Leadership – What is It?
- Influence on people, so that they feel the desire to achieve personal and team goals (Koontz & O’Donnell, 1976).
- Desire to work to achieve a positive aim, satisfy personal ambitions, and try to prove professionalism.
- The exercise of authority aimed at the development and improvement of personal and interpersonal relationships (Shafritz, Russell, & Borick, 2015).
Striving for competent leadership helps a worker not only to achieve high labor efficiency but also to establish good relations in the team. Training team management skills is quite an effective technique of self-development.
- The ability to motivate people to do what managers want for the company’s better work.
- Formal or informal leadership helps people to disclose their working potential and self-develop.
- The ability to adapt to any working conditions and to inspire colleagues by personal example.
There are two main stages of leadership: internal and external. At the first stage, a person assumes responsibility and keeps the situation under control. During the second stage, a leader takes the initiative in particular situations. Gradually, moving from simple to complex, a person can develop leadership qualities and improve his or her working effectiveness.


Qualities of an Effective Leader
- Vision. A real leader knows how to lead.
- Motivation. A leader can stimulate the team.
- High sensitivity. An effective leader is attentive and is able to react to changes quickly.
- Flexibility. A leader has different strategies of behavior and can find an approach to everybody, while performing a productive work (O’Leary, 2013).
In general, it is difficult to predict how good a leading person will be only on the basis of personality traits. Therefore, over time, researchers have become inclined to the view that it is not enough to mention solely personal characteristics. It is necessary to take into account the situation in which these features are manifested.

Types of Leadership Styles
- Team approach. A modern manager is able to adapt to competitive environment (Shafritz et al., 2015).
- Laissez-faire approach. A leader is characterized by a laissez-faire orientation, democracy (Shafritz et al., 2015).
- Benevolent approach. A leader is broad-minded and kind, he or she considers a team’s wishes.
- Autocratic approach. A leader has unlimited power.
Successful ownership of these leadership styles ensures a quality and effective work. Compliance with corporate behavior is another essential condition for a good manager. The active participation of a leader in the work of a company motivates the rest of employees to more productive activities and self-development.

Correlation of Organizational Performance with Leadership Styles
- Effective introduction of different styles of leadership positively influences a certain company’s performance.
- Attempts to use different styles of leadership ensure a constant personal and career growth.
- Participation in the life of the team excludes possible dissent and encourages employees to engage in dialogues and discussions (O’Leary, 2013).
The existence of several types of leadership styles gives managers the opportunity to use different methods for their work and implement certain techniques. An effective leader is someone who is able to be flexible and can apply any type of behavior in practice. Any form of non-compliance with these types can prevent a successful work and affect the authority of a leader.

How Important is a Leader?
- Every person, as a rule, has leadership potential; however, not everyone develops it properly enough.
- The manifestation of leadership qualities motivates also other employees who are less creative and hard-working.
- An independent coordinator regardless of gender and race can increase the profit of a certain company and support the least developed departments (Stivers, 2002).
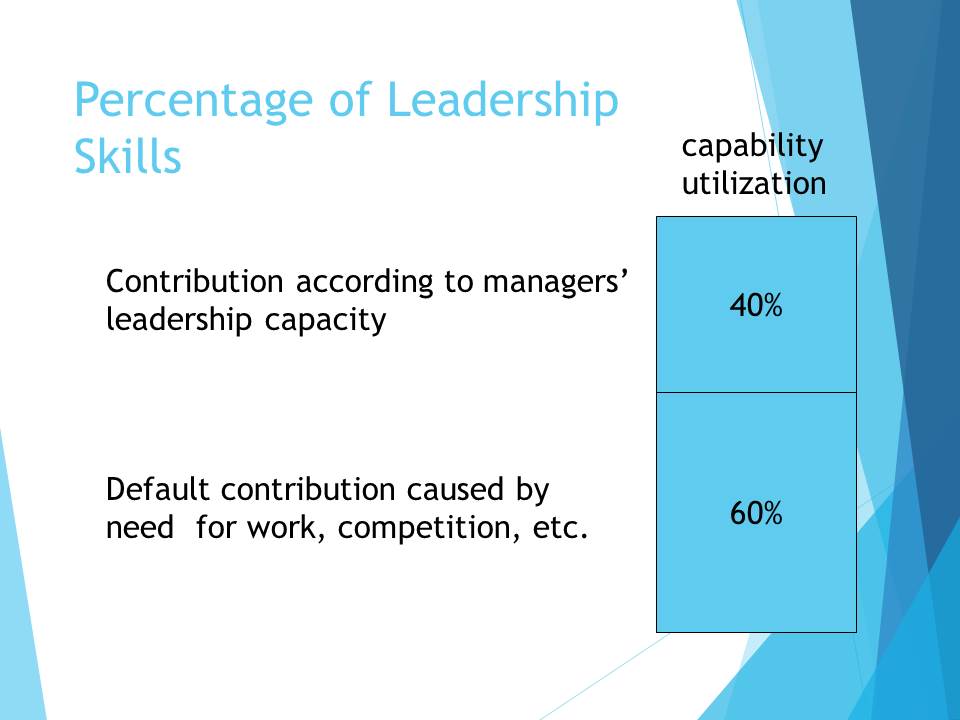
As a rule, employees perform about 60% of their working potential without leadership manifestation. Thus, the remaining 40% can be used if management is reasonable. In order to develop specific skills and properties, it is worth paying attention to the basic styles of leadership, the image of the behavior of a successful manager, as well as advice and recommendations of specialists.

Percentage of Leadership Skills
capability utilization
Contribution according to managers’ leadership capacity 40%
Default contribution caused by need for work, competition, etc. 60%
Two dimensions of management
Economic or productivity-based dimension of management:
- concern for production and company’s profits;
- the creation of an effective management apparatus.
Employee status and ethical dimension of management:
- concern for personnel and their successful work;
- maintenance of a favorable microclimate in a team.
The emphasis of a leader’s work is usually done on one of the two above-mentioned dimensions. If a person is able to apply both approaches correctly, it means that his or her leadership skills are at a rather high level. Using these techniques allows establishing an effective work and, at the same time, feeling the favor of all the members of a team.

Possible Dimensions of Management
Initiating structure for independent search for solutions:
- attempts to implement new constructive ideas;
- the desire to develop and learn independently.
Consideration, which means following the team’s ideas:
- teamwork by solving a common problem;
- group work to improve the microclimate.
The initiative of leaders is often successful as a professionally trained person usually offers rather constructive ways of solving certain tasks (Shafritz et al., 2015). It is also not superfluous to take into account the opinions of other competent employees. The concept of “brainstorming” has spread in many large enterprises. The general solution of a problem makes it possible to rally the collective.

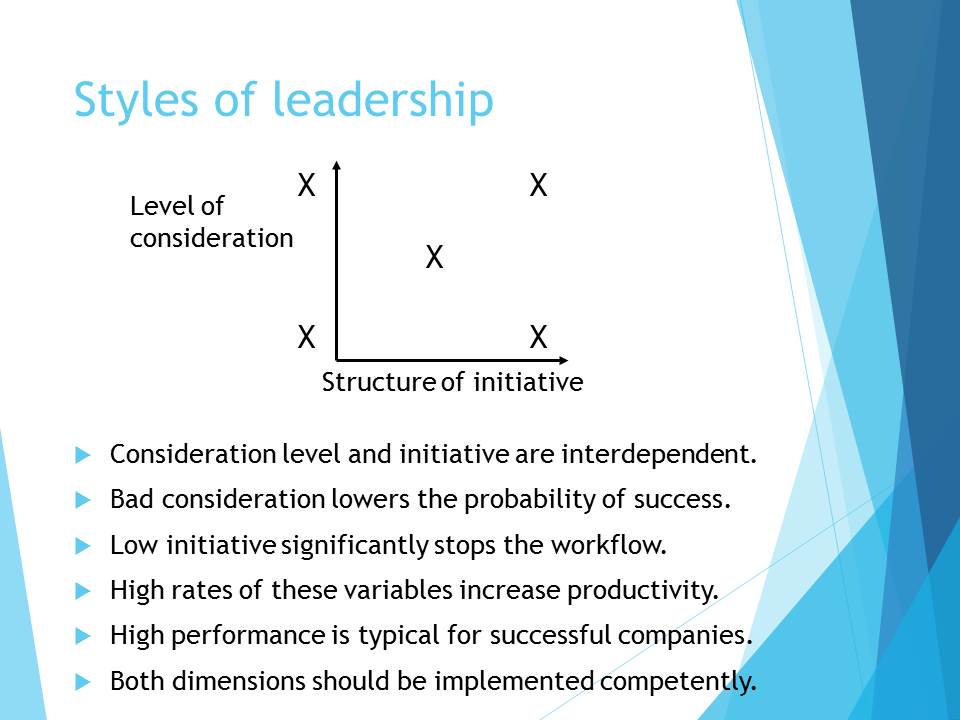
Styles of leadership
- Consideration level and initiative are interdependent.
- Bad consideration lowers the probability of success.
- Low initiative significantly stops the workflow.
- High rates of these variables increase productivity.
- High performance is typical for successful companies.
- Both dimensions should be implemented competently.
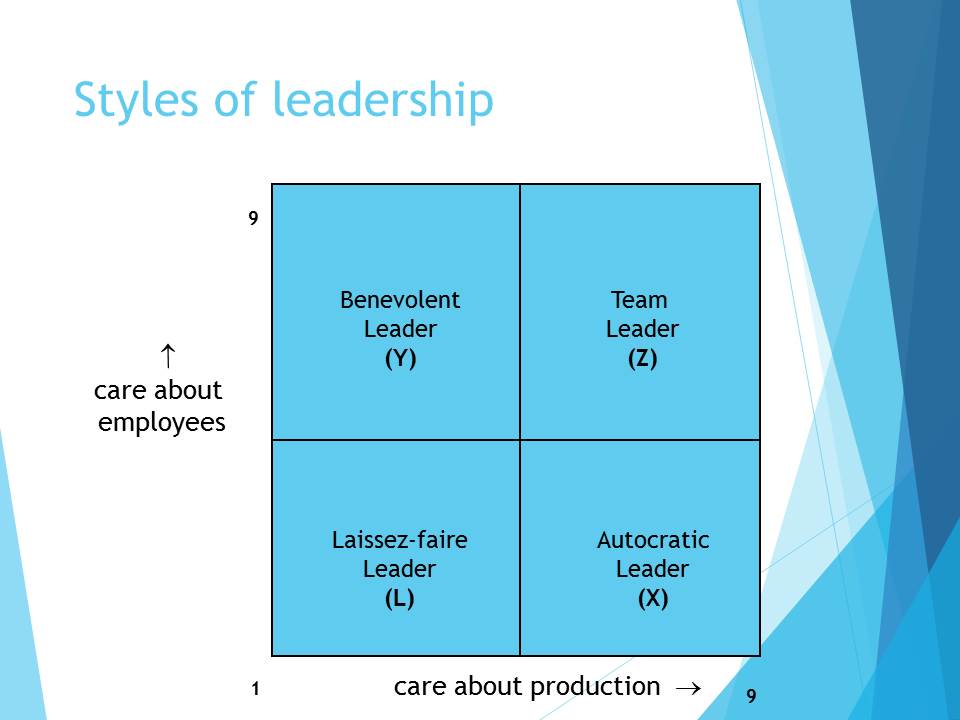
Theory “L”: Laissez-faire Leader
- Uninvolved and rather an indifferent person.
- Sees the primary role as just informer.
- Lets other employees make important decisions.
- Removes responsibility from performers or groups.
- Tries to avoid taking part in teamwork.
- Gives quite much freedom to subordinates.
This type of leadership is characterized by a poor participation in the work of the team. Such manager, as a rule, is very indifferent to specific problems and does not think seriously about his or her role in the collective. The influence on workers is too weak due to the lack of interest.

Theory “X”: Autocratic leader
- Lacks flexibility and loyalty to subordinates.
- Controlling and demanding type of a leader.
- Quite outdated “carrot and stick” approach.
- Concentrated exclusively on efficiency and results.
- Aimed at achieving goals by any means.
- Forgets about the needs of employees.
An autocratic type of leadership is a rather outdated and unclaimed model of behavior today. In the modern world, other management styles are more effective. This type is quite often associated with rudeness, which is completely unacceptable by the rules of corporate ethics. Attempts to establish good relationships in are unlikely to succeed.

Theory “Y”: Benevolent Leader
- People-oriented and too encouraging approach.
- Organizes work around people and trust them.
- Can be paternalistic and sometimes non-professional.
- “Country-club” atmosphere: non-competitive environment.
- Constant encouragement even for minor achievements.
- Lacks any form of personal initiative.
This type of behavior is characterized by a too friendly environment. The emphasis is not on achieving better results but on preserving current. Much attention is paid to the collective; however, this style of leadership does not foresee strict control over the work of team members.

Theory “Z”: Team leader
- Balances effective production and personnel issues.
- Creates an ambitious team of initiative employees.
- Team approach: involves subordinates into work.
- Organization serves to implement plans jointly.
- Can adapt to a competitive environment.
- Creates the atmosphere of interpersonal support.
The effectiveness of this type of leadership is due to several positive characteristics. Thus, it is the ability to work in a team competently, monitor the current results of employees, and set clear goals. This method of control allows adapting to almost any situation. As a rule, no complaints from the authorities and colleagues occur.

Results of Leadership Styles
Theory L: “missing management” and indifference:
- Significantly low productivity of employees.
Theory X: “wants to know nothing.”:
- Job stress, low satisfaction, unions form.
Theory Y: “country club” with constant encouragement:
- Low achievements, constant encouragements of workers.
Theory Z: “good manager” with a clear strategy:
- High productivity, cooperation, employee commitment.
All the four leadership styles have some distinctive and specific features. Some of these styles have rather serious weaknesses that can negatively affect the capacity of the team and the final results. According to the types presented, it is possible to conclude which of them is the most effective from the point of view of productivity.

Which Style of Leadership Works Best?
- Team Leader (Z) is the most effective style.
- Helps to adapt to modern changing conditions.
- Concern for the team and its success (Shafritz et al., 2015).
- Balances between too soft and tough approach (O’Leary, 2013).
- Certain situations may require using other styles.
- Covers both production and personal sphere of work.
- Compliance with some standards for successful implementation.
In accordance with the analyzed types of leadership, the most effective and acceptable is the team style. This variant of professional behavior consists in adherence to the company’s interests, but leaves an employee the opportunity to self-develop independently and take a personal initiative.

Origins of Leadership. Are Leaders Born or Made?
- Both personal qualities and environmental factors influence.
- Leadership does not depend on sex or race (Stivers, 2002).
- Training of special skills is significantly important.
- Following specialists’ advice allows developing necessary skills.
- Management is power; leadership is trust (Shafritz et al., 2015).
- Lifestyle influences the manifestation of leadership qualities.
- Awareness of the team importance increases productivity.
The development of leadership qualities is promoted by both personal initiative and environment. Training of proper skills is impossible without necessary knowledge. It is important to realize that the collective is a cohesive team, and then it will be easier to develop the qualities of the leader.

My Personal Type of Leader
If I had a chance to choose, I would definitely try to adhere a team-leader type. In my opinion, this style of leadership is the most effective today of all the other types; it has all the features that are significantly necessary for successful work. The most prominent merits of teamwork leadership, as for me, are:
- The opportunity to participate in the collective’s life.
- The ability to grow rapidly in career.
- Teamwork training increases credibility among colleagues.
- This style is suitable for any business.
- Constant creative growth is an indispensable condition.
- Tight communication with people is always interesting.
Perhaps, this type of leadership is the best from different points of view. Both a manager and an employee could benefit from it, and the key moment is to try to develop necessary skills for gaining certain features and traits.

Summary
- Team leadership is the most effective type.
- Theory “Z” environment is usually competitive.
- Other styles of leadership are not successful enough.
- Training is the best for self-development.
- Changing a type requires taking efforts.
- Initiative is important for achieving good results.
Thus, the most effective style of leadership is teamwork. The development of certain skills allows gaining respect and trust in the team, as well as establishing contact with subordinates and colleagues. The competent distribution of responsibilities and moderate encouragement are integral components of successful management. The opportunity of career and personal growth depends on the desire of an employee.

References
Koontz, H., & O’Donnell, C. (1976). Management: A system of contingency analysis of managerial functions. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
O’Leary, R. (2013). The ethics of dissent: Managing in guerrilla government (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Shafritz, J. M., Russell, E. W., & Borick, C. (2015). Introducing public administration (8th ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Stivers, C. (2002). Gender images in public administration: Legitimacy and the administrative state (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.