Introduction
Definitions and a short discussion
Job satisfaction is a significant part of social well-being (Cakmur 1). An evaluation of job quality offers a good interpreter of future labor-market performance. As such, job satisfaction influences employees’ decisions with respect to working hours, job selection, and turnover (Han 84). Three of the definitions used in the article are illustrated below:
- Job satisfaction refers to the level of gratification workers attach to their labor.
- Subjective well-being is used in reference to how individuals acknowledge the value of their existence. It and comprises of both thoughtful responses and mental decisions.
- Organizational citizenship behavior refers to a theory that defines an individual’s voluntary obligation in a firm that is not a portion of his or her prescribed responsibilities.
Literature review
One study indicates that employees in OECD countries believe that financial recompenses are prioritized after other features of a job such as employment security, job interest, promotion prospects, and independence (Clark 4).
Another research noted that organizational commitment deserves further attention in the workplace because there was a robust academic support for its influence on organizational citizenship behavior (Williams 601). A third study focused on subjective well-being (Diener 71). The research noted that three components of subjective wellbeing existed. They are positive effect, negative effect, and life satisfaction.
Hypotheses
The first hypothesis for the study suggests that employees in UAE are more likely to feel job difficulty compared to workers in OECD countries. The second hypothesis claims that hours of work and remunerations influence job satisfaction. On the other hand, the third hypothesis suggests that there are many aspects of quality of job that affect job satisfaction other than the above mentioned two features.
Method
Subjects
The study utilized 265 participants. The table below illustrates the percentages of our subjects:
Fig 1: A summary of the seven items
Questionnaires used and reliability of analysis result
The research utilized three articles to come up with good questioners. They are Job Satisfaction, Organizational Citizenship, and Life Satisfaction Questionnaire. The questionnaire developed had five items. The participants were required to indicate if they approved or differed with the question posed. They utilized a 1-5 Likert scale to note down their expressions. The scaled ranged from I strongly agree to I strongly disagree. The reliability scores of Likert scale were low because they were subject to social desirability.
A short description of how the survey was conducted
The survey utilized interviews to collect the required data. Through this, researchers questioned participants in person to collect their personal views. The queries used during the studies were close ended.
Results
Tables
After the results had been collected, they were analyzed to illustrate their mean and standard deviation. The variables used in calculating correlation were salary, work time, opportunities, security, and job content. The table representing the mean and the standard deviation of the results obtained is indicated below:
Figure 2: table showing mean and standard deviation
A short discussion of statistical methods
After that, a correlation, regression, and t-test analysis were undertaken. Correlation and regression table is indicated below:
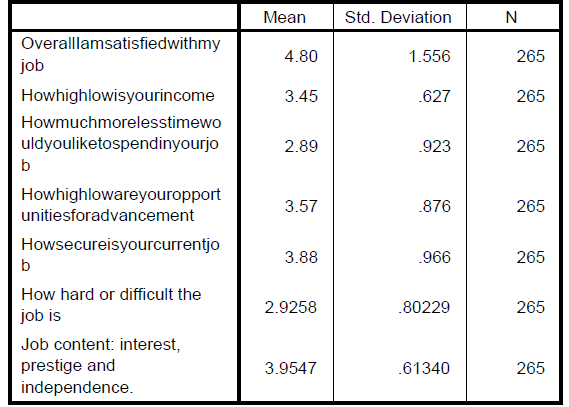
Fig 3: Regression analysis of overall job satisfaction
Discussion
Interpretation of results
To sanctify the connection of general job gratification to the integral portions described above, the researchers came up with a regression examination. The figure above illustrates the outcomes of the regression analysis conducted on seven variables. As indicated in the table, the assessed figures show that all seven variables of quality of job are considerably related to overall job satisfaction.
The biggest impact on general job gratification is linked with job content. The above variable is followed by job security. The third feature that affects jobs satisfaction is income. The table indicates that the time spent working has the least impact on job satisfaction.
Study limitations
During the research process, the researchers experienced many problems that might have affected the outcomes of their results. For instance, access to the target institutions identified as the study population was a major challenge. Equally, the process of convincing employees to be part of the study was complicated.
For example, most workers did not like to be involved in procedures that tend to question or investigate their work practices. Secondly, the process of recruiting the most skilled employees to be participants in the study was relatively long because most of them had tight schedules due to the nature of their work.
Future research
In the future, researches should be focused on determining the effects of the levels of job satisfaction on employee performance. The general statement suggests that low levels of job satisfaction are to be blamed for the ever-increasing workplace-related stress and turnover (Abdulla, Djebarni, and Mellahi 130).
Therefore, organizations should enhance their job satisfaction levels to address conflicts and enhance productivity in the workplaces. The initiative will enable the employees to develop a positive staff culture, boost their morale and motivation, and improve employer and employee relationship.
Works Cited
Abdulla, Jassem, Ramdane Djebarni, and Kamel Mellahi. “Determinants of Job Satisfaction in the UAE”. Personnel Review 40.1 (2011): 126-146. Print.
Cakmur, Hulya. “Concept and Evaluation of Job Satisfaction: Developed Job Satisfaction Index”. TAF Prev Med Bull (2011): 1-2. Print.
Clark, Andrew. “Measures Of Job Satisfaction: What Makes A Good Job? Evidence From OECD Countries”. OECD Labour Market and Social Policy Occasional 34.12 (1998): 3-41. Print.
Diener, Eid. “The Satisfaction with Life Scale”. Journal of Personality Assessment 49.1 (1985): 71-75. Print.
Han, Yi. “The Relationship between Job Performance And Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment, And Goal Orientation”. Acta Psychologica Sinica 40.1 (2008): 84-91. Print.
Williams, Larry. “Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment as Predictors of Organizational Citizenship and In-Role Behaviors”. Journal of Management 17.3 (1991): 601-617. Print.