Introduction
The paper discusses the labor market in the United Kingdom and its effects on the economy. It provides information on income inequality from 1980 up to date. Analysis of the data provided shows that there was a huge growth in income inequality that occurred during these boom years of the 1980s. Between 1979 and 1991, for example, the richest groups saw their incomes grow substantially while the incomes of the poorest groups hardly changed at all. The paper document data on the trends on the United Kingdom labor market, inequalities and its causes during this period in time. Lastly, it highlights the strategies the governments can adopt to tackle the effects of inequalities and reasons behind reducing inequality in United Kingdom.
Definition of labor market and inequality
Labour market cab be defined as the market in which workers compete for jobs and employers compete for workers (Card, 1991). It includes the number of people available for work considered together with available jobs. Inequality on the other hand, refers to all disparities in distribution of resources among individuals and groups within a society. For example unequal distribution of economic assets and income.
Trends in the labour market
There has been rapid change in the labour market since 1990’s as a result of rapid industrialization and globalization. Labour markets have been making adjustments to respond to the changes. The effects of globalization and technological change manifest through need for labor and their pay. It has also influenced structure of the labour market which is a shift –up trend towards demand for high skilled workers. Industrialization calls for intensified workers in the industry. Technological changes influences production and organizational processes. There is improved working conditions and labour relations through the use of advanced technology. It results to demand for high skilled workers in economy. There has increased entry of new graduates onto the labour market over the years hence flooding the market resulting to unemployment. This is because there are more workers looking for jobs when jobs available are limited. The planning especially on the vacancies and graduates released from higher institutions of learning are not well matched. There is also low quality of graduates who have successfully gone through the education system. Education systems have been changing over the time and this has had an impact on the labour market trends (Freeman, 1993). It ha also resulted on increased competition for jobs among professionals.
Causes of inequalities
Inequalities in the society have a great impact on the labour market. It has significantly increased due the following reasons. First, the effect of income inequality on labour market. Income and wealth differences among individuals lead to inequalities whereby a portion of population will have more income (the rich) than the other portion having low income –that is-the poor (DSS, 1999). This leads to unequal distribution of income. Secondly, differences in the education levels. In society, there are those who are more educated than others. The rich have the money and thus their children are provided with the best education possible by providing conducive learning environments, enough learning materials, have mentors to look upon to, and thus excel well in their examinations. This puts them in a better position on job markets which enhances their income hence maintaining the status quo. The poor on the other hand lack the resources to sustain there children to access a better form education to enhance their skills to participate in economic development. This automatically cut them off from employment opportunities hence inequality in access to education and access to better jobs. There results to two inequalities : inequalities to get better education for the poor and inequality to get a well paying job for the poor after a subsequent poor education.Gender, race, and culture is also another factor contributing to inequality in the society. They are some jobs on the labour market which are believed to be for men while others are deemed feminine. These stereotypes existing in the society limit and disadvantage women hence leading to inequality. For example, women are supposed to take care and nurture the family hence cannot go for high paying and challenging jobs. For example in a developed nation like the United States of America, women CEOs are only 3 % compared to their male counterparts. Employment opportunities given on racial grounds limit the contribution of other races hence inequality among different races in a given nation. Lastly, differences in abilities also results to inequalities. People have different abilities such as intelligence, motivation levels, individual wealth and strength. These causes inequality as intelligent and well motivated people are likely to get well paying jobs that increase their income.
Reasons for reducing inequalities
The government has to strive to reduce inequality in the society due to the following reasons; it will help promote national unity and social cohesion. It ensures everybody in the society can access all the basic needs that they require. For example, health services, educational facilities, and housing. It will ensure equal distribution of income as poor people will have higher income hence be able to meet their basic needs. This is a way of distributing national wealth to all the social stratification classes. It also increases supply of skilled labour hence reducing shortages in the labour market. This is as result of improved educational facilities and resources as provision to educational sector improves with improved inequalities.
The government can reduce inequality through the following economic initiatives. First, through public education in which every body will be able to access the education he or she wants to attain. This also increases supply of skilled labour hence reducing income inequality. Secondly, the government can reduce inequality through efficient tax system (Goodman et al., 1997). This is through taxing the rich proportionally more than the poor which will bring about income balances between the rich and the poor. Thirdly, by use of minimum wage legislation in which the government puts in place the minimum wage which an employee should be paid. This helps protect the poor from earning extremely low income (Champernowne &Cowell, 1998). Lastly, provision of subsidies where the government provides incentives to producers and manufacturers, which reduces production costs hence reduced prices for goods and services. This helps in providing cheap or free goods and services to all people in the nation.
Determination of equilibrium wage
The diagram below shows the equilibrium wage at point WE and equilibrium labor at point LE. The equilibrium occurs at the point where demand curve for labour intersect with the supply curve for labour.
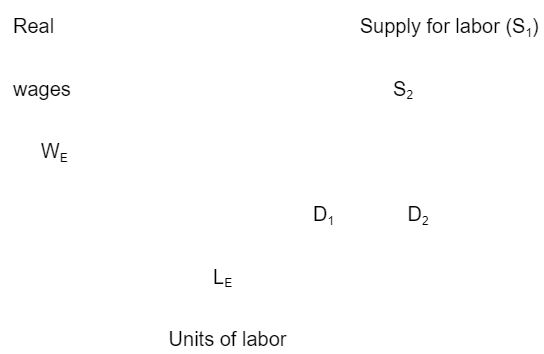
Shifts in the demand for labour curve from D1 to D2 is caused by the need to increase production by companies as they will require more labour. Shifts in the supply for labor curve shown by movement from S1 to S2 is caused by improvement in education resources hence increasing the number of skilled labor resulting to increased supply for labor.

The wage determined by the forces of demand and supply are considered to be very low therefore the government sets a minimum wage above the equilibrium wage (WE).

Gin Coefficient
This trend of declining inequality was abruptly reversed as the gap between the rich and the poor began to widen, marking the start of a period of more than a decade during which inequality rose on an unprecedented scale.
During the period of economic recovery 1984-1990, inequality rose quickly. Post 1990, there was a slump as a result of boom that effectively checked the inequality, until 1993- 1996, when the economy started recovering. In the most recent two years of economic growth 1996–97 and 1997–98, inequality seems to have started rising once again.
Conclusion
From the discussion above, it is evident that there are high inequalities in United Kingdom as shown in the discussion above. Governments should aim at reducing inequalities to help in economic development through distribution of wealth and resources across the nation.
References
Card, D. (1991), The effects of unions on the distribution of wages: redistribution or relabelling?,Princeton University, Industrial Relations Section, Discussion Paper no. 287.
Champernowne, D. G. and Cowell, F. A. (1998), Economic Inequality and Income Distribution, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
DSS (1999). Households Below Average Income 1994/5–1997/8, London: Stationery Office.
Freeman, R. (1993). How much has deunionisation contributed to the rise in male earnings inequality? in S. Danziger and P. Gottschalk (eds), Uneven Tides: Rising Inequality in America, New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
Goodman, A., Johnson, P. and Webb, S. (1997), Inequality in the UK, Oxford: Oxford University Press.