Overview
This project was initiated after eliciting user requirements. Fiction Corporation has been in operation for the last few years with considerable expansion opportunities evident from their annual turnover records. Because of this, it has been profitably envisaged to network the corporation’s sparsely distributed resources to meet the client’s requirements effectively while providing a centralized management approach. This plan is about this process.
Project Purpose, Objectives, and Criteria
The purpose of this project plan is to describe the necessary details that must be followed to ensure a successful networking project completion based on the project management standards and budget. This is necessary because the company’s customers have had delays that have negatively affected Fiction Corporation. The main business objective is to satisfy customer requirements in a manner of the reliable and efficient intranet to expedite processing and share resources between remote sites thereby generating profit for Fiction Corporation. The main stakeholders are the customers of Fiction Corporation who will be able to benefit from improved service delivery, in this case, the turnaround time that will be reduced considerably. Fiction Corporation is also expecting to double its profits in the next three months after its inception.
Project Deliverables
On the completion of this project, the major deliverable is the corporate intranet that will be delivered to Fiction Corporation. The method of changeover will be direct to ensure seamless integration with minimal interruption to the normal operations of the company (Duncan, 1996).
Table 1: Project deliverable summary details
Assumptions, Dependencies, and Constraints
It is assumed that the project will proceed as planned, and within the budget, and the sponsor who is Fiction Corporation will cater for the necessary expenses and requirements fully funding the project to completion. It is expected that the project will run on schedule and be completed within three months. It is assumed that the project support staff will be sourced from within Fiction Corporation whereas the technical expertise will be outsourced.
Project Organization
The project management team will provide the interface between the project, and other external entities. The suppliers of hardware and software required during the project will be liaising with the project management team to ensure this.
External Interfaces
BIG-PROJ Consultants has initiated this project and will carry out all the necessary activities to ensure that the resulting system interfaces well with Fiction Corporation. The progress of the project will be reported after stipulated periods. The project management team will organize briefings on the progress of the various stakeholders as and when required.
Internal Structure
BIG-PROJ Consultants will run this project professionally with a defined project team in place led by the project manager. The project manager is charged with the responsibility of ensuring that the team works in a coordinated manner and that the deadline is met. Under the project manager are the technical network support and hardware, software lead, and quality assurance teams
Roles and Responsibilities
The following are the likely team members and their roles:
- Project Manager: In charge of the planning of the project
- Technical Network Support Lead: Will handle the technical networking aspects of the project. (Operating system and network)
- Software Lead: Will handle the software aspects of the project.
- Hardware Lead: Will take care of the hardware requirements of the project.
Besides the technical and managerial personnel directly involved with the project, there are also subcontractors who will supply the necessary hardware and software. Main and sub-contractors must work closely to ensure that the project progresses as required. BIG-PROJ Consultants will liaise with Open Systems Limited who will deliver the operating system and network management software. They will also liaise with Bell Computer Hardware Suppliers who will supply the needed hardware to run the project
Start-up Plans
The project undertaken here is a medium-scale one. Fiction Corporation is a medium-scale business enterprise with a call center, hundreds of outlets, and three warehouses. The corporation has a workforce of 10,000 people.
Estimation Plan
This project is employing the necessary project management requirements as stipulated in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) (Duncan, 1996). The project manager can use various methods and tools to estimate the size, cost, and effort to be expended by the project. This will help him to schedule project time and appropriately allocate the available resources. Among the methods used include the Net Present Value (NPV), Discounted Cash flows (DCF) for cost estimates, Project evaluation, and Review Techniques (PERT) for schedule planning (Schwalbe, 2010). These estimates will be prepared by the project team, and the findings will be well documented to ensure reviews.
Staffing Plan
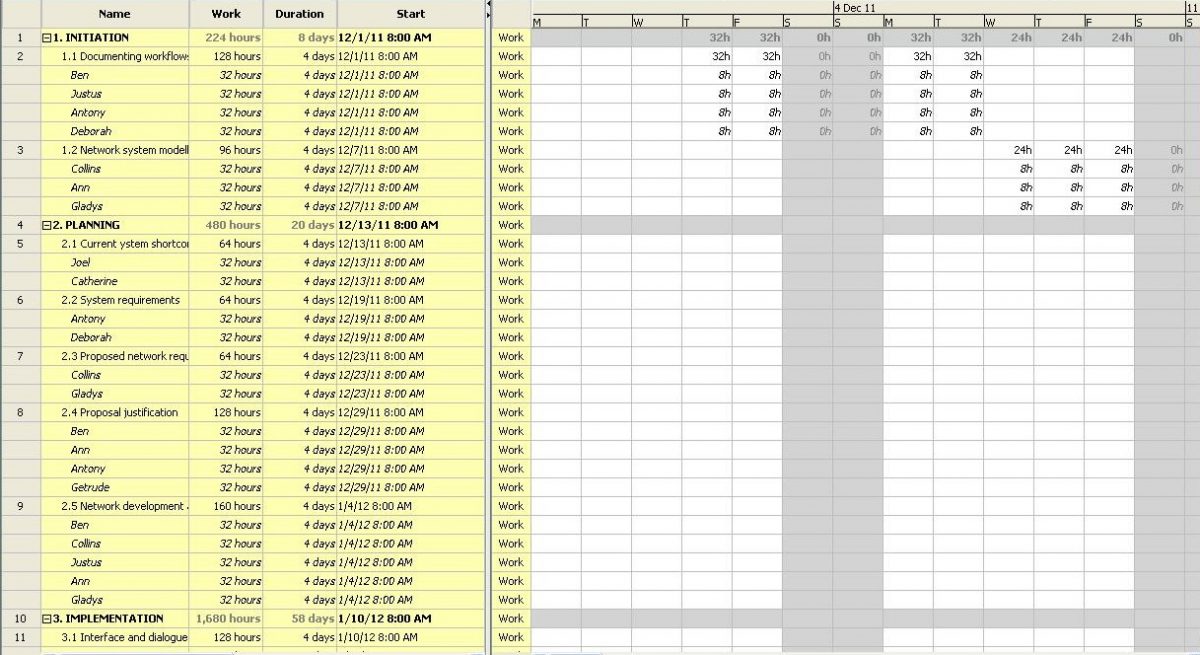
This is a medium-scale project that will require at minimum a team of twelve people, one project manager, four technical network support lead people, four software lead people, and two hardware lead people. The manager must be skilled in practical project management. He is an appointee from BIG-PROJ Consultants. The technical network support lead must be vast in knowledge about operating and networking systems.
The software lead will take charge of software requirements for the project, managing such aspects as configuration management. The hardware lead will liaise with the team to ensure the supply of all the necessary hardware needed to complete the project. All these staff will be sourced from within BIG-PROJ Consultants apart from the subcontractor support team.
Staff Training Plan
A developed staff training program will be elaborated and executed in parallel to the final phase of implementation to ensure smooth and minimal disruption to the normal processing at Fiction Corporation. Any unlikely situations will be well covered within the documentation that will accompany the eventual system.
Resource Acquisition Plan
The details here specify the acquisition plan for other resources apart from the personnel required to complete the project successfully (Marchewka, 2009; Schwalbe, 2010). Most of these resources will be bought or acquired from suppliers whom the project manager identifies through competitive bidding. These resources will be required at the design and development phase of the project before testing. These can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Development resources are the software and hardware tools needed during the project. This will be acquired from suppliers who will be subcontracted by BIG-PROJ Consultants.
- The test plan will require at least three networked computers running a network operating system preferably Windows Server 20XX or an open-source version such as Linux. The normal office automation software for documentation will also be needed.
- Product resources needed may include memory, disk, optical disks, and other resources required by the team to offer offsite backup.
Work Plan
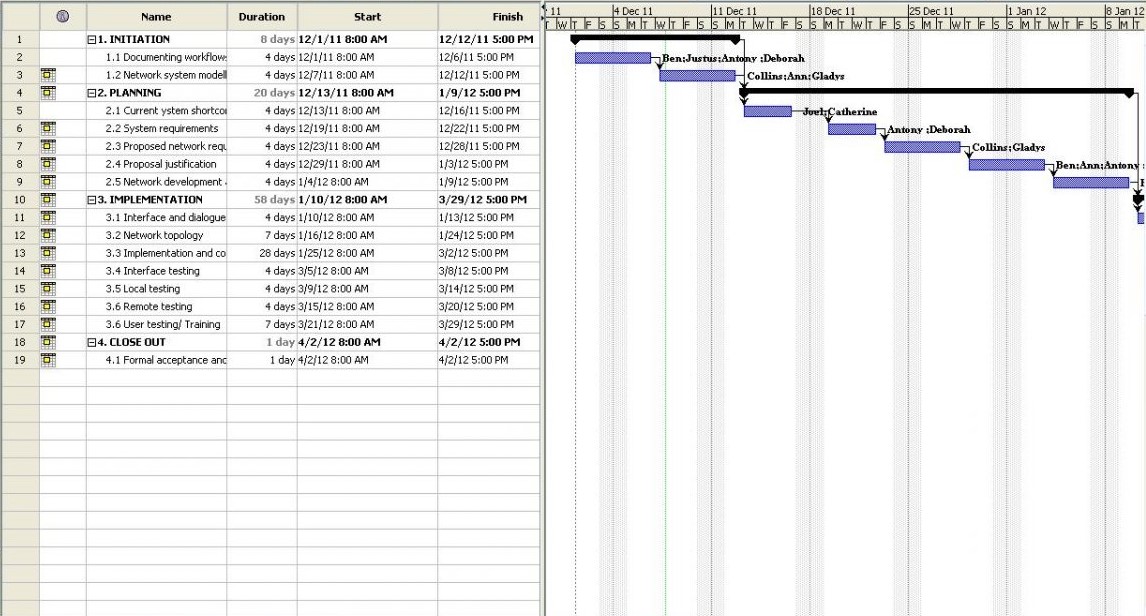
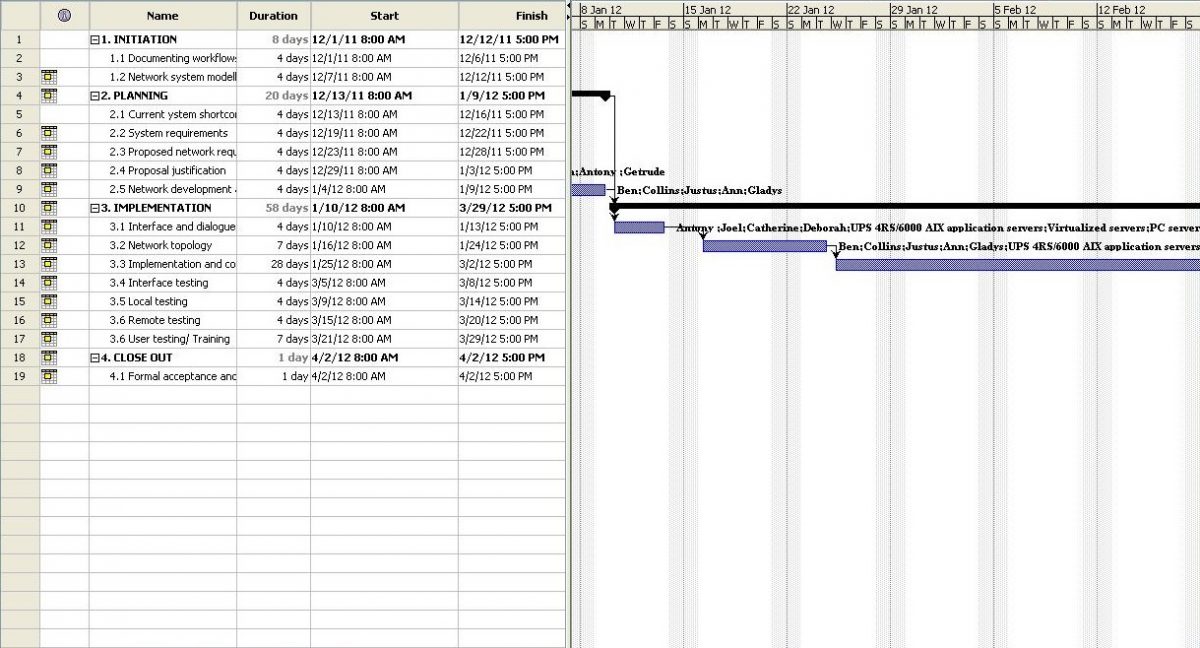
Networking Project Work Breakdown Structure (WBS):
Control Plan
The project progress will be monitored according to the project management standards with a proper feedback mechanism to ensure that every phase proceeds according to the cost and time stipulated (Schwalbe, 2010). The control plan will heavily lean on the communication tracking and report plan.
Data Control Plan
The data control plan will cover a number of areas during this project. These include:
- Types of data to be managed on the network include test data, and live data.
- Description of the format and content where relevant that includes the templates to use related to interface design.
- Data requirements list for suppliers that will relate to the database design.
- Privacy requirements related to confidentiality of the data on the intranet.
- Security requirements and procedures
Budget Control Plan
A number of tools will be used to cater for the budget control within the project set at $500,000. Net present value and discounted cash flows are some of the tools used. Earned value management within project management is important as a practice. This analytical technique enables a project manager to determine the cost and schedule requirements as the project progresses (Schwalbe, 2010). This can be compared to the budgeted indicators to determine if the project is under-budgeted. The main indicators to deriving earned value management are cost and schedule performance indexes. The former represents the earned value over the actual cost ratio while the latter represents the earned value over the budgeted cost ratio.
Communication, Tracking, and Reporting Plan
The table below here indicates the communication, follow-up, and report procedures for this project.
Table 2: Project Communication Matrix
Risk Management Plan
Within this project, there may arise several risks that must be handled effectively so that the project proceeds on time (Schwalbe, 2010). Typical this project may have risks like schedule and budget that must be addressed by involving all the stakeholders and keeping them updated. There may also be the risk of achieving customer acceptance of the deliverables. This can be achieved by carrying out an iterative and user-oriented process involving the user at all levels.
Project Close-out Plan
This project is the medium scale and therefore, envisaged that the changeover will be direct. The support staff used within this project is recruited internally and therefore, the learning curve will be greatly reduced. The project team has the collective responsibility of maintaining documentation throughout the project. Another close-out method that could also be considered includes pilot and phased changeover. However, based on the user requirements, this project is expected to proceed with minimal disruption. The direct changeover, though, expensive will be most suitable to achieve this.
Process Model
This project being medium scale will be carried out iteratively to ensure that Fiction Corporation has what they requested. The system must conform to the requirements as elicited at the beginning of the project. This includes a process that will involve the network user’s input more frequently and at various stages of network testing and integration (Refer to the project work breakdown structure and resource sheet below).
Methods, Tools, and Techniques
The hardware needed will include two UPS 4RS/6000 AIX application servers, 10 virtualized servers, 20 PC servers, 500 remote client computers, and 10 routers. Software tools include those for requirements management, the Windows Server 20XX operating system that can support the network environments for development, test, and operation design models, coding, and documentation as well as version control, compiler, or integrated development environment (IDE). Development approaches that include requirements development practices such as those stipulated within the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK). Quality assurance processes that support technical peer reviews, interface testing, and local, and remote testing.
Configuration Management Plan
This project is partly software and therefore, a configuration management plan is vital to set up and describe important aspects such as version control to ensure change is properly covered (Marchewka, 2009; Schwalbe, 2010). The configuration management process will also cover the hardware infrastructure that will support Fiction Corporation’s intranet
Quality Assurance Plan
The project management will incorporate a quality assurance model based on the international standards organization- ISO 900X quality assurance procedures. Because the project will not be formally evaluated by an international standards organization.
900X auditors, the full extent of normal ISO 900X procedures are not necessary. A formal quality plan will be created. This plan will define the following:
- All the networking project deliverables are verified against their objectives;
- A procedure is in place for ensuring project deliverables are checked before being released.
- All partners concur that their deliverables are of the required standard;
- Quality reviews are included as formal agenda items at project control committee (PCC), and plenary meetings, such discussions.
- The issue of quality is addressed also in the peer reviews.
- All meetings, email discussions, and deliverables are formally logged in the project archive.
- Demonstrator test reports are formally logged, and a review of item inconsistency is properly tackled by the development team.
References
Duncan, W.R. (1996). A guide to the project management body of knowledge. Sylva, North Carolina: Project Management Institute.
Marchewka, J.T. (2009) Information technology project management (3rd ed.). London: Wiley.
Schwalbe, K. (2010). Information technology project management. Boston: Course Technology-Cengage.