Iteration Structure
The offered programming solution for the library reference system is required for proper data analysis and search. End-users input the initial search data, while the search engine offers the most suitable variants, that coincide with the initial request. The iterating part of the program code involves the data analysis part, as data matching part of the code will be repeated for several hundred times until the entire data base is scanned.
Programming Solution
The offered solution for data analysis and search may be regarded as the basic technology for the referencing system. However, this does not involve the opportunity of search result restriction, or advanced search.
Setting of the search parameters part will stay the same, while the search part requires cycling. Therefore, the entire data base should be divided into interconnected blocks in alphabetic and research sphere order. When the search parameters are set, the program starts searching.
- object item;
- item = author;
- item = publishing;
- item = title;
- item = year;
- Item = key word
- if key word = sphere block;
- then start from this block;
- else read the first letter of the author or title;
- start searching from the corresponding block;
for (search cycle)
{
search item.position;
add to output results;
}
Block +1 (start scanning the next block)
Repeat search cycle
Therefore, the “Sphere” data blocks will be assigned with numbers, and alphabetic blocks – with letters (alphabetic blocks will be divided into two categories – Author and Title. So any book will be belonging to at least two blocks, and more, if there are two or more authors. The system reminds a data base table, so any duplicates will exist). The search parameters will define the blocking structure, and the search cycle will scan all the blocks continuously, starting from the adjusted.
The search request is:
- Stephen Covey. Seven Habits of Highly Effective People.
- Keyword: Psychology
- The program reads the keyword, and finds the corresponding block.
- The search structure is defined (sphere blocks);
- Then, it starts searching author, and title;
- If there is a misprint in a title, the system will find all the books by this author.
If the keyword is not stated, or given improperly (i.e. there is no such sphere in the referencing system, but popular psychology instead). Then, system reads the first letter of the surname, and starts searching in C block. All the matching results are added to output. If author is not stated, the system will start searching in S block.
Scanning other blocks will be needed for searching similar titles of the book; however, they will be added after the results from the initial block. This will add relevance to the search results.
Flowchart
The offered flowchart gives the representation of the basic algorithm of the presented code. This defines the key steps of the search algorithm. (Blank and Barnes, 1998)
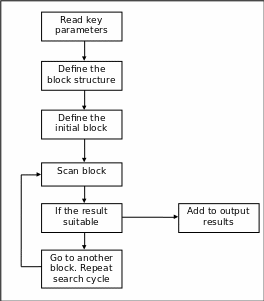
The modules of the flowchart are helpful for imagining the basic outline of the entire search algorithm, as well as for defining the key tasks for the system. The key advantages of such an approach are linked with the opportunity of modular solution of the problem, while each module defines the particular set of tasks for more effective problem solving. (Sidky, Sud, et.al. 2002)
Reference List
Blank, G., & Barnes, R. (1998).The Universal Machine, Boston, MA: WCB/McGraw-Hill.
Sidky, A.S., Sud, R.R., Bhatia, S. & Arthur, J.D. n.d.(2002)Problem Identification and Decomposition within the Requirements Generation Process. Web.