Introduction
Felix intends to start a new venture of retailing Orehana Pearls after retirement. Felix has the means necessary to launch a new business venture because he received a retirement fund as payment for the work, he completed for the chocolate company. He is, therefore, free to make investments and start a new company. In addition to the expenses related to the existing business, every new start-up has additional expenses (Voinea, Logger, & Roijakkers, 2019). In Felix’s hypothetical situation, he intends to sell natural pearls. When Felix decides to start a business selling pearls, he must first choose a name for it and register it with the appropriate authorities so that Felix can conduct business legally both from the standpoint of his suppliers and that of his customers (Tchamyou, 2017). There would be start-up charges associated with these registrations and the determination of Felix’s legality. In addition, there are expenses related to buying pearls from vendors.
The cost of importing the pearls from Tahiti to Zurich would include import duties. In addition, the cost and quality of pearls should be considered, as well as the amount spent and any additional expenses. Felix’s plan must therefore include a list of all the expenses he expects to incur in connection with the new firm, given only these details. Business-related expenses include; start-up costs, inventory costs, and importation charges. Felix must ensure the supplier has enough high-quality pearls to cover the purchase cost. Felix must approach this rationally and account for the probability of price volatility in his estimation.
Felix must ensure that the overall costs incurred are, at most, the retirement benefits he received. Once Felix has completed this, he should research the potential earnings from starting this firm (Edman, 2021). Felix should push for it if there is an income. However, if there is a loss, Felix must reconsider whether he wants to open the business. The start-up costs incurred only in the first year cause the loss, and their removal in succeeding years may result in a gain. When there are no start-up costs, but the business would still experience a loss, Felix must reconsider whether he wants to open the business.
Registration of Felix’s New Venture
According to the Swiss Business Act (2018), it is a requirement that all ventures or businesses should be registered. Before any business is legalized and allowed to operate in any country, it is a requirement that it passes through the registration process of the Business Registration Act (Williams, Martinez, & Kedir, 2017). The Business Registration Act is the body obligated to legalize businesses to operate its main activities.
Reasons for Registering Felix New Venture
According to Gottschalk & Buzzeo (2017), it is important to ensure a business is registered. Felix is advised to register his new venture for the following reasons; first, he will have limited restrictions and liabilities. This implies that Felix’s liability in case of loss or circumstances that may affect the business will be limited. The government will intervene if the business is insured. Secondly, the venture is acknowledged as the legal body. This is where when the new venture is registered will be granted recognition or legal privileges in a particular jurisdiction. This establishes the venture’s existence independently of its investors.
In the corporate sector, ventures that are properly registered are appreciated. Therefore, registering a business typically aids in market expansion and commercial growth. The third reason for registering the venture is that it will be simple for the business to access its account and request alone. Loan lending organizations trust a legally registered business as it is easy to follow in case of loan default. Another reason is that a registered business has a minimal tax obligation. A venture unit may be eligible for marketing, improvements, research, and teaching tax breaks. If Felix Venture registers, its tax burden will be decreased.
Registration of the Venture will help Felix protect the name of his venture due to the acquisition of the trademark, and it will assist Felix in stopping other firms from using the name of his firm to confuse his customers. Registration of a business will also help in avoiding additional costs and penalties. Felix might have to pay late fees or face other legal repercussions if he does not register his firm. He must register his business on time because doing otherwise could incur extra costs.
Procedure for Registering Felix New Venture
Registering a business or a company is a step-by-step process that has to be followed for the registration to be successful. Felix needs to follow a well-laid procedure for registering his venture. The first step will start with Felix searching for the business’s name (Belitski & Desai, 2019). For a business name search, Felix must offer at least three distinct company name choices in the order of preference. The intended company name must be held in custody pending registration. In conjunction with the registration, a request for a name search of a potential business name is submitted. There are no additional name searches done.
Felix must remember that hundreds of thousands of names have already been registered when deciding on a business name. To gain a name or two right away, he should make it as distinctive as he can. The second step is for Felix to apply for a business registration name. The application for registration will be completed using the required BN registration form when the selected name has been looked up and reserved by the Registrar of Business Names. Through the online platform, all online business registrations are completed. The application will be accepted upon submission and prepared for certificate issuing.
Before the approval is termed valid, some rules are followed; the name should differ from the existing businesses. This ensures the identity and uniqueness of the business. It also eliminates the confusion of the stakeholders. The name of the business should also be clear. It should be concise and precise. The business’s name should not suggest a royal, national, or international connection. Lastly, the registrar goes through all documents and, once satisfied that the requirements have been complied with, will issue a certificate of Registration of the Business Name, commonly known as BN 3. The certificate marks the birth of the new venture.
Requirements for Venture Name Registration
Before the name Felix has suggested for his venture be registered, it must meet certain requirements. There have to be proposed business names for reservation and search. A search is done to ensure the proposed business name is distinct from an already registered business. It is reserved for 30 days after approval. Another requirement to be taken into consideration is the business’s nature. Due to the nature of the responsibility, it is permitted to operate in one industry. Felix must also provide his new venture’s postal address, allowing his customers, investors, and other stakeholders to access the business easily.
He must provide the physical address of his ventures, such as the name of the road close to his venture and the town and county in which it is located. It is also a requirement for Felix to provide a copy of his passport to the registrar of business. It is a requirement for Felix to create the email of the new venture that is distinct from his email and submit it to the registrar of the business. Besides all this, Felix must provide his physical address, including the name of the nearby road, the plot number, the town, and the county. This will enable his potential customers to easily access him in case any vital information may be required.
Sources of Funds for New Venture
Felix must write a strong business plan that will assist him in looking for money. His plan should specify how much money he requires and its uses. Felix needs to source funds that will help expand his venture’s size and composition. Ideally, any business needs to source funds. Felix requires financing to maintain a healthy cash flow since its venture is a starting business. While Felix can use his own money to launch the business, it will take more work for him to sustain it. As a result, the business owner will need to look for outside capital, such as bank loans and government grants.
Felix’s venture needs funds to build on its working capital. A crucial component of Felix’s new venture will be financial health through having enough working capital, and a lack of it can harm the venture. Felix can request outside finance to generate enough working cash to support their expansion plans. A loan can fill in the shortfall between client orders and supplier payments to help the firm fulfill its financial obligations, or it can bridge that gap and provide the business with the money it needs to expand (Lerner & Nanda, 2020). The availability of working capital financing can also help Felix’s new venture seize new possibilities and expand by enabling him to invest in fresh goods and services.
Enough funds will enable Felix to invest in assets like new machinery or vehicles, enabling him to grow his venture and increase sales. The expense of purchasing a costly new asset can be divided up with the help of an asset funding loan. Felix may arrange his cash flow in advance to take full advantage of his opportunity for growth with the aid of fixed monthly repayments and loan durations. Funds will also ensure the venture is financially stable and can remain stable in case of any ups and downs that the business will face. Adequate funds within the business will ensure the stakeholders that the business will operate as a going concern.
Factors to Consider in Selecting the Source of Funds
There are many sources of funds that owners can choose to obtain funds for running their businesses. Different sources of funds have their implications and effects on the business. Before deciding on the appropriate source of funds, the owners have to consider various factors. While considering these factors, the business is better positioned to make an objective decision. Felix needs to consider the following factors before deciding on the appropriate source of funds to fund his new venture; first, analyzing the cost of each type of fund is needed. Different funds have costs to be repaid. Therefore, Felix should choose a fund source with minimal cost.
There is also a need to consider the risks associated with each source of funds. Some sources of funds have high financial risks; hence there is a need to choose the one with low leverage with low financial risk. There is also a risk of diluting ownership of the business; hence Felix should ensure its business will be maintained. The best source of funds is the one that one has acquired and should not affect the control of the business. For example, Felix should consider equity financing only to a certain level to avoid diluting ownership of the firm. Lastly, Felix should secure a flexible source of funds. He should analyze all sources and identify a more flexible capital structure.
Major Sources of Funds
After considering all the factors required when deciding the type of fund sources to use, Felix should adopt the following funds. Felix should borrow a loan from the bank. For a set time, the bank normally lends this money at an agreed interest, together with collateral security (Belz & Binder, 2017). A bank loan is one of the most appropriate sources of funds since it enables the business to grow and expand quickly. The money obtained through the bank, if appropriately invested in the business, will lead to a rapid increase in the size of the business. Also, Felix, the new venture owner, will be able to maintain total control over the business.
The bank does not take any ownership of the business, like in the case of equity funding, where it will obtain a share of the business. Therefore, the owner will be satisfied when a bank loan is employed. Another advantage is that when the business can make repayment within the agreed time, there will be no bank interference. Also, the interest of the bank is favorable. The bank does not charge too high interest on the loan rendered to the business. However, various limitations come with borrowing loans from the bank. Felix must be aware of the following disadvantages of a bank loan; obtaining a bank loan has very strict eligibility requirements. Many formalities are involved before awarding a loan is awarded. The borrower is required to provide a lot of legal certifications and even provide information about the grantor.
The process of acquiring a bank loan has a protracted application process. The process is very long and tiresome to complete, making many unable to access the loan. Another source of funds that is appropriate for Felix is a personal investment. This is where Felix is advised to use his investment to start his new venture. He may also use his retirement money to start his new Venture (Sudiyatno, Puspitasari, & Sudarsi, 2019). Their investment in Felix for running his new venture will be most appropriate since it will be easy to use the money. This is because the money is readily available and does not require time to search for it. Another benefit of using personal savings is that there will be no loss of control over the business. Felix will be dealing with his funds without interference from other parties who may require acquiring some venture shares. Therefore, the ownership of the venture will remain intact with Felix. Using personal savings will also be advantageous since all the profits from the business remain within the business, as there is no sharing of the profit with other partners who contribute their shares to the running of the business.
Besides personal savings having many benefits to the Business, Felix should be aware that the same personal savings have their limitations. One important limitation is that more than personal investment may be required to run the business. Felix may need more adequate savings to ensure all the operations within the venture. To be sufficient, he will be required to mix it with other sources of funds. There will also be a danger of having low profit as the profit generated will be highly taxed. Depending on personal savings without borrowing is disadvantageous as there will be no tax deductions on the venture’s profits.
An equity investment grants investors a stake in the business, giving them the right to a share of the profits. Equity refers to a long-term investment in a company that the company does not repay afterward. A properly defined investment should be present in a fully functional corporate organization. Due to the absence of interest payments, equity financing will reduce the strain on the venture. Felix may form unofficial partnerships with those with more expertise or talent in equity finance. Some may be well-connected, allowing his company to utilize their knowledge and network of contacts. Since investors will also want a piece, equity financing will lower the venture’s profit. Furthermore, Felix can lose control of his project if investors demand shares, which would dilute corporate ownership.
Sensitivity Analysis
This analysis determines how venture-independent factors affect a dependent variable in a given set of circumstances. Sensitivity analysis will help Felix know if its venture’s working capital affects the profit margin. Other variables that affect the profit margin of the venture, and Felix needs to do sensitivity analysis, are the cost of goods sold, workers’ wages, and managers’ wages. Working capital should be analyzed well to ensure the venture’s current assets are capable of meeting the venture’s obligations (Vander & Ding, 2017). If this is impossible, then Felix should find a way of increasing its working capital to ensure there is a stable financial base. The venture should critically analyze the goods sold. This will assist in knowing whether the company will be earning profit or loss. A good venture should generate significant profit with less cost of sales. Workers’ and managers’ wages should also be analyzed to ensure workers’ and managers’ production benefits are more than the cost of paying their wages.
Evaluation of Venture Viability
Venture viability is analyzing the venture to determine if it can survive in the future and become successful. An unviable venture is difficult to operate and recover in case of failure. To avoid the venture becoming unviable, it needs to increase revenue and cut costs (Greene & Hopp, 2017). Felix’s project needs to be built in two steps to succeed. It starts with creating a marketing strategy by determining the brand, the target market, and other rival businesses to sell. Maintaining order in the finances is another requirement. Information will be necessary to develop a marketing plan to make Felix’s new venture viable. The venture should have a unique selling proposition.
Having a successful business depends on its unique proposition of sales. Therefore, being distinctive keeps the company ahead of the competition. This is because customers will be attracted to the unique services that Felix’s new venture will offer. A stable customer base will guarantee the business’s future viability. For the new venture to be successful, Felix must understand the target market’s demographics. This can be done by conducting a study to identify individuals and focus on satisfying their needs. This will enable the venture to retain existing customers and attract many new customers, who will increase the venture’s sales, increasing its profit which will later translate to increased profit. For Felix’s new venture to remain viable, it needs to have a competitive advantage: Felix must always consider the competition, even if the product is unique, and he has to be aware of the target market.
As Felix develops the marketing strategy, he has to identify his competitors and keep them in mind. He also needs to identify ways of staying ahead of his competitors at any time. Along with the marketing plan, maintaining attention to the company’s financial health will help it become a viable enterprise (McLaney, & Atrill, 2020). This will involve a sustainable and stable cash flow. In this case, having enough assets in cash and other reserves for everyday operations and withstanding the business challenge is the most crucial component that can make a Felix venture profitable. Stabilizing cash flows takes time since it entails practicing restraint, avoiding excessive expenditure in advance, and minimizing one’s impact on the company.
Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting is a way of predicting revenue from sales. It shows what the new venture expects to sell during a specific period. To forecast sales appropriately, Felix must answer how to produce the products and services and how much goods should be produced to satisfy customers. He should also know who the customers are to align the production to their needs.
Objectives of Sales Forecasting
Any business plan should include a sales estimate. A sales forecast is used to manage time and resources for the salesperson and the entire company and to predict future sales. A successful forecast should have numerous goals that all work toward figuring out what a business sells when to make sales, and to whom the product will sell (McLaney & Atrill, 2020). Accuracy is the first goal of a sales prediction. The creation of forecasts can be assisted by sophisticated forecasting software. However, the software needs to be more frequently. Software often uses prior sales to forecast future patterns.
The market and the consumers’ shifting demands and objectives are also considered in an accurate projection. An element of creating an accurate sales forecast is researching industry trends and speaking with clients to learn about their future needs. To discover new markets, sales forecasting is helpful. Accurate sales projections should be segmented by market for both items and services. A realistic sales prediction should include information on who buys the most products and when to buy on top of what has been sold. It is much simpler to decide who should receive the most of the time.
Sales department projections are kept on a firm’s file. Hence, Felix can make a projection plan due to the compiled forecasts. Felix will use this data to plan operational budgets and foresee staffing requirements. The marketing division can use sales projections to decide which goods and services should be highlighted in advertisements or promotions. Suppliers and other business partners also value sales predictions since they can use the results to anticipate their demands. Accurate prediction sharing builds trust between suppliers and business partners.
Amount of Cash Needed by the Venture to Get Started
Felix Venture is a new venture that is supposed to start operating as usual start-up ventures that demand money to pick up. This venture requires much capital to make all the operations active and valuable. The following table summarizes the total cost required by the business to get started. Table 1 below represents the initial capital requirements.
Table 1: Cash Needed for Start-Up
Note: All Transactions Are in Swiss Francois
Marketing Strategies
The new venture will employ marketing strategies to draw clients to its doors. The plans will also guarantee that the venture knows its clients, comprehends the goods and services it provides and adheres to its financial plan (Ferrell, Hartline, & Hochstein, 2021). Felix will employ various marketing methods to guarantee that the target clients are reached. To communicate with the customers, any tactic will be employed. Digital marketing methods will give customers a larger selection of communication options because most of the target demographic is informed. Among the tactics are;
Close-Range Marketing Strategy (CRM)
Under this strategy, the venture sends advertisements through Wi-Fi or Bluetooth to customers within a closed radius. Felix will install Wi-Fi in the business, and the marketing team will send quality video ads, advertisements, and other promotional messages to all internet users within a radius of two miles (Daulay & Saputra, 2019). According to Tamulienė, Rašimaitė, and Tunčikienė (2020), ads may be annoying to some customers, and excessive use of ads may lead to customers not buying the products or even blocking the ads. For this reason, the venture will design the ads to be entertaining and appealing to view to minimize the risk of being annoying. The new venture will also use social media and YouTube ads for our close customers.
Direct Strategy
Direct marketing strategy involves direct communication with the customers. The marketing team will meet the customers and talk to them directly about the products and services. In addition, the availability of a subscription option ensures that members know about the products and promote them to others (Daulay & Saputra, 2019). Felix will also conduct corporate social responsibility within the farm to ensure direct advertisement and marketing of products and services.
Financial Statements of Felix’s New Venture
Financial statements were prepared to assist in analyzing the intended Venture of Felix. Three significant financial statements have been prepared for this case. These include; income statements, statements of financial position, and cash flow statements (Well, 2022).
Assumptions of Financial Statements
The Consistency Assumption
In light of this supposition, Felix Venture must employ the same accounting approach for all accounting practices and reporting periods. The venture should also consistently employ the same accounting principle from one period to another. For example, Felix’s venture may decide to employ first in, first out principles where all the pearls that were bought first should be sold before selling the following stock (Chudziak, 2022). Also, when it decides to use the straight-line depreciation method, it should apply it throughout the period without frequent adjustment. This premise only deviates from when a different approach would be more appropriate and effective. Accounting records from different periods can be easily compared with consistent accounting practices.
Going Concern Assumption
This assumption suggests that the Felix Venture will carry on doing business for the foreseeable future. It assumes that the venture will not file for bankruptcy and can carry out its duties and achieve its goals (Trpeska, Atanasovski, & Lazarevska, 2017). The going concern assumption assumes that the venture will continue to operate, carry out expected plans, and achieve anticipated goals after its next fiscal term (Zhang, 2017). Felix needs to identify and come up with factors that will assist its business to be functioning for the foreseeable future. He also needs to focus on the venture’s objective of maximizing profit to ensure the firm does not make losses. Felix should refrain from defaulting on a loan payment to avoid the venture’s dissolution.
Period Assumption
This concept states that Felix Venture’s accounting procedures and techniques should be preserved and reported for particular time intervals. Additionally, each year the business is in existence, these times should remain constant (Miller & O’Leary, 2019). Time intervals can be monthly, quarterly, biannually, or annually, but they must be constant to compare records over predetermined intervals.
Reliability Accounting Assumption
According to this assumption, only transactions that can be verified should be recorded in accounting procedures. Because of this, firms must be able to prove transactions using documents like bank statements, invoices, billing statements, receipts, and other supporting documentation (Kieso, Weygandt, & Warfield, 2019). Before a transaction can be recorded in a business’s accounting records, there must be some independent proof.
Economic Entity Assumption
This presumption suggests that a business’s and its owner’s accounting records will be kept apart. In accounting procedures, business and personal owner transactions should never be combined (Russell, Milne, & Dey, 2017). Small, family-run enterprises are particularly troubled by this issue
Profit and Loss Statement for The First Year of Operation
This type of financial statement assists Felix and Potential investors know whether the intended business will make a profit or loss within the financial period ending December 2023, assuming Felix will officially start his venture in January 2023. This statement shows the sales that will be made by the new venture, purchases to be made by Felix’s venture, expenses the new venture will incur, and any income that will be received, like discounts received by Felix. In addition, the profit and loss statement shows the tax to be paid for the venture and all compliance that Felix requires.
Estimates Made in Preparation of Profit and Loss Account
Exchange Rates and Discounts
It is estimated that the venture will start operating with an exchange rate of 1XPF= 0.0082CHF hence all goods and raw materials purchased will be converted into Swiss currency. In addition, Felix receives a discount on all purchases made in cash from overseas from reputable suppliers. The discount made on the supply of goods is allowed at 5%, and the period for purchases will be estimated at 30 days.
Matching Principle
The venture operates on a matching assumption that all expenses are matched against the business’s revenues. Felix is likely to incur on acquiring alarm and racking services and business safety. In addition, web design costs are likely to generate revenue at the end of the operational period of the venture.
Revenues
Sales revenue is the money a business makes through selling products or rendering services. Felix venture will receive revenue of 810000 CHF from the sale of its pearls in Switzerland. Felix needs to innovate ways of ensuring its sales are growing yearly (Phillips, 2021). Felix may increase its sales by marketing its products. This will make potential customers aware of Pearl’s products in the Venture (Morano & Tajani, 2017). The marketing strategies that Felix may employ include creating websites where customers can access their products at any time, doing promotional campaigns, and involving in advertisements (Schroeder, Clark, & Cathey, 2022). Felix may also ensure it provides quality products to satisfy the customers. Satisfied customers will tend to visit the venture frequently to acquire more products. Hence, having quality products may also attract more customers to continue purchasing the new commodities in the firm.
Purchases
A purchase is an action that a business takes regularly. This financial transaction aims to transfer ownership of a piece of property, whether tangible, intangible, virtual or something else. The right to use or dispose of the property however the owner chooses is a benefit of acquiring it (Gagnon, Raskin, & Sack, 2018). The business will also incur costs in purchasing. This cost will include cost CHF 5,700 for buying racking and special cost, cost of CHF 550 for purchasing a small drill and jig, cost of CHF 25 per set of silver chains and clasp. The items purchased by Felix Venture will help it start its operations efficiently and effectively without facing operational challenges.
Costs
The costs a business incurs to conduct its operations, whether fixed, variable, direct, or indirect, are all included in the cost of the business. It is similar to correct or actual expenses, including all receipts for payments, all obligations under contracts, and the book cost of depreciation on both plant and equipment (Jensen & Meckling, 2019). A new venture will also incur start costs like registering the business to acquire its brand name. The firm will also incur a total cost of CHF 167147.26 on freight costs, rent expenses, alarm installation costs, monitoring fees, website designer costs, market study costs, packaging and shipping costs, salaries, loan interest, salary, and salary and delivery costs. The venture incurs costs in acquiring all the necessary items and services that assist the operation of the business.
Incomes
Income from tangible and intangible property is included in business income if the taxpayer’s usual trade or business operations entail the property’s purchase, management, and disposal. Business income is. The venture is expected to earn a profit after tax of CHF 391832.32 at the end of the first year. Felix needs to identify ways of generating more income to ensure the effective and efficient running of the business. Felix can use the following ways to generate more revenue; he needs to increase revenue by cutting expenses.
The information is represented in the income statement prepared below.
Note: All Transactions in Swiss Francois where all XPF amounts were converted to CHF. The exchange rate was 1 XPF= 0.0082CHF.
Balance Sheet at the End of the First Year
A balance sheet is a specific financial statement showing how a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity are related at a specific time (Carpenter, Quinn, & Boote, 2018). This financial statement will assist Felix in understanding the venture’s financial situation.
Assets
It is a resource with the economic worth that a company holds or manages in the hope that it will be beneficial in the future. The business plans to acquire assets to help its day-to-day operations benefit the company by realizing a future profit (Langley, 2020). Felix plans to use CHF 19,954.00 to acquire a website designer, racking and safe, alarm system, drill and jig, silver chains, and clasps to generate the venture’s revenue.
Liabilities
The venture’s liabilities are an enforceable debt to another individual or organization (Kevorkova, Petrov, & Savina, 2019). Felix plans to borrow a bank loan of CHF 75,000 for the business start-up. He will also buy pearls on credit at CHF 9,720 to acquire the stock for starting a business.
Capital
Ventures capital is money on hand to cover its ongoing expenses and potential expansion. Felix will also use the retirement amount of CHF 900,000 as capital for starting its new venture.
The venture balance sheet is illustrated as shown:
Note: All Transactions in Swiss Francois where all XPF amounts were converted to CHF. The exchange rate was 1 XPF= 0.0082CHF.
Cash Flows for The First Year of Study
The cash flow statement outlines the sources and uses of money coming in and going out of Felix Venture. It lists the reasons for variations in a Venture cash position (Trejo & Bruhin, 2021). The cash flow statement will show the cash Felix Venture will generate in terms of operating, financing, and investing activities.
Operating Activities
This involves the activities under venture that will help Felix to generate revenue. A firm’s operating activities indicate the ability of Felix’s venture to generate sufficient funds to run its operations (Hayek, 2018). Net cash from operating activities was CHF 1,843.67. These are the funds that Felix Venture will employ to run its activities.
Investing Activities
These are all the activities that Felix’s venture will involve in acquiring and disposing of its asses. It shows how much generated revenue meets the expenditure (Bajra & Cadez, 2018). The net cash from operating activities will be -2,880 CHF. This implies that a new venture cannot meet its expenditure in the first year. This is because starting a business incurs more costs that the generated revenue cannot meet.
Financing Activities
These are the activities that will lead to an increase in the size and composition of the venture. The firm borrowed money that will be used to expand its size and structure. The net cash from investing activities was -79500 CHF. This implies that the company had no plans or has yet to lay investing plans. The cash flow financial statements are shown below.
Felix Monthly Cash Flow Statement
For the First Year of Operation
Note: All Transactions in Swiss Francois where all XPF amounts were converted to CHF. The exchange rate was 1 XPF= 0.0082CHF.
Annual Cash Flow For further years of operations
Note: All Transactions in Swiss Francois where all XPF amounts were converted to CHF. The exchange rate was 1 XPF= 0.0082CHF.
Break-Even Analysis
Using a break-even analysis, a Felix business can estimate when a new venture, product, or service will become profitable. It is a mathematical formula to determine how many goods or services a business must sell to at least pay its manufacturing costs (Langfield, Thorne, & Hilton, 2018). For instance, a break-even analysis could assist Felix in figuring out how many Orehana Pearls he needs to sell to cover the cost of storage or how many service hours he will need to charge to cover the cost of the office space (Weygandt, Kimmel, & Kieso, 2018). Anything Felix sells above his break-even mark will increase his venture’s earnings. Felix needs to know his fixed and variable costs to comprehend break-even calculations for his new business; fixed costs are fixed regardless of how much the business sells, while variable costs change according to production or sales volume.
Table 2: New Venture Total Fixed Cost
Note: All Transactions in Swiss Francois
Table 3: New Venture Total Variable Cost
Note: All Transactions in Swiss Francois
To determine the break-even analysis of Felix Venture, the following formula was used;
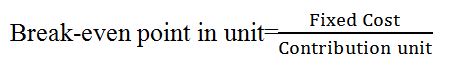
Contribution= selling price- variable cost
Contribution=270-203.49=66.51
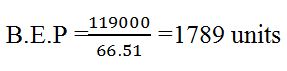

B.E. P= 1789 X 270 =483,085 CHF
The analysis results imply that Felix’s venture has to sell above 1789 units to realize a profit. Otherwise, it will incur losses.

The results from this break-even analysis imply that for the venture to attain its target profit of CHF 384044.32, it has to sell more than 503 044 units.
Conclusion and Recommendations
From the analysis of all the available information and financial statements, it is clear that Felix has the means necessary to launch a new business venture because he received a retirement fund as payment for the work, he completed for the chocolate company. He has also laid plans on accessing funds such as bank borrowing. Felix has also laid ways of acquiring all the requirements to start their new business venture, including renting a place to operate his business. Consequently, he is entitled to make investments and start a new firm.
Critical Reflection
From the analysis of all the relevant information and financial statements, Felix should start the new venture as there are high chances of the venture being profitable. Felix should ensure enough pearls are available in his store to satisfy his customers’ demand, which will increase over time. Felix should ensure the availability of funds that will enable him to cater to all the required costs to avoid the venture’s collapse at any given time (Hayek, 2018). He should ensure a rapid increase in sales to maximize its profits. He should also focus on cutting costs and increasing revenues.
References
Bajra, U., & Cadez, S. (2018). Audit committees and financial reporting quality: The 8th EU company law directive perspective. Economic Systems, 42(1), 151-163.
Belz, F. M., & Binder, J. K. (2017). Sustainable entrepreneurship: A convergent process model. Business Strategy and the Environment, 26(1), 1–17. Web.
Carpenter, S., Ihrig, J., Klee, E., Quinn, D., & Boote, A. (2018). The Federal Reserve’s balance sheet and earnings: a primer and projections. International Journal of Central Banking. Web.
Chudziak, S. (2022). The sources of economic growth, structural consistency of agent-based models, and mental-accounting consumer behavior. Structural Consistency of Agent-Based Models and Mental-Accounting. Consumer Behavior. 28(3), 61–67. Web.
Daulay, R., & Saputra, R. (2019). Analysis of customer relationship management and marketing strategies against competitive advantage on the company’s distributor. In Medan City. Web.
Ferrell, O. C., Hartline, M., & Hochstein, B. W. (2021). Marketing strategy. Cengage Learning. Web.
Gagnon, J., Raskin, M., Remache, J., & Sack, B. (2018). The financial market effects of the Federal Reserve’s large-scale asset purchases. 24th issue (Mar 2011) of the International. Web.
Gottschalk, P., & Tcherni-Buzzeo, M. (2017). Reasons for gaps in crime reporting: The case of white-collar criminals investigated by private fraud examiners in Norway. Deviant Behavior, 38(3),267-281. Web.
Greene, F. J., & Hopp, C. (2017). Are formal planners more likely to achieve new venture viability? A counterfactual model and analysis. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 11(1), 36–60. Web.
Hayek, M. A. (2018). The relationship between sales revenue and net profit with net cash flows from operating activities in Jordanian industrial joint stock companies. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 8(3), 149–162. Web.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (2019). Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs, and ownership structure. In Corporate Governance (pp. 77-132). Gower. Web.
Kevorkova, Z. A., Petrov, A. M., & Savina, N. V. (2019). Towards liabilities of corporate systems. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 10(2), 1582-1593. Web.
Kieso, D. E., Weygandt, J. J., Warfield, T. D., Wiecek, I. M., & McConomy, B. J. (2019). Intermediate Accounting, Volume 2. John Wiley & Sons. Web.
Langfield-Smith, K., Thorne, H., & Hilton, R. W. (2018). Management accounting: Information for creating and managing value. Sydney: McGraw-Hill Education. Web.
Langley, P. (2020). Assets and amortization in financialized capitalism. Review of International Political Economy, 28(2), 382–393. Web.
Lerner, J., & Nanda, R. (2020). Venture capital’s role in financing innovation: What we know and how much we still need to learn. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 34(3), 237-61.
Linden, A., Mathur, M. B., & VanderWeele, T. J. (2020). Conducting sensitivity analysis for unmeasured confounding in observational studies using E-values: the value package. The Stata Journal, 20(1), 162-175.
McLaney, E., & Atrill, P. (2020). Accounting and Finance: An Introduction with MyLab Accounting (10 ed.). Pearson. Web.
Miller, P., & O’Leary, T. (2019). Accounting and the construction of the governable person. In Management Control Theory (pp. 411–442). Routledge. Web.
Morano, P., & Tajani, F. (2017). The break-even analysis applied to urban renewal investments: A model to evaluate the share of social housing financially sustainable for private investors. Habitat International, 59, 10-20. Web.
Phillips, R. L. (2021). Pricing and revenue optimization. In pricing and revenue optimization. Stanford University Press. Web.
Russell, Milne, & Dey. (2017). Accounts of nature and the nature of accounts: Critical reflections on environmental accounting and propositions for ecologically informed accounting. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal. Web.
Schroeder, Clark, & Cathey. (2022). Financial accounting theory and analysis: Text and cases. Web.
Sudiyatno, Puspitasari, & Sudarsi. (2019). Working capital, firm performance, and firm value: An empirical study in the manufacturing industry on Indonesia stock exchange. Economics World. 444-450.
Tchamyou, V. S. (2017). The role of knowledge economy in African Business. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 8(4), 1189–1228. Web.
Trejo-Pech, C. J., Bruhin, J., Boyer, C. N., & Smith, S. A. (2021). Profitability, risk, and cash flow deficit for beginning cow-calf producers. Agricultural Finance Review.
Trpeska, M., Atanasovski, A., & Lazarevska, Z. B. (2017). The relevance of financial information and contents of the new audit report for lending decisions of commercial banks. Accounting and Management Information Systems, 16(4), 455-471. Web.
Voinea, C. L., Logger, M., Rauf, F., & Roijakkers, N. (2019). Drivers for sustainable business models in start-ups: Multiple case studies. Sustainability, 11(24), 6884. Web.
Well, J. (2022). Financial statement analysis. In Evaluating Corporate Financial Performance (pp. 131-212). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Weygandt, J. J., Kimmel, P. D., & Kieso, D. E. (2018). Financial accounting with international financial reporting standards. John Wiley & Sons. Web.
Williams, C. C., Martinez–Perez, A., & Kedir, A. M. (2017). Informal entrepreneurship in developing economies: The impacts of starting up unregistered on firm performance. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 41(5), 773-799. Web.
Zhang, J. H. (2017). Accounting comparability, audit effort, and audit outcomes. Contemporary Accounting Research, 35(1), 245–276. Web.