Abstract
When creating a promotion plan, global corporations’ marketing strategies rely on many factors. In fashion and luxury goods, mainstream trends are heading east, leading to marketing changes for companies like LVMH. They must adapt and pay more attention to current trends to maintain a good market share in Asian countries. Thus, this paper is intended to review the holding’s current marketing strategies and what will determine its direction in the future. This is important for understanding how the market forms the offer and what goals fashion brands and luxury goods manufacturers set for themselves today.
Introduction
The Eastern market is a significant aspect of the global economy. Most Asian countries have large populations and economic opportunities, resulting in high luxury and branded goods sales. Thus, LVMH must increase its presence in these markets and improve its distribution strategies through branded boutiques and arrangements with local department stores. This will allow the corporation to strengthen its capabilities in the context of increasing profitable offers for the local population. As the focus of the fashion and luxury industry shifts to the East, LVMH’s new marketing strategy will focus on innovation and a stronger focus on traditional cultures and e-commerce.
Background
LVMH (Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton) is a holding company for luxury goods sold worldwide. This brand has established itself as a productive luxury clothing and accessories. The conglomerate was founded in 1987 during the merger of Moët et Chandon, which produces champagnes, and the luxury fashion brand Louis Vuitton (Lai 549). Since then, the company has had a strategy of constant expansion by acquiring many brands and expanding its scope of activities.
The core of the company’s activity focuses on providing luxury goods and innovation in fashion and accessories. Today, the holding portfolio includes many companies systematically joined throughout the brand. Thus, it is helpful to break down the significant mergers and acquisitions of a holding to understand the marketing focus better. Christian Dior has become one of the largest and most influential brands, merging into the holding in 1987(Lai 549). This deal allowed LVMH to concentrate many fashion clothes under one brand, dividing them into categories and niches.
Such an operation also allowed the holding to significantly expand its customer base through people who bought Christian Dior items. The acquisition of Fendi was another milestone for the holding company. It ended in the first year of 2001, further expanding the organization’s scope in fashion (Gonda and Farkas 20). By analogy with Christian Dior, this brand has significantly expanded the possibilities of LVMH, allowing them to present more fashionable clothes and accumulate a sufficient amount of luxury goods.
Some internal reshuffles also characterize the organization’s policy of acquisitions and mergers. For example, the holding united the newer and extravagant luxury watch brand Hublot with the traditional manufacturer Zenith because it bought both companies (Zorzi 53). This allowed both companies to benefit from collaboration and technology sharing. Watch companies exist under separate brands today but share joint marketing, distribution, and research and development approaches. Another vital company acquisition is the Italian house of prestigious jewelry and watches Bulgari, which joined LVMH in 2011 (Zorzi 51). The merger marked a significant expansion of LVMH’s product range, which began to branch into its brands in every category, such as watches, clothing, and jewelry.
Recently, the holding has expanded its activities beyond luxury goods. This became possible due to the purchase of Belmond, a company that provides services in luxury tourism(Zorzi 68). Thus, the organization entered a new field of activity and organized the combination of tourism options with other services provided. The strategic development of Belmond is fully utilized under the overall concept of LVMH luxury goods. LVMH’s strategic acquisitions and mergers have systematically focused on luxury brands in any product category. Thus, the holding has a common focus for all its companies that can develop widely, supported by each other’s technologies and research. This allowed us to expand our presence in many markets by increasing the reach of the audience.
One of the critical roles in the success of LVMH holding is a multi-brand approach to business organization, which provides opportunities for regulating various sales areas. A multi-brand approach is critical for an organization experimenting with marketing strategies (Lai 554). Spreading across multiple divisions is essential for the brand, as many companies within the holding are unidirectional. This opens up the possibility of using the strengths of each brand by combining them, as was done with the example of Hublot and Zenith.
Current Marketing Strategies
LVMH’s marketing approach in the eastern region is also focused on finding a compromise between the display of luxury and its discreet display. This approach is based on understanding the psychology of people with high incomes for whom a demonstration of purchasing power combined with restraint is essential. Thus, the holding is faced with a difficult task, such as demonstrating luxury goods without excessive pathos and limited marketing tools.
Some of the holding’s competitors, such as Chanel use a similar approach (Yu 666). At the same time, the widespread use of the brand can hurt advertising objectives. For example, television advertising can blur the difference between a mass brand and a luxury brand, so the company is aiming for more targeted tools to increase influence in its approach.
Specific fears are associated with the fact that the fashion and luxury industry is moving to the East. According to Murru, the holding’s sales performance in the Asian region is growing but has not reached the pre-Covid period (5). This means that the company should make more marketing efforts to compensate for the losses caused by the pandemic. In the future, the underlying distribution strategy may move away from the concept of online trading and focus on flagship distribution points.
LVMH’s current marketing strategies are focused on responding to customer needs as effectively as possible. The luxury goods market in Asia differs significantly from those in Europe or the United States, which leads to a specific approach (Yu 664). This is ensured by the decentralized operations of the holding, which provides the company with an effective decision-making strategy based on approaching its customers. Thus, LVMH’s marketing system may have the side effect of increasing the motivation of its employees, which has a positive effect on the company’s overall performance.
One of the critical concepts of LVMH’s marketing strategy is organic growth, characterized by allocating significant resources and capital investments to subsidiaries. This allows them to develop independently, creating stand-alone development campaigns that positively influence growth. Organic growth is characterized by the fact that LVMH regards human resources as the driving force behind the holding’s progress, which is a substantial capital. This approach allows them to create a comfortable environment that affects the marketing strategy as it is created, considering the staff’s opinion.
The vertical integration of a corporation’s marketing strategy can support marketing claims. This is ensured by ascending and descending directions that allow control of all links in the supply chain (Lai 551). Products reach boutiques quickly and without loss. This way, marketing can be carried out through complete control over the brand image. The group shares marketing efforts in connection with the powers of subsidiaries, resulting in a branched system that separates all brands connected in one chain. For example, Zenith and Hublot, being merged into one company within the holding, have different positioning and separate marketing approaches, allowing them to provide unique products.
The company does not focus on the history of its brands and systematically develops a modern vision and innovative marketing approaches. This includes the frequent involvement of celebrities who advertise items from different LVMH brands at fashion shows or film festivals (Yu 665). This allows one to increase the visibility of jewelry, clothing, or watches by encouraging the press to discuss these items.
The Holding pays excellent attention to brands’ storytelling, allowing them to reveal their historical value, thus raising the price of each luxury item. At the same time, the coverage of each brand of the company takes place according to certain unique aspects that distinguish them from other holding companies. For example, Dior focuses on elegance and a more classic focus, while Louis Vuitton has a more modern approach.
Another option for promoting their brands is using limited product versions and cross-organizational collaborations. These strategies are especially evident in the watch business. As mentioned, the holding owns several luxury watchhouses that can produce limited-edition items dedicated to special events or brand history. Such versions, in turn, have an increased value and uniqueness, which is determined by their complexity in manufacturing and unique parameters. Limited editions are also in high demand in fashion and can cost more than regular collections (Yu 665).
However, they are often marked by collaborations with various artists. The company’s marketing has also been essential in modern technologies since the holding began to pay great attention to e-commerce. Digital transformation for the fashion industry may also be necessary as potential clients need to understand how modern and relevant the things they invest in are. The company’s current aspirations are manifested in improving the shopping experience for people, including by transferring this process to online platforms.
Future Direction and Strategies
LVMH’s current marketing focus is showing positive sales growth results. This focuses on the Japanese market, with an increase of 17% in 2022 (LVMH). In addition, growth in China is quite noticeable, which characterizes the organization’s successful strategy for Asian countries. This is consistent with the general orientation and reorientation to the East. Thus, it becomes clear that the holding highly appreciates these markets and plans to develop and increase its presence. To maintain high positions and recruit new customers for the organization, it is necessary to introduce specific innovations that could interest the public.
The Eastern region is of great importance for all brands due to the large population and the concentration of people with high incomes. Thus, this region becomes a profitable target for a holding that distributes luxury goods. According to a study by the Financial Times, the economic growth of the Asian region over the next few years will significantly outpace the growth of Europe or America (Ahya). This is one of the good reasons why many global corporations see this market as more profitable and begin to develop their strategies in this direction. The region’s enormous economic volumes and dense population are essential components for which the organization is considering increasing its focus to the East.
The shift in focus to the East is primarily because the fashion industry has a strong fixation and is increasingly focused on this region. Many brands are beginning to focus more actively on Asia due to its promising and developed market (Ahya). One potential step a holding can take to shape its new marketing strategy is to apply experiential marketing and events. The company can carry out this method in the format of events that can be partly held both online and offline. An important aspect is that these events should have a specific national focus that will be unique to the countries of the East. This approach will create an emphasis on the specifics of the culture of Asian countries, which can positively affect the corporation’s popularity in this region.
The marketing strategy in this direction is somewhat different from the brand’s global approach. Despite this, some common aspects are carried out primarily in attracting celebrities to the corporation’s advertising campaign. One such factor is the involvement of celebrities in promoting products. For example, the South Korean boyband BTS is the brand ambassador for Louis Vuitton, and they often appear in everyday and public life in clothing companies, significantly affecting their popularization among the band’s fans (Mauliamala 53). Such collaborations and representations strengthen brand support among the population of the eastern regions and worldwide.
The shift of the fashion and luxury industry to the East has led not only to the focus on Asian countries but also to the representation of their features in other places around the world. In this way, for example, a company can keep this trend alive by creating Asian-inspired fashion items. It can be both clothes and accessories. Since LVMH Holding has many watch brands, presenting models dedicated to the Chinese horoscope is the appropriate solution. This strategy is popular among luxury watch brands that produce limited edition models in high demand yearly (Liu).
Competitors of the LVMH group brands, such as Blancpain and Vacheron Constantin, use this strategy regularly, which allows them to gain much attention among the public in China, Korea, and Japan. At the same time, this industry has a trend for the complication of models, which is more prevalent in the Asian markets than watches without additions (Liu). At the same time, Zenith, Chaumet, and Hublot do not currently use strategies in their models that could allow them to increase their popularity in the markets of the East.
The general concept and positioning of the brand in Asian markets do not differ from the generally accepted one. Thus, the holding continues the policy of no discounts and releasing luxury items from rare materials that add value. However, some aspects resonate with modern marketing targeting, such as promoting group products through mobile applications.
For example, the company released the mobile phone game “Louis the Game,” which ranked first in the list of downloadable apps on the day of release (Wang and Yu 104). In the game, users can visit Beijing and Paris, which allows them to associate with their countries. At the same time, the main character is the mascot of Louis Vuitton, Vivienne, which also allows for the conducting of an associative series for users to learn more about the brand.
In addition to attracting electronic marketing, the holding pays excellent attention to co-branding and associating with creators from Eastern countries to create unique products. Louis Vuitton, for example, had a history of collaborating with Japanese artist Takashi Murakami in 2003, indicating the brand’s longstanding focus on expanding into the Asian market (Wang and Yu 105). This allows one to combine traditional Asian motifs with fashion brands interweaving, thus creating unique products primarily aimed at users from the Eastern region. Collaborations continue the corporation’s universal marketing approach, which aims to expand influence by increasing potential consumers’ awareness of the company’s products.
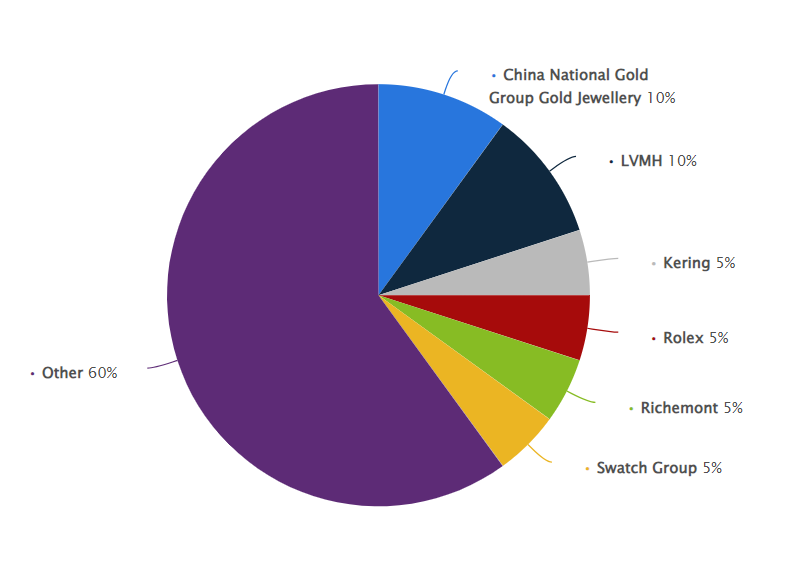
LVMH’s eastward marketing approach can be seen in detail in the example of China, as this market is one of the largest and most potentially profitable for the holding brands. As shown in Figure 1, LVMH has a 10% share of the luxury goods market in China, a significant figure not exceeded by other brands. Thus, the focus on holding these positions is imperative for the holding. In the Chinese market, Louis Vuitton introduced a strategy of making more affordable products such as key chains and card holders (Yu 665).
This approach is justified by targeting a younger audience, allowing the company to expand its customers and create a springboard for future purchases that these people will make from this brand. The company also demonstrated the brand’s attention to the Chinese market by holding the Spring and Summer 2021 show in Shanghai (Yu 665). This made it possible to gain a foothold in this market, showing how attentive the holding is to Chinese customers.
LVMH emphasizes localizing marketing communications to establish a deeper connection with consumers. This means translating key slogans, marketing slogans, and other inscriptions into local languages, which the company does not do for other countries (Chen 95). This approach may signal the organization intends to increase its presence in the eastern markets through closer customer communication.
The expansion to the East, considering the mixing in this direction of the fashion industry, is characterized by increased local attention. This is demonstrated by defining not universal but specific campaigns for holding and transferring fashion shows. Thus, the companies in the conglomerate support and contribute to transferring the fashion industry’s focus to Asian countries.
Despite recovering security indicators after the pandemic, LVMH continues to develop an e-commerce policy in Asia, especially in China. One of the cutting-edge inventions in this context was the Mini program, which made it possible to successfully combine all the functions that are important for buyers, such as a sales assistant (Selvanathan 7). In this way, the holding has indicated a clear focus on further development in the online sales segment, which is a reasonable decision, as it helps to increase the overall income, including in offline boutiques. For example, this is indicated in Shanghai Plaza, where LVMH set record sales in 2020 (Selvanathan 22). As such, LVMH may continue to use the same tactic by expanding its online presence.
The digital experience of promotion in the markets of the East has advanced significantly during the application of quarantine measures in connection with the coronavirus pandemic. The company was forced to take several measures to continue trading in the markets of all countries. Thus, the company’s online platforms’ commercial basis was greatly improved, allowing brands to sell their goods during the lockdown. LVMH’s digital experience can also be seen in virtual and augmented reality. These aspects could become a reliable basis for the holding, with the help of which it is possible to continue active promotion to the eastern market.
One of the solutions in this context could be the organization of shows of extravagant collections in a particular theme in the AR or VR space. Several companies have used this approach and have received relatively positive reviews for its manufacturability and innovative approach (Silvestri 64). Thus, by applying this approach, LVMH will achieve a better representation in the Asian markets, making it possible to increase customer focus among people interested in technology.
Visualization with AR and VR is also a suitable solution for helping customers to choose clothes. These methods can be used in conjunction with specially developed applications for mobile phones. Thus, customers can try on clothes or accessories without leaving their homes. This is a convenient way for the corporation to improve the customer experience. At the same time, this approach will allow opportunities for cooperation with such technological platforms as WeChat, Weibo, and Douyin. This will increase the influx of customers and brand awareness due to the infusion of a new audience.
In addition to strengthening the information and technology approaches, the corporation can increase its physical presence in Asian countries. This is justified as the competitive market is an extensive collection of diverse brands that can pressure LVMH to compete for space in densely populated areas. In addition, the economic development of Asian countries such as Japan, Korea, and China allows more customers to be covered due to better solvency. This option is essential for strategic planning. This niche also has many opportunities for cooperation with other brands or stores. An example of a successful collaboration is LVMH’s early collaboration with Supreme and off-white, which attracted a younger audience (Yu 665). Attracting a new target audience is an imperative step to strengthen its presence in the markets of the East.
Conclusion
The orientation of the fashion and luxury industry to the East causes specific changes in the marketing of companies that work in these areas. LVMH is leading sales in the Asian region, but they are significantly lower than pre-pandemic figures. Thus, recent trends create the basis for expanding marketing opportunities in China, Japan, and Korea.
Paying more attention to innovative strategies that the company has used before and has experience in may become a key area for this. This can benefit the promotion of products among a critical audience and attract a new one. Collaboration is also one of the essential aspects of the future direction of marketing, as celebrities can draw attention to the things they wear. Strategic approaches to branding have a strong inclination towards the online segment, which helps expand the boutiques’ audience.
Works Cited
Ahya, Chetan. “Asian Economic Growth to Outstrip Americas and Europe.” Financial Times. 2022. Web.
Chen, Muhan. “Luxury Brand Prada’s Digital Multinational Marketing Strategy in China.” Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, vol. 13. 2023, pp. 91-97. Web.
Gonda, Gyorgy, and Maria Fekete Farkas. “Trends in Fashion Retail-Global Expansion and Centralization of the Most Competitive Players.” Journal of Management, vol. 1, 2020, pp. 1-112. Web.
Lai, Chi Suen. “The Strategy and Competitor Analysis of LVMH.” 2nd International Conference on Financial Management and Economic Transition (FMET 2022). Atlantis Press, 2022. Web.
Liu, Ming. “Zodiac Watch Interest Wanes as Chinese Year of the Rat Starts.” Financial Times. 2020. Web.
LVMH. “New Record Year for LVMH in 2022,”. 2023. Web.
Mauliamala, Cut, and Adiasri Putri Purbantina. “Strategi Marketing Global Luxury Brand “Louis Vuitton” Dalam Value Creation Melalui Figure Korean Wave.” Jurnal Ekonomika dan Bisnis, vol. 9, no. 1. 2022, pp. 45-62. Web.
Murru, Martina. The new luxury era-LVMH confirms its solid position as the market leader. 2022. Dissertation. Web.
Selvanathan, Shamini. What is the future of Richemont, Kering and LVMH´ s online-offline strategies in China? 2021. Dissertation. Web.
Silvestri, Barbara. “The future of fashion: How the quest for digitization and the use of artificial intelligence and extended reality will reshape the fashion industry after COVID-19.” ZoneModa Journal, vol. 10, no. 2. 2020, pp. 61-73. Web.
Statista. “Breakdown of the luxury goods market in China as of March 2022,” by brand. 2023. Web.
Wang, Jingyi, and Lushan Yu. “The Analysis of Louis Vuitton’s Marketing Strategy in China Based on the 4P Model and Brand Marketing.” BCP Business & Management, vol. 16, pp. 99-108. Web.
Yu, Senhuizi. “Research on the Marketing Strategy of Luxury Brands in China.” 2022 7th International Conference on Social Sciences and Economic Development (ICSSED 2022). Atlantis Press, 2022. Web.
Zorzi, Riccardo. “Growth through Mergers and Acquisitions in the luxury industry: the LVMH case.” DSEA. Web.