Introduction
Utilizing metrics is a crucial aspect of an organization’s HR operations. Applying specific metrics makes it impossible to assess the efficiency of the recruitment process and the workforce. This paper will examine the five key HR metrics: revenue factor, human capital value added, labor cost-to-revenue ratio, cost per hire, and employee turnover costs. It will discuss the importance of these metrics and how they can influence HR decisions.
Revenue Factor
The first fundamental metric HRs use is the revenue factor. The revenue factor refers to the relationship between an organization’s revenue and labor costs. Calculating this metric is necessary when determining compensation costs, staffing levels, and other essential aspects (Lawler, 2020).
An example of calculating the revenue factor is as follows: the company’s revenue is $ 1 million, and the labor costs equal $500,000. Then, the revenue factor will equal 500 thousand ÷ 1 million, or 50%, meaning that 50% of the total revenue is spent on labour costs. Based on the revenue factor calculation, HR might consider the indicator too high, indicating low workforce efficiency (Qamar & Taab, 2022). This can be used to decide on reducing staffing levels, resulting in decreased labor costs.
Human Capital Value Added
The second of the five most critical metrics to an organization’s HR function is Human Capital Value Added (HCVA). HCVA represents the value that its employees add to the company. It is calculated by measuring the employees’ contribution to the profit after eliminating costs (Lawler, 2020). This metric provides a clear understanding of the organization’s workforce effectiveness. Identifying areas that need improvement in productivity, costs, and revenue is also impossible without considering this metric.
An example of HCVA in numbers is as follows. A company’s revenue is $1 billion, while its number of full-time employees is $5,000. The total costs are $800 million, with employee costs accounting for $300 million. HCVA will equal 1 billion – (800 million – 300 million) ÷ 5000, or 100,000. If this number is not sufficient, the company may hire a specific number of employees or implement measures to enhance productivity or reduce costs.
Labour Cost Revenue Ratio
The labour cost revenue ratio metric involves comparing a company’s labour costs with its revenue. This metric is crucial for understanding whether the company’s spending on its employees should be reduced, as it does not align with the amount it earns (Lawler, 2020).
An example of a labor cost-to-revenue ratio could be the following: the company’s revenue equals $20 million, while its labor costs constitute $8 million; the labor cost-to-revenue ratio will equal ($8 million ÷ $20 million) × 100% or 40%. In other words, 40% of the company’s gross sales are directed to compensation and benefit costs. Based on these calculations, the company’s HR can later decide how effective the workforce management strategies are, and if the percentage is too high, cutting costs might be necessary.
Cost per Hire
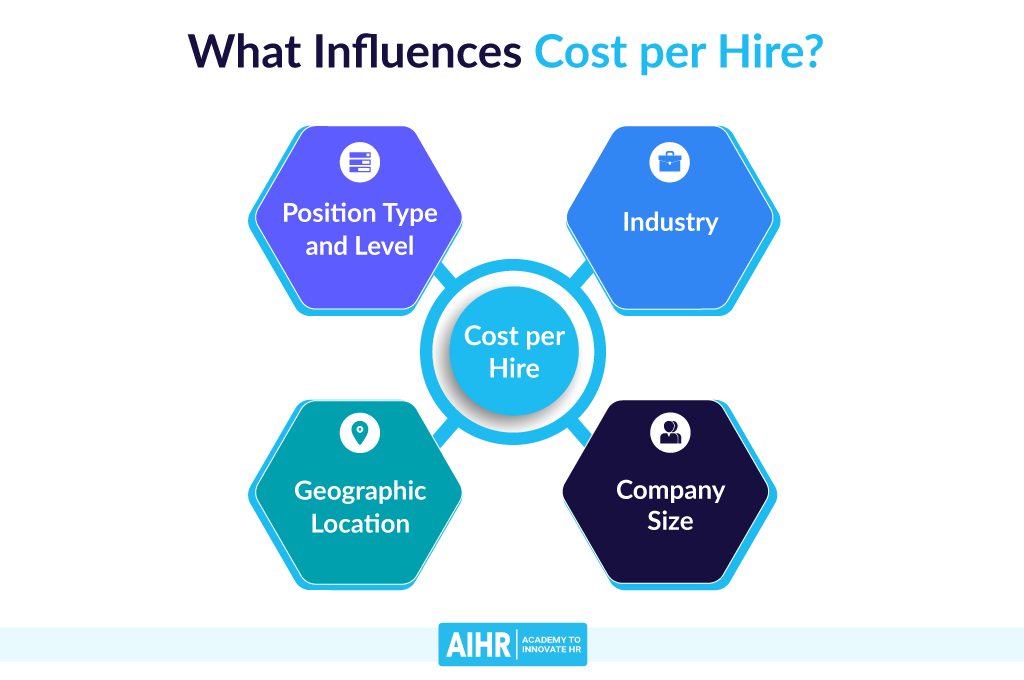
Cost per hire is another important metric that needs to be considered to determine how effective and efficient the hiring process is. Figure 1 shows all aspects to consider when calculating cost per hire. To calculate this indicator, it is necessary to divide all the expenses on the hiring process, such as advertising expenses, agency fees, recruiter’s salary, and others, by the total number of hired employees in the chosen period.
An example of calculating cost per hire could be the following: if the company spends 50 thousand dollars on recruiting in one year and hires 25 employees, the cost per hire would equal 50 thousand ÷ 25, or 2 thousand dollars. Assessing this indicator can help the recruitment team to evaluate if the hiring expenses need to be reduced (Edwards, 2019). For example, HR might reduce the amount spent on advertising or choose other methods of attracting new employees if the process is ineffective.
Turnover Costs
The last critical metric HRs apply in their work is turnover costs. Turnover costs are measured as the organization’s expenses after an employee leaves the company and the company needs to find a new employee (Khan & Millner, 2020). Turnover costs can include hiring and training costs and termination costs. This metric is essential as it shows whether the organization needs to improve its retention strategies (Edwards, 2019). If turnover costs are too high, HR might consider ways to decrease the turnover rate, which can be done through raising salaries, for example. Increased compensation expenditures will have a less significant impact on the business than increased turnover costs (Armstrong & Taylor, 2020).
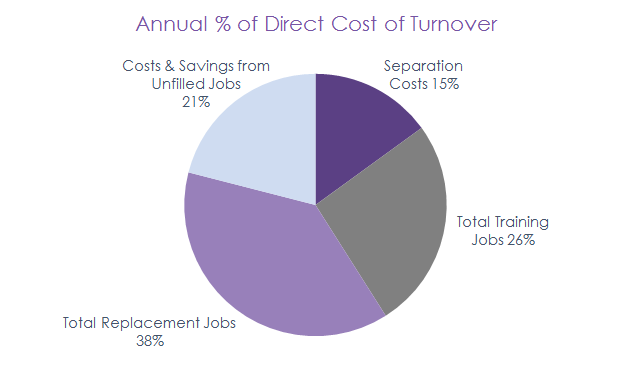
An example could be the following: if the company spends 10 thousand dollars on the replacement of each employee and the total number of employees who left the company is 10, the total turnover costs will equal 10 thousand dollars. The chart below represents a company’s total direct turnover costs.
Conclusion
The five key metrics for an organization’s HR are revenue contribution, added value of human capital, labor costs to revenue ratio, cost per employee hired, and employee turnover expenses. These indicators help to determine what changes need to be introduced in the human resource management and recruitment process, such as cost reduction, retention strategies, staffing levels, and other important decisions. When analyzed together, the efficiency of these processes can be improved significantly.
References
Armstrong, M., & Taylor, S. (2020). HR analytics. In Armstrong’s Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice, (15th ed). Kogan Page, Limited.
Edwards, M. (2019). Predictive HR analytics: Mastering the HR metric (2nd ed.). Kogan Page, Limited.
Khan, N., & Millner, D. (2020). Looking to the future. In Introduction to people analytics: A practical guide to data-driven HR. Trident Library Online.
Lawler, E. (2020). Effective human resource management: a global analysis. Stanford University Press.
Qamar, Y., & Taab, A. S. (2022). Human resource analytics: a review and bibliometric analysis. Personnel Review, 51(1), 251-283. Web.
Van Vulpen, E. (2021). Cost per hire: Definition, formula, and calculation. AIHR. Web.