Introduction
This report is a study of different types of organizations operating in an international business environment. It will be conducted as a compare-and-contrast analysis of three companies conducting operations in the smartphone market. They are Apple and its competitors – China-based Hisense and Pakistani QMobile. The rationale for choosing these rivals is the fact that they differ in type. Apple is a public-private corporation; Hisense is a public corporation, and QMobile is a private corporation.
It is critical to note that even though Hisense is as well a public organization, it is state-owned, i.e., the state is the only owner of the company and all liabilities are laid on the government. Moreover, the motivation for selecting them is the current challenge of being outperformed in the region faced by Apple. Because Apple’s smartphones are easily replaceable and imitable, it is crucial to pay specific attention to all potential competitors, even if they are smaller and the scope of their operations is national or regional.
Overview of Different Types of Organizations
There are different types of organizations based on ownership and purposes for being established. The first type is referred to as public organizations. They are also known as governmental entities. The rationale for setting them up is the protection of local communities, contributing to their development and welfare, as well as satisfying their fundamental needs. Some examples of public organizations are hospitals, fire departments, public universities, state-owned businesses, etc.
Private organizations are the second type. They are non-governmental, i.e., are owned and ruled by private individuals or a group of people, stakeholders, families, etc. This kind of organization is made up of all businesses and entities that aim both at gaining profits and helping people in need. Finally, there are non-profit organizations. They are also known as voluntary organizations because their primary objective is to benefit a community without turning profit-making into the central strategic objective of their operations.
Instead, they are task-oriented and aim at eradicating some critical problems that have a detrimental influence on human life and health (Rogers 2016). Some appropriate examples are the Red Cross, the International Organization for Standardization, Oxfam, Greenpeace, etc. It is essential to note that some organizations are a hybrid type. It means that they incorporate features of all types of organizations mentioned above. For instance, they might combine business purposes with addressing social needs or create public-private partnerships (Billis 2010).
Moreover, there is a distinction based on the legal structure of the business. That said, there are sole proprietorships, partnerships, limited liability companies, and corporations. A sole proprietorship is an organization managed by one person. Sometimes, it has no employees and all operational functions are carried out by an individual, the one who established it. A partnership is a legal association with two or more partners sharing ownership, risks, and profits.
There are two types of partners – general having control over operations and limited without the right to influence business operations. A corporation is an association of stakeholders – those possessing shares. The volume of given authority differs according to the number of shares owned. A limited liability company is a combination of corporations and partnerships. Partners are referred to as members and their liabilities and assets are limited (Richmond & Powers 2010).
Finally, organizations differ in the size and scope of operations. That said, there are small, medium, and large enterprises and the scope of their activities varies from local to national, regional, and international (Seitanidi 2010). Also, the scope of an organization can be determined by a sector or industry of operation, such as operation in health care, entertainment, or manufacturing (Anheier 2014).
The type of organization has a direct impact on its internal and external environment and business opportunities because it affects access to resources and authority as well as a potential influence on sectors of operation. For instance, governmental organizations are more powerful than private firms because they are run and backed up by the state. At the same time, large enterprises and those operating within broader scopes are more influential than smaller firms due to the vast resources and potential. Moreover, they affect business objectives, which can as well be explained by limited resources and access to authority.
Finally, it has a bearing on liabilities and powers. For instance, in the case of corporations, authority is divided based on the number of shares, while liabilities are granted to a corporation itself; and, when speaking of sole proprietorships, all responsibility and authority are given to one person (Richmond & Powers 2010).
Growth of International Business Environment
The international business environment is constantly changing. Several reasons are leading to its evolution and expansion. First, the global economy, as well as the business environment, features constant creation and growth of new companies operating in different sectors. As technologies become more intricate, further specialization and manufacturing are imperative to meet the changing consumer demand.
Even though the global business environment is sometimes crashed because of difficult-to-forecast economic and financial crises, globalization and interconnectedness are among the primary causes of its expansion and constant change. Moreover, legal regulations are constantly reviewed and unified, which contributes to the further interconnectedness of states because it becomes easier to operate in foreign countries and enter new markets. Finally, the international business landscape affects environmental issues. Because companies pay specific attention to sustainable development, it benefits them in the long run, thus creating the foundation for the further boosting of global business operations (Hamilton & Webster 2015).
Description of the Chosen Organizations
One way to determine the size of the company is to estimate its annual revenues. From this perspective, a small company is making less than $9 million in revenues. A medium company is one, which manages to earn between $10 and $24.9 million. Finally, if annual revenue exceeds $25 million, a company is viewed as a large one (Flamholtz & Randle 2016).
Apple
Apple is one of the most successful and desirable manufacturers of smartphones. As of 2016, its market share is 13,5% with more than 200,000 million smartphones sold during 2015 and 75,000 phones in the first quarter of 2016 (Statista 2016a). Because the 2015 revenue was almost $234 billion, Apple is a large company (Statista 2016b). The company was founded in 1976 and the first iPhone was introduced in 2007. Since then, it became the most wanted smartphone.
Besides, the company offers other electronic products, such as tablets, personal computers, audio players, laptops, etc. The vision of the company is to avoid settling for anything less than excellence. As for Apple’s mission, it comes down to making great products, always be innovative and creative, and possess and offer the best available technologies (Hull 2012).
Apple is a private-public organization. By legal structure, it is a corporation (Valentin 2015). Because it is a multinational corporation represented in all regions around the globe, the size of this organization is large and the scope of its operations is international. It is owned by shareholders and the volume of authority is determined by the number of possessed shares. As for now, there are almost 2,500 shareholders.
The primary holders of institutional holdings are Vanguard Group, State Street Corp, Blackrock Institutional Trust Company, FMR LLC, and Blackrock Fund Advisors (NASDAQ 2016). All of them, as well as customers and governmental agencies, are stakeholders. Apple’s business objectives are the following: creating innovative and groundbreaking products, building an outstanding corporate culture based on the significance of research and development, drive the process of introducing innovations and the newest technologies in everyday life of ordinary people, expand worldwide and make company’s product available in every corner of the globe, remain a premium manufacturer of electronics, increase profit margins, and strengthen brand image (Burnette 2015).
Hisense
Hisense is a Chinese public organization. It was created in 1969 and it specializes in manufacturing electronics and home appliances. As of now, the company is one of the leading smartphone manufacturers in China. Its first smartphone was introduced in 2013.
Compared to Apple, Hisense’s market share is insignificant; it sold 12 million smartphones with 10 million units sold in China. Hisense’s 2015 revenue was 30.19 billion yuan (approximately $4.5 billion), which makes it a large company (Statista 2016c). The mission of the company is to focus on customers’ needs and satisfy them by creating an innovative and excellent product. Its vision is to become a globally recognizable brand (Hisense 2016).
Hisense is a public, state-owned enterprise ruled by the Chinese government. Its legal structure is a corporation. The scope of its operations is international because it is represented in 130 countries around the globe. However, based on its insignificant market share, it can be said that the company is not influential in the international smartphone market. Moreover, its smartphones are popular in Asia. That is why the scope of this segment of the company is international.
Still, it has the potential of outperforming Apple in the Asian regions due to offering more affordable smartphones with strong performance features and options. Its primary business objectives are the further growth of brand popularity internationally, serving society by creating innovative but affordable products, preserving its focus on a consumer, and boosting performance (Hisense 2016). Its primary shareholder is Qingdao State-Owned Assets Supervision and Administration and there are no company-based shares (4-Traders 2016). Together with the Chinese Government and customers, they are the primary stakeholders.
QMobile
QMobile is a Pakistani smartphone manufacturer. It was founded in 2009. Its market share in Pakistan exceeds 50% and it significantly outperforms Apple having 3% of the local market (Baloch 2016). QMobile’s annual revenue is around $14 million, which makes it a medium company (Baloch 2016). Because Apple aims at becoming a global leader, it should outplay QMobile. The company’s vision is to empower consumers by introducing innovations and creative products to make their lives brighter and better.
Its mission is constantly to innovate the communications sector. As for business objectives, the company aims at maintaining its leading positions in a nationwide context and boost its activities internationally (QMobile 2016). It is a private enterprise. QMobile stores are located only in Pakistan. Its scope of operations is national. As for stakeholders, they are customers, CEO, and local governmental agencies, as the company benefits the national economy.
Explaining the Functions of an Organization
Apple is a traditional example of a hierarchical organizational structure. It means that there is one primary leader, who manages the working process and business operations. As for organizational functions, they are divided into front-office functions and back-office functions. Apple is involved in carrying out both types of functions mentioned above. For instance, marketing, industrial design, software development, device and software engineering, retail, and manufacturing are front-office functions, are they are directly connected to generating revenues. On the other hand, HR, financing, and general counsel departments, as well as warehousing, are examples of back-office functions, as they contribute to the company’s flawless and sustainable operation.
This distribution of functions links to the hierarchical organizational structure because everyone responsible for performing both front-office and back-office functions reports on performance to upper-tier executives and CEO. At the same time, it matches the company’s major objective – remaining creative and offering products of exceptional quality, as a division into numerous functions and departments is beneficial for staying focused on particular goals. For a better understanding of organizational hierarchy and distribution of functions within an organization, refer to the organizational chart below (Figure 1).
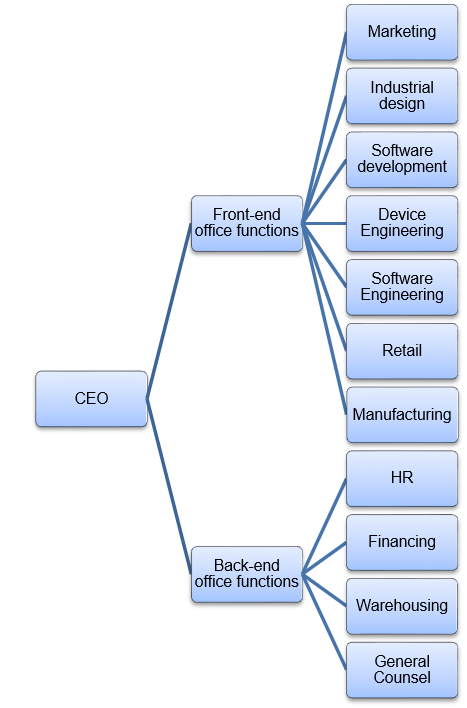
Hierarchy has both advantages and disadvantages. First of all, it is advantageous for supporting strong control over conducted activities, which helps achieve business objectives. Moreover, it is beneficial for addressing specific needs because of strict management measures. Nevertheless, it is disadvantageous for flexibility because all decisions should be negotiated at the highest levels (Meyer 2015).
Conclusion
The modern business environment is characterized by the operation of different types of organizations, which determine their internal and external atmosphere, distribution of function within an organization, and ways for developing relations with competitors. Moreover, the global business landscape features interconnected national economies. That is why it is of critical importance to investigate the operations and performance of all competitors, especially in the regions of being outperformed by them, to craft effective strategies for boosting growth. Even if a company is small and operates within a national frame, it does not guarantee that it would not attract adequate resources necessary for using global interconnectedness as a tool for becoming an international entity.
References
4-Traders 2016, Hisense Electric Co. Web.
Anheier, H K 2014, Non-profit organizations: theory, management, policy, Routledge, New York, NY.
Apple 2016, Executive profiles. Web.
Baloch, F 2016, Studying Pakistan’s growing obsession with smartphones. Web.
Billis, D 2010, Hybrid organizations and the third sector: challenges for practice, theory, and policy, Palgrave McMillan, New York, NY.
Burnette, B 2015, Apple Inc. objectives and strategies. Web.
Flamholtz, E G & Randle, Y 2016, Growing pains: building sustainably successful organizations, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ.
Hamilton, L & Webster, P 2015, The international business environment, Oxford University Press, New York, NY.
Hisense 2016, Hisense faiths. Web.
Hull, P 2012, ‘Be visionary. Think Big’, Forbes. Web.
Meyer, P 2015, Apple Inc. organizational structure: features, pros, and cons. Web.
NASDAQ 2016, Apple Inc. ownership summary. Web.
QMobile 2016, Our brand. Web.
Richmond, T & Powers, D 2010, Business fundamentals for rehabilitation professionals, Slack Incorporated, Thorofare, NJ.
Rogers, A T 2016, Human behavior in the social environment: mezzo and macro contexts, Routledge, New York, NY.
Seitanidi, M M 2010, The politics of partnerships: a critical examination of nonprofit-business partnerships, Springer, New York, NY.
Statista 2016a, Apple iPhone’s market share of new smartphone sales worldwide from 2007 to 2016, by quarter. Web.
Statista 2016b, Revenue comparison of Apple, Google/Alphabet, and Microsoft from 2008 to 2015 (in billion U.S. dollars). Web.
Statista 2016c, Revenue of the Chinese electronics manufacturer Hisense from 2012 to 2015 (in billion yuan). Web.
Valentin, E K 2015, Business planning and marketing strategy, SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA.