hurley (Eds.), Practical management of pain (5th ed.) (pp. 56-78). Philadelphia, PA: Mosby.
The National Learning Consortium. (2013). Continuous quality improvement (CQI) strategies to optimize your practice.Web.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2011). Developing and implementing a QI plan. Web.