Many scholars agree that the behaviour of business people affects their businesses. Recently, it was realized that there are other factors that also shape a business. Some of those factors include the culture of the society, the type of businesses that hold the economy of the country and the quality of goods and services in the country. It suffices to mention that scholars have also argued that there are several factors that contribute to the decline of a country’s economy, thus affecting its businesses. This essay summarizes the book called “Limits to Growth: The 30-Year Update” by Donella Meadows, Jorgen Randers and Dennis Meadows, which highlights several factors that limit the growth of businesses. The concepts explained in the book can also be applied to world economies. The essay includes a discussion on sustainability, while tying the definition to success in companies and world economies.
Summary
The book, “Limits to Growth: The 30-Year Update” by Donella Meadows, Jorgen Randers and Dennis Meadows is the third book in the series. The book focuses on an analysis and summary of data collected over forty-five years. In particular, the data collected revolves around current policies that can affect world economy in both positive and negative ways. The authors also pay attention to some of the things that can be done to ensure that the economy provides for all.
One of the major arguments proposed by the authors is that technology has affected the economy by both improving it, and making it worse. The authors argue that whereas technology has made life much easier and given people a lot of ways to make money and boost their countries economy, it has also made life expensive. Other scholars including Liu and Xie (2013) support this premise. Meadows, Randers and Meadows explain that a major concern when discussing the economy and technology is the growing costs of exploiting natural resources. They explain that many centuries back, it was very difficult for people to exploit all that the earth has to offer, especially with regards to minerals. This changed with the inception of technology.
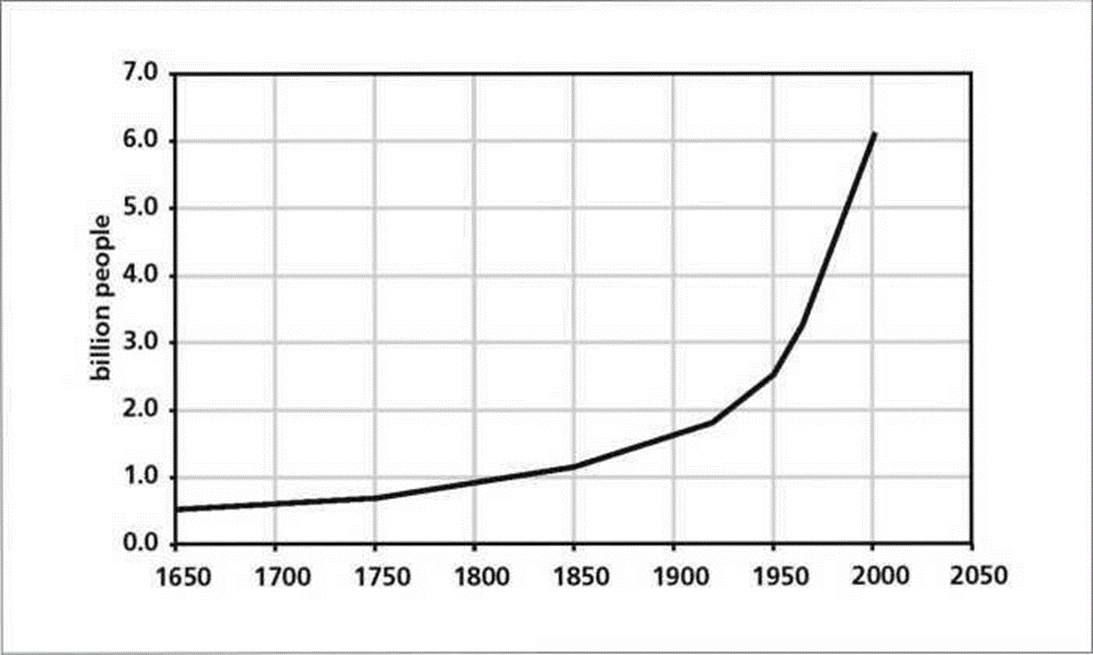
People were not only able to reach the deepest part of the earth in search of natural resources like oil and minerals but they were also able to convert them into things that could be used in trade. Technology also allowed people to create minerals and other resources from the natural things they could attain from the earth. However, in the same breath, technology also made acquiring these things very difficult. Currently, even the most basic things that nurture life are not affordable to half the world’s population. Things like milk and water are sold to the public, yet they can be found naturally. The main reason behind this is the fact that technology has been used to deplete the natural resources such that they are currently very little. Take for example the destruction of trees to make houses, papers and many other products. The destruction of the trees destroys the natural habitat for cows and other animals that provide food to man. The table below shows just how far humanity has ridden natural resources.
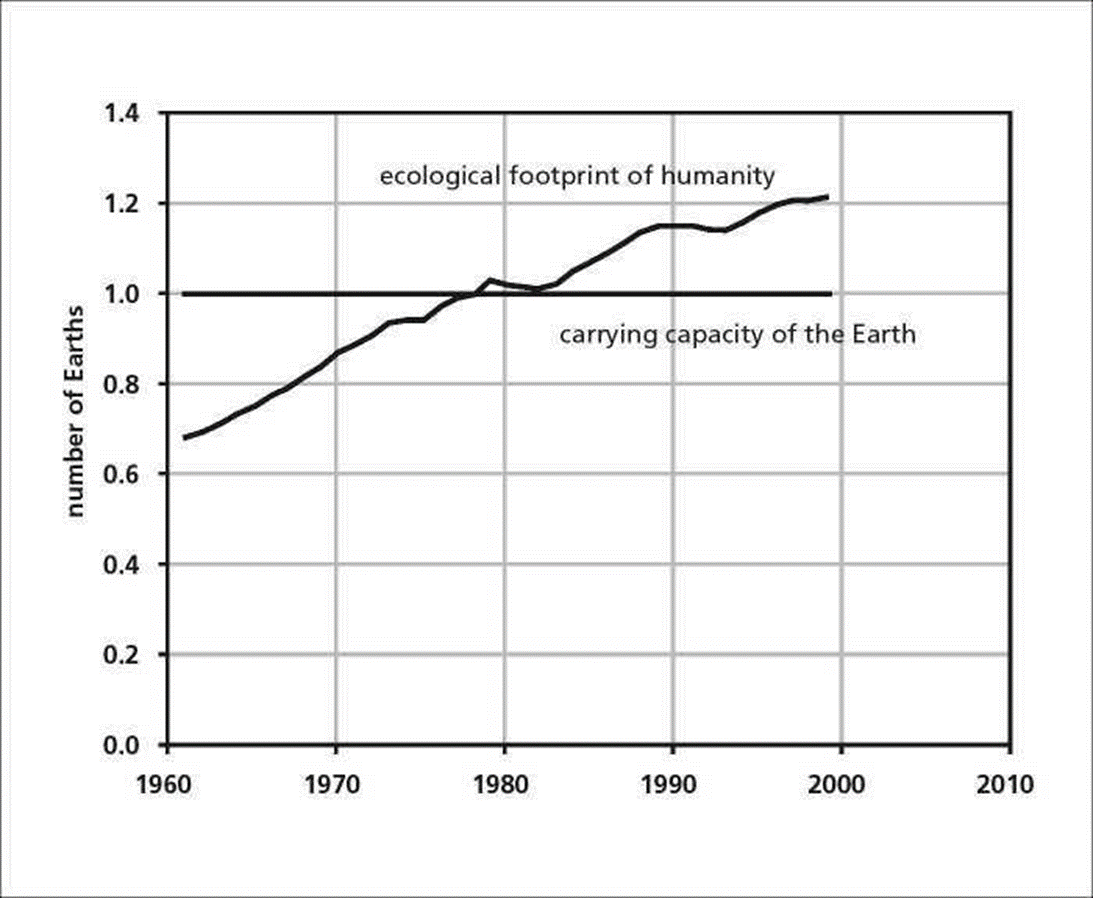
The ever increasing population of mankind does not help the situation. Putting all this together, one will notice that all odds are against nature. The population clears out land to make room for houses, schools and other things while at the same time reducing space for the cattle to feed. In turn, the cows reduce in number making milk a luxury, and also making it good for business. Many scholars have rightly argued that milk that is sold in supermarkets has added chemicals and water due to its scarcity and high demand. The graph below shows the rising human population.
Additionally, Meadows, Randers and Meadows also add that businesses fail not only because of technology and depletion of resources, but also because of overshooting. They explain that overshooting is simple the act of going too far or beyond limits. In many business classes and books, people are told that businesses are all about risks. However, according to the authors there are businesses that go too far unintentionally. When not planned for, risk can be life changing; in a negative way. This then leads to over-shooting. The scholars give the example of rising up from a chair too fast and one feels dizzy and disoriented. Businesses that overshoot also go through the same process. They became ‘dizzy’ and cannot really control what they want to do, and how they want to do it. In addition to this such companies and businesses also lack plans on how to deal with the sudden rise, therefore, leading to their failure. As many have quoted, becoming number one is very easy compared to remaining number one. It is crucial that businesses do not rise too fast, and without plan, so that they can remain at the top.
In regards to world industrial growth, the scholars assert that the definition of money determines industrial growth. They agree that there is a difference between what people believe money is and what money actually stands for. In particular, the scholars emphasize on the importance of physical economy. This is defined as the real things that money stands for. For instance, machines in the industry and so forth. These machines can be perceived to be money because they were bought and can be sold. The physical economy is heavily affected by technology, thus, can make or break a company. With this in mind, the scholars argue that industrial output is also determined by the physical economy. Therefore, in order for businesses to succeed, they have to closely monitor their physical economy; invest in the right equipment and it will ensure that the business is successful.
Meadows, Randers and Meadows argue that growth is also affected by long term trends. Many business owners tend to follow each trend they come across. However, as the scholars explain, some of the trends conflict with one another. Thus, if a business is using trend A and then adopts trend B and they conflict, then the whole business will be affected, despite the successes already registered by trend A. They give the example of the world population. It is very evident that the population of mankind is rising. However, it is also very evident that birth rate is going down. People prefer getting less children than before with some opting not to have children at all. In addition to this, in third world countries, the child mortality rate is very high, with many dying at infant stage. It is thus, ironical that the population is getting bigger by the day.
In order to understand why this is so, it is crucial that people understand the death rate of adults. Due to technology and advanced healthcare, people are living way longer than expected. The young children that survive childhood, end up living longer than the given life expectancy span. The same can be applied to world economy and business. When two trends go against each other, it is crucial for the business to pick one common trend and use it, or to leave out one trend. For example, if one technology works best for meeting planning, a company will buy it. After the use of that specific software, one of the staff suggests different software claiming that it is better but upon installation, the software confuses each other. There are only two options in such a scenario, either the company removes one software, or they remain with both. Ignoring the problem and remaining with both will eminently lead to disaster. Therefore, it can be suggested that one software be removed. However, in the same breath, the company can decide to get better software that combines the advantages of the uninstalled software.
Meadows, Randers and Meadows argue that discipline is also very crucial for modellers and business owners. Many critics have also agreed with this premise. Lack of discipline in an organization’s executive, will ensure that the employees will also not be disciplined. In fact, as many scholars agree, discipline goes hand in hand with performance levels. For instance, rules and regulations that monitor and manage a country’s economy instil discipline in that economy. Another example that can be cited is that of working. Discipline allows an employee to come in to work at the specified time, unless there was an emergency. In the same breath, discipline also allows another employee of the same company to come in at whatever time he or she wants to, but to ensure that all his or her deadlines are met.
Managers might argue that the first person is more disciplined than the second person. However, when it comes to performance levels, they might both attain the same goals. It is crucial that economies not dictate the amount of hours, and the times necessary for people to work. For example, an economy that works only within the eight hours of normal day light suffers more compared to an economy where people work at times that are best suited for them. In such economies, one will find that people are more at ease and more productive. The authors conclude the book by stating that predictions of the future can make or break a company. A warning of the future can led to more problems because the future is unknown. Thus, business should thrive in the here and now, while at the same time embrace change so that they can survive the future.
What does Sustainability really mean?
Diaw and Lessoua (2013) define sustainability as strategies that employ the use of present resources in an amicable way to ensure that a valuable outcome is achieved in the long run. There are two aspects of sustainability that have to be considered. The first is the depletion of the resources and the second is the nurturing of resources.
As mentioned, one of the limits to growth discussed by Meadows, Randers and Meadows is depletion of natural resources. This goes hand in hand with the first aspect of sustainability mentioned. Marin, Navas-Alemán and Perez (2015) assert that for businesses to grow, they have to use resources. However, the constant use of resources leads to depletion. The example of an oil company can be used to explain further. Oil is a natural resource and has to be drilled from the ground. At times, the section where oil is pooled underground is under water. In addition to this, the equipment has to drill the oil several feet below the sea level. It, therefore, goes without saying that the equipment used to get the oil is very high technology and expensive. As the world population keeps rising, the use of oil keeps going up. This has made the commodity expensive and those selling it, some of the wealthiest people on earth. However, with the high demand come the reducing levels of the resource. In fact, many critics have argued that the fast depletion of oil resources will ensure that future generations will have to depend on synthesized oil, and not the real product. The table below shows how some world resources are being used.
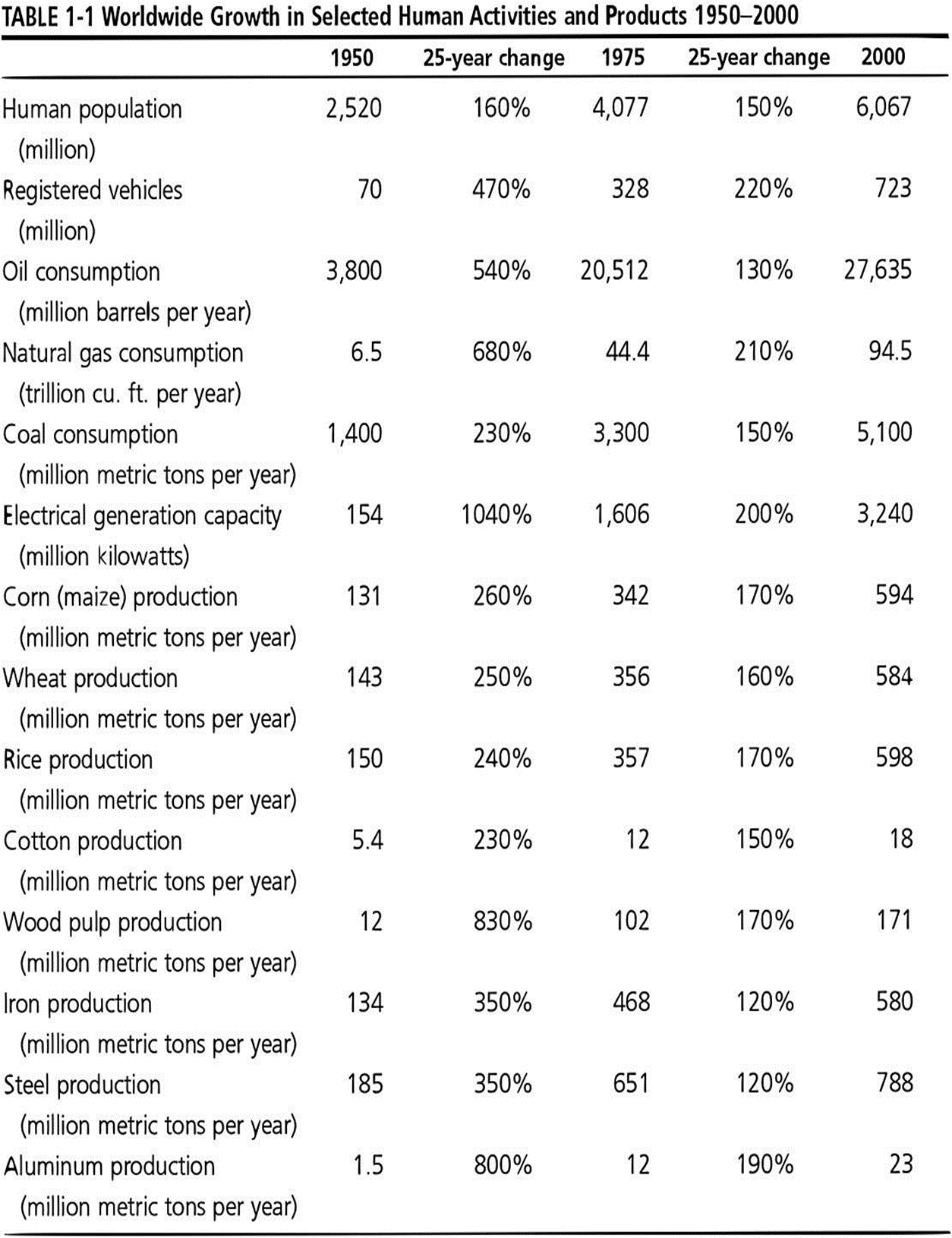
At this juncture, the example stated will be used to describe the two sustainability concepts mentioned. The first concept would encourage the continuous drilling of oil as long as it is used for a greater good. Indeed oil is drilled and used to make life easier. It is used in automobiles, at homes, in industries and even in luxurious places. Without oil, human kind would in fact be arguably miserable. World economy is heavily dependent on the trading of oil. In fact there are countries whose sole economy holder is oil. The Middle East and even Nigeria have been in war due to oil resources as it is very precious. The fact that it is business to some, and holds the economy of the world makes its use important. Therefore, it makes all the sense in the world for people to continue drilling oil, until they have exhausted the product.
On the contrary, the other component of sustainability states that present resources should be used but they should also be nurtured to ensure that they are not depleted. Using the same example, thus, it would be wrong for people to overuse the oil and not nurture it to produce more. A product like oil is very difficult to nurture, unlike trees. For trees, all people have to do is not cut them down, and grow more. However, despite the difficulty, it is not impossible to produce oil. As mentioned, the current overuse of oil will ensure that people in the future have to synthesize the product. The same can be done today, to ensure that the natural oil is only used when necessary. Technology can allow scientists to make oil in the lab. People should then be encouraged to use the manufactured oil instead of natural oil to allow it to pool up again.
Now that sustainability has been discussed, it is crucial to apply the concept to everyday business. All business people will agree that sustainability in business refers to the second component discussed. It refers to using while nurturing in order to get more. In such cases, therefore, the business has to ensure that they keep checking their resources. It does not matter whether these resources are natural occurring or not. For example, a company has to keep tabs on its use of money, use of time and the performance levels of its employees among other things to ensure that it is on the right track. Many a time, business people only focus on the money aspect of their business. In doing so, the other resources are left to wither, or rather deplete, while the money aspect is accounted for. It suffices to mention that ignoring one resource will eventually lead to the failure of the whole company.
In the same vein, businesses and the economy also have to nurture their resources. The example of a farmer can be cited to explain further. In order for the farmer to get good crop at the end of the season, he or she has to ensure that the farm is weeded properly, and that the plants are watered regularly. Additionally, the farmer also has to ensure that he or she puts fertilizer and sprays pesticides on the crops. Any simple mistake will ensure that disease catches the crops, leading to poor, if any, harvest. The nurturing process is crucial for companies, and its starts with the nurturing of the employees. The company has to shape its employees regardless of age, gender and seniority on what the company expects, and how it plans on getting things done. In addition, the company also needs to nurture a client base such that they are very loyal to the company. This can be done with good customer service, high quality products and good services. When a company observes all this, then going by the arguments raised by Meadows, Randers and Meadows, the company will be very successful.
It is crucial to point out that there are very many challenges to sustainability in business. Companies cannot miss challenges and having challenges does not mean that the company will not grow. In order to tap the best out of a challenge, the employees have to be equipped with the right skills. Critics have argued that the employees are the first investment of a company. Not only should the recruitment process have this in mind, but the company should be willing to invest more in the staff as they are the people who will ensure success. Training of the employees will ensure that they are not only sharp, but they are also still prioritizing the goals of the company, and their own goals. Thus, companies have to include employees in their sustainability discussions. In fact, as Kester, Moyer and Song (2015) observe, employees would be the best people to explain what is happening in a company. They also understand what has to be done to improve performance levels. In addition, company managers need to encourage their employees to give suggestions whenever they feel necessary. Suggestion boxes can be placed at several places and the employees can give their opinions unanimously.
What can businesses do to build strategies for Sustainability?
As mentioned, sustainability involves strategies and these strategies have to be developed by the company. Meadows, Randers and Meadows argue that strategies are best built within the organization and not outside. Even though business owners outsource companies to develop strategies for them, it is crucial that the outsourced understands everything about the company in question. For example, if the strategy to be developed is on communication, the company has to inform the consultants their organizational culture, and their communication strategy that is already in place and so forth. This section of the essay looks at the ways business people can build strategies for sustainability.
The first thing business people need to know when they are building strategies for sustainability is public policy. This goes hand in hand with sustainability. Every business has a target audience, whether it is individuals or the company. The company’s public policy will dictate how the company interacts with its clientele. Thus, it has to be designed well. Mudakkar et al. (2013) reveal that public policy should also include the things that are of value to the community targeted. For example currently, people are concerned about the environment. Thus, the public policy could also include ways the company conserves the environment. In the same breath, corporate social responsibility also falls in this section. CSR has been used by many corporates to improve public image. The activities highlighted under CSR help a company appear as genuine and caring over the environment and the society in general.
In order to build the right strategies for sustainability, business people also have to ensure that they have clear organizational structures. Kennedy and Tiede (2013) explain that organizational structures are definitions of activities in the organization. They include task allocation and even performance levels of employees. It is crucial for companies to have clear organizational structures as this in turn determines their goals. In defining company goals the company will also define how they want to achieve their goals, thus, directly giving a plan on sustainability strategy. It is also important that the organizational structures go hand in hand with sustainability. If not, then the structures have to be revised so that they support sustainability before the company can develop a sustainability strategy.
Organizational culture also has to be considered when developing a strategy for sustainability. Papyrakis (2011) argues that organizational culture affects how the company performs when ranked against other companies in similar field. It is so crucial that many companies have called in experts to develop proper culture. Like all other types of culture, organizational culture has to be learnt. This, therefore, means that the employees have to be taught organizational culture of the company they are working for. Schäfer (2014) argues that leadership changes in companies also affect organizational culture. In fact, when a new CEO is installed, possibilities of the organizational culture changing are very high. The new leader will come up with a different way of doing things regardless of whether the old way was working or not. Papyrakis (2011) argues that such transition should be well done to avoid difficulties later on. The employees have to be informed of the new changes, and even trained on what is now expected of them. So, why is this important for building strategies of sustainability? Change is good however it can at times limit growth.
It is up to the people in charge to also inform new management of the things the company believes will help with sustainability. In fact, company policy can be used to ensure that sustainability is the key agenda of every leader who comes into the company.
Business people also have to consider communication when developing strategies for sustainability. Schäfer (2014) explains that communication is at the core of sustainability. For any organization to be successful, it has to have a very well planned communication system. It is due to this exact reason that companies have opened up to using a flexible communication system. This flexible system allows people to communicate freely regardless of their status and age. In the same breath, Communication moves all ways and does not necessarily follow one channel. For example in a rigid communication system information and communication only flows from top down. This means that only the bosses give information while the juniors do not give any information. In a flexible system, both the executives and the junior staff give information. The biggest advantage of such a system is that information gets to the person intended quickly leading to quick action. In the same vein, junior staff has very good information that can help the company make more profits, and they can tell such information easily in a flexible communication system, compared to the rigid one.
There are many other things that business people have to consider when developing strategies for sustainability, however, the discussed are the most important. Papyrakis (2011) argues that the process of developing a strategy for sustainability can take a long time. Due to this, the company can be encouraged to start implementing obvious strategies as the process continues. Additionally, business people have been advised to always use their company vision, mission and values when developing strategies for sustainability.
Given that sustainability revolves around resources, it also touches on employees. As mentioned, employees are the biggest investment of a company. Sustainability should, therefore, not only aim at improving and growing the company, but also growing the employees. Schäfer (2014) argues that one mistake many employers make is assuming that the goals of the company are similar to the goals of individual employees. This could not be further from the truth. Different people work for different reasons. For some it is to pay their bills while for others it is to pass time, other people work to accumulate money and then go and do their own things and at the same time, there are those employees who work to learn and improve the company they work for. It is impossible for employers to know why their employees are working at the company and unfair for them to even ask. Thus, the sustainability strategy should be flexible enough to ensure that each employee grows in his or her way and expectations. Whereas many employers believe that doing everything possible to keep the employees in the company is best, others believe that employees should move on whenever they feel like it. New employees offer new perspectives and ideas that can actually help the company sustain itself, they should, therefore, not be hushed or looked down upon.
How to sustain economic growth in UAE that take into account every dimension – social, economic, cultural and environmental – of the environment in which a business operates
The economy of the United Arab Emirates is estimated to have a GDP of approximately US$570 billion as of 2013. The main industries of the country are petroleum, fishing, aluminium and cement among others. However, the country has been known to also encourage tourism and other similar trades. Toledo (2013) adds that the economy of UAE is the second largest in the Arab world after that of Saudi Arabia. The country has received a lot of praise due to its diversity. Many people would think that the country has only invested in petroleum and oil industries. However, as Al-mulali and CheSab (2011) reveal it is very diverse that oil based industries only take up 39% of the economy. It suffices to mention that one of the biggest cities in UAE, Dubai, suffered a financial crisis between 2007 and 2010. This in turn, affected the economy of the whole country. Dubai is well known as a tourist destination. Toledo (2013) argues that even though the country has focused on other things like tourism to boost their economy, the oil business still plays a big role. The country has taken oil drilling slow due to the depletion of the resource, but it still trades in oil. The diversification of the economy has been attributed to quick need to start investing in other things as the world oil reserves dry up. In every sense of the word, therefore, UAE is trying to sustain itself, even though it does not appear to have clear strategies for sustainability. This section of the essay will apply the factors mentioned by Meadows, Randers and Meadows to UAE economy while giving different ways the country can employ to sustain its economy. In determining the different ways the economy of the UAE can be sustained, it is crucial to look at the social, economic, cultural, and environmental aspects of the country.
Cultural
The UAE, just like other countries in the Arab world, is deeply rooted in Islamic culture. Everything is defined by their religion, including government and business policies. Thus, all the businesses that have taken up in the UAE have had to adhere to the people’s culture. So how can these businesses sustain the economy of the country using its culture?
Globalization has led to the interaction of different cultures from all over the world. However, one has to understand that even though globalization has integrated cultures countries still hold on to their specific cultures. Thus, when making strategies to penetrate markets in the UAE, business people have to have Islam in mind. Therefore, one way to maintain economic growth while still respecting the culture is to embrace the culture.
A second way to sustain growth in the region while still preserving the culture is to encourage the locals to invest in the country. The locals know their beliefs and values best. Thus, investing more in the region will ensure that business is done in an undisputed way. Such investments will also increase the GDP of the country, while at the same time support the individual cities. As mentioned, diversity has helped ensure that the country also focuses on other things apart from oil. For instance, Dubai has focused on tourism. Sustainability can be achieved if the locals are encouraged to invest in these other activities that also boost the economy. It suffices to mention that holding on to one’s culture does in no way negatively affect sustainability. However, such deep cultures should also embrace change. For example, in the case of Dubai, despite holding on the fundamentals of Islam, the government of Dubai agrees that women should not be treated differently from men such that they are not taken to school, or even allowed to work and vote. The government has made efforts to educate girls, and also given them jobs to show that men and women are not very different while at the same time keeping their culture and dealing with the issues of women and men separately.
Economic
Looking at the economic aspect of the country, it is clear that in a few years’ time, the country’s economy will drop. As mentioned, the core business in the UAE and other Arab countries is oil. Despite the efforts made by the UAE to pull out of the grasp of oil, its economy is still held by this particular trade. Toledo (2013) argues that the process of accepting other products as important in the economy has been painfully slow. Of the 71% of the economy, various products take up little percentages. This in turn makes oil the lead product of trade for the country. With the depletion of oil reserves all over the world, this grasp appears to be a curse more than a blessing.
When developing strategies, it is crucial to also include the other options that can be used in case the economy fails due to overdependence of oil. Toledo (2013) argues that when the economy of a country fails, many of the businesses will also be affected. However, even with a failed economy, there are some businesses that still make profit. Therefore, a business should have a strategy for sustainability through such crises. As mentioned, Dubai had a financial crisis from 2007 to 2010. The businesses that had no sustainability policy suffered the most during this time. This is because they could not find ways of surviving the economic hit. The good thing about economies is that they get back up, even if not to the position they were before. Dubai’s economy recovered, but it has a lot of debt. Due to this, taxation has gone up in order to repay the debt and this has in turn affected businesses because costs have also gone up.
All these factors have to be considered when making a sustainability policy. For the UAE, the businesses also have to consider the impact of their currency in future. Currently, the Dirham is performing quite well against the dollar. However, this has been attributed to the oil industry. With less reliance on oil, and depletion of the reserves, it is possible that the currency will get weaker if the government does not also attain a sustainability policy. In such a dire case, businesses that export things will get more losses than those that import.
Environmental
In regards to the environmental impacts, the country has been on the limelight for not taking care of its environment. Dubai is the only artificial city in the world. Toledo (2013) reveals that the city was built on top of water and that even the soil in the city was imported from other cities in the country. It is indeed incredible that such can be done. However, due to the constant drilling of oil, the country’s environment has been widely affected. The waters nearest to the UAE have also suffered from the negligence. Toledo (2013) argues that oil transportation nearest to the UAE has led to water pollution. In fact, there are tanks that transfer their oil to other tanks while still on water. This has led to oil spillage, which has affected many living things that leave closest to the waters of the UAE.
It is crucial for businesses in the UAE to also include policy on environment. This not only refers to the physical environment, but also the business environment. Al-mulali and CheSab (2011) are of the opinion that for some companies, the two types of environments can interlock. For example, in the printing industry, the physical environment goes hand in hand with the business environment. Trees are used to make paper, and it is this paper that is then used for printing. Therefore, with depletion of tress, there is also depletion of printing services. Initially, the depletion of trees will make printing services very expensive, and later on the industry will die completely. However, with a sustainability policy, a printing company will have measures on alternative things to use for printing when trees run out.
Since the UAE also relies on natural occurring resources, it is important for the country to have alternatives to ensure that when the environment shuts down on them, they can still move on. The strategy should give guidelines on what can and should be done when the country’s oil reserves are depleted.
Social
When discussing social issues in the UAE and business, it is tempting to state that social and cultural issues are the same. However, some differences can be used to make the perfect strategy. Toledo (2013) argues that the UAE has numerous other cultures within it. These cultures are smaller than the Islamic culture that is associated with the UAE, but they are very influential in the society. As mentioned, tourism is also very important to the UAE’s economy, especially for Dubai. When tourists visit the country, they affect the social makeup of its citizens. Citizens then borrow ideas from the visitors. Many have argued that it is through these interactions that Dubai saw it prudent to allow women to vote, and work unlike other cities in the country.
Additionally, when the UAE citizens visit other countries either as students or tourists, they are also affected by the behaviour of their guests and they in turn take the same behaviours home, and incorporate them into their culture. Therefore, the question here is how business in the UAE can use this to ensure that they sustain their businesses.
As mentioned globalization has made it easier for people to live and work in different countries from where they are originally from. Thus, such people will expect to get services that are very similar to what they are used to in their home countries. Businesses can incorporate this in order to survive. In the near future, the UAE will have more foreigners and its citizens will also have left for other countries to look for greener pastures. Businesses that have the needs of the foreigners in mind will, therefore, weather the storm, unlike those that will not.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are numerous factors that can limit the growth of a company or a country’s economy. Meadows, Randers and Meadows argue that the most crucial factor to consider is depletion of resources. Many economies all over the world depend on natural resources. However, with the rising population of mankind, such resources are being depleted by the day. This has, in turn, led to scarcity of products making those products that are available very expensive. In the same breath, technology can also be considered a limiting factor of growth if not well used. The concepts that have been explained by Meadows, Randers and Meadows can indeed be applied to world economies as well. A critical look into the economy of the UAE shows that they rely heavily on oil, a natural occurring product. Scholars have asserted that oil reserves are drying up due to constant drilling. Therefore, without a good sustainability policy, then countries like the UAE will be in problems once the oil reserves are completely dry.
References
Al-mulali, U., & Che Sab, C. B. (2011). The impact of oil prices on the real exchange rate of the dirham: a case study of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). OPEC Energy Review, 35(4), 384-399.
Diaw, D., & Lessoua, A. (2013). Natural resources exports, diversification and economic growth of CEMAC Countries: On the impact of trade with China. African Development Review, 25(2), 189-202.
Kennedy, R., & Tiede, L. (2013). Economic development assumptions and the elusive curse of oil. International Studies Quarterly, 57(4), 760-771.
Kester, J., Moyer, R., & Song, G. (2015). Down the line: Assessing the trajectory of energy policy research development. Policy Studies Journal, 43, S40-S55.
Liu, Y., & Xie, Y. (2013). Measuring the dragging effect of natural resources on economic growth: evidence from a space–time panel filter modeling in China. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 103(6), 1539-1551.
Marin, A., Navas-Alemán, L., & Perez, C. (2015). Natural resource industries as a platform for the development of knowledge intensive industries. Journal of Economic & Social Geography, 106(2), 154-168.
Meadows, D. H, Randers, J. & Meadows D. L (2004). Limits to growth: The 30-year update. Chelsea, UK: Green Publishing.
Mudakkar, S. R., Zaman, K., Khan, M. M., & Ahmad, M. (2013). Energy for economic growth, industrialization, environment and natural resources: Living with just enough. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 25, 580-595.
Papyrakis, E. (2011). Resource windfalls, innovation, and growth. Journal of Economic Policy Reform, 14(4), 301-312.
Schäfer, A. (2014). Technological change, population dynamics, and natural resource depletion. Mathematical Social Sciences, 71, 122-136.
Toledo, H. (2013). The political economy of emiratization in the UAE. Journal of Economic Studies, 40(1), 39-53.