Executive Summary
The United Arab Emirates constitutes a federation of states that were formed by the Trucial States immediately after Britain attained self-government. The commanders are in charge of appointing the chief minister and the cabinet. The relative political and financial factors among other elements that are influential within the country are directly reflected in the allocation of positions in the federal government. To lessen its reliance on natural gas and oil revenues, the country has undertaken measures to diversify the economy, especially by investing in tourism, telecommunication, aluminum production, and re-export commerce.
Introduction
The United Arab Emirates is a federation of seven independent states that are located near the southern edge of the Arabian Peninsula. Since the early 1960s, the UAE emerged from being insignificant, particularly in terms of global affairs, to becoming one among the wealthiest small countries around the globe (Young, 2014; Coleman, 2014). I have invested in the country because it has taken several measures to guarantee the adequate provision of high living standards, thanks to the advanced human resource skills among its citizens (O’Neill, Hodgson, & Mazrouei, 2015; Goby, 2015).
According to Aartun (2002), the UAE has had a developed diversified economic base with sophisticated and modern cities that are sufficiently equipped with advanced telecommunications, utilities, and electricity among others (Ahmed, & Zain, 2015).
This remarkable progress distinguishes the country from others. For instance, for a long time, the UAE government has demonstrated a special interest in nurturing its citizens and human capital (United Arab Emirates Country Review, 2011). The report provides a detailed political economy analysis of the UAE. After explaining what political economy entails, including its significance, the paper tabulates the UAE’s political, economic, and legal systems with the view of comparing their benefits, risks, and costs.
Political Economy Analysis
Political System
According to Young (2014), political economy refers to an interdisciplinary subject that revolves around a country’s money matters, political atmosphere, history, and legal environment among other disciplines that explain the significant role that political factors play in determining the economic outcomes of a certain country. A political system denotes the structure of politics and administration in a given country. This structure is weighed against a country’s legal framework, monetary system, cultural arrangement, and other public schemes. The UAE has adopted a political structure that recognizes the centralized, presidential, absolute kingdom as the three main political pillars.
Economic System
On the other hand, an economic structure refers to the means via which nations allocate capital and trade commodities and services. In the UAE, such systems dictate the five components of products that comprise employment, assets, entrepreneurs, material possessions, and information capital. Besides recording a 2014 GDP of $570 billion, the UAE has been productively expanding its financial systems.
Legal System
The legal framework denotes the formula or practices that a country adopts to understand and implement the law. The UAE’s legal structure is drawn from the universal law framework and the Sharia law. The court arrangement comprises the civil bench and the Sharia judges who have restricted control to address numerous scandalous matters such as infidelity, burglary, and alcohol abuse among other wrongdoings.
Significance of the Political Economy Analysis
The political economy analysis will be significant in analyzing the UAE’s situation since it will reveal how the country has developed and executed its public policy. Table 1 below shows the country’s economic outlook. From the table, it is clear that the UAE’s economic performance is on the right track.
Table 1: The UAE Economic Outlook. Source: IMF (2015)
The political economy analysis in the UAE as shown in Table 2 will reveal any interactions involving political economic and legal processes that create, sustain, and transform specific relationships that have been observed for a long period between the states, market forces, and civil society.
Political Economy Analysis Table.
Table 2: Political Economy Analysis.
Recommendations
The UAE government should completely adhere to the public policies by getting rid of its reservations and fully prohibiting any form of gender-based violence that hinders the progress of its political economy. For instance, the government should ensure that the women are encouraged to go for high political positions since their contribution in collaboration with their male counterparts will boost the UAE’s political economy (Mahdavi, 2013; Pinto, 2012; Al Rashedi et al., 2015). Additionally, the UAE government should focus on improving its economic statistics by initiating and implementing projects that can easily boost its international investments and hence its political-economic capability (United Arab Emirates Country Monitor, 2014).
Conclusion
The UAE has been the most attractive country for Foreign Direct Investment among all the Arab countries. It appears in the 11th position worldwide (Augustine, 2014). However, it has lately experienced a drop in its FDI attractiveness compared to its situation in 2013. Graph 1 below shows the country’s FDI position from 2010 to 2013 relative to other states around the globe.
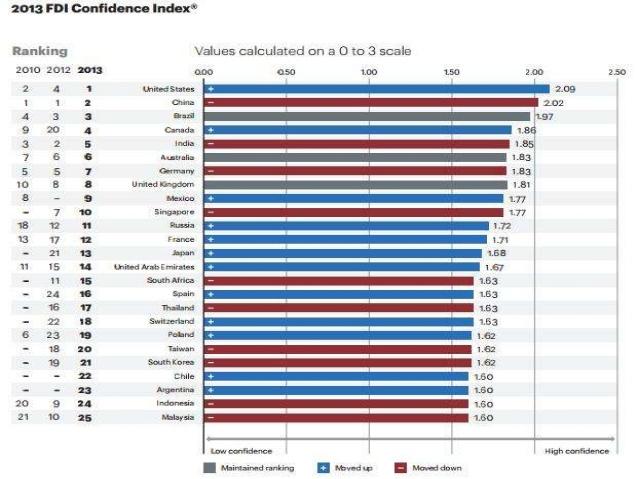
The ultimate result of the analysis is that the Foreign Direct Investment smoothly flows towards the initial attraction point, which is largely dependent on the relative size of its domestic investment (Mina, 2014). For countries such as the US among others, which have an upper hand in terms of their FDI, natural resources are a significant attribute that defines their general FDI attractiveness.
Reference List
Aartun, A. (2002). The political economy of the United Arab Emirates. Web.
Augustine, B. (2014). UAE 11th Most Attractive FDI Destination. Web.
Ahmed, E., & Zain, A. (2015). The role of diversification strategies in the economic development for oil-dependent countries: – The case of UAE. International Journal of Business & Economic Development, 3(1), 47-57. Web.
Al Rashedi, N., AlShamsi, A., Rashed, M., Sinczak, T., Hodgson, S., & O’Neil, K. (2015). Social Marketing, Education and the Female Workforce: A Comparison of United Arab Emirates and Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Middle East Journal of Business, 10(1), 39-49. Web.
Coleman, D. (2014). United Arab Emirates: 2014 Country Review. United Arab Emirates Country Review, 1(1), 1-237. Web.
Davidson, C. (2009). The United Arab Emirates: Prospects for Political Reform. Brown Journal of World Affairs, 15(2), 117-127. Web.
Goby, V. (2015). Financialization and Outsourcing in a Different Guise: The Ethical Chaos of Workforce Localization in the United Arab Emirates. Journal of Business Ethics, 131(2), 415-421. Web.
IMF. (2015). United Arab Emirates: Economic and political outline. Web.
King, D. (2008). United Arab Emirates. New York, NY: Marshall Cavendish Benchmark. Web.
Mahdavi, P. (2013). Gender, labor and the law: the nexus of domestic work, human trafficking and the informal economy in the United Arab Emirates. Global Networks, 13(4), 425-440. Web.
Mina, W. (2014). United Arab Emirates FDI Outlook. World Economy, 37(12), 1716-1730. Web.
O’Neill, K., Hodgson, S., & Mazrouei, M. (2015). Employee Engagement and Internal Communication: A United Arab Emirates Study. Middle East Journal of Business, 10(4), 3-28. Web.
Pinto, V. (2012). Nation-building, State and the Gender framing of Women’s Rights in the United Arab Emirates. Reading, England: Garnet Publishing. Web.
Spraggon, M. (2014). Managing Organizations in the United Arab Emirates: Dynamic Characteristics and Key Economic Developments. Virginia, NY: Palgrave Macmillan. Web.
UAE Oil & Gas Report. (2015). Web.
United Arab Emirates Country Monitor. (2014). Country Reports: Country Outlook: Economic – United Arab Emirates. Web.
United Arab Emirates Country Review. (2011). Political Conditions. Web.
Young, K. (2014). The Political Economy of Energy, Finance and Security in the United Arab Emirates. Basingstoke, United Kingdom: Palgrave Macmillan. Web.