Introduction
The dependent variable of interest in this project is the national savings. The national savings is a vital part in macroeconomic analysis of an economy because it is an integral part of economic development. It combines both public and private savings. The total national savings of an economy has attracted a number of research studies over the years because of its importance in economic growth and development.
For instance, the classical and neoclassical models emphasize on the need for higher savings for long run growth (Baltagi 2011). The neoclassical model examines whether the development between steady states, positive changes in the savings ratio may stimulate the growth rate in the economy. Also, the endogenous growth model was developed by Romer and Lucas (Arnold 2011). The authors indicate that savings, human capital, and technological change are the most significant determinants of economic growth rate.
The models developed by these two groups are consistent with the economy of the UK. For instance, the foreign sector inflow in the UK has played a significant role in the investment process in the UK. This can be attributed to improvement in technology, liberation of trade, and openness of the financial sector. Also, in the UK, it is believed that the low national savings rate has been one of the major obstructions to attaining high levels of sustainable economic growth. Therefore, it will be important to evaluate the impact of the determinants of national savings in the United Kingdom.
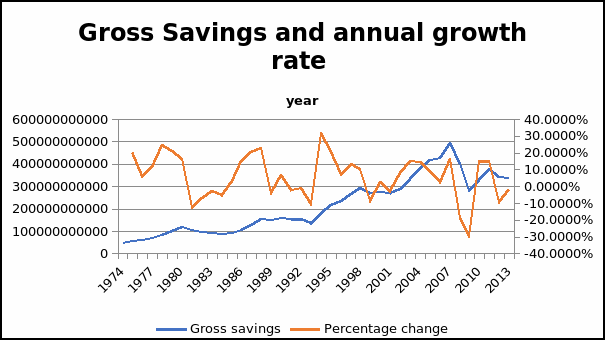
The data of gross savings will be collected for a period of 40 years that is, between 1974 and 2013. The country of interest is the United Kingdom. The data are collected from the World Bank Group Website (The World Bank Group 2016). Further, the values of gross saving are measured in current US dollar. The graph of both gross savings and annual growth shows that there has been significant fluctuations of the values the two variables (Dunn 2005). The data and trend of the dependent variable are presented in Table 1 and Figure 1 respectively.
Table 1: Data for dependent variable.
Model
In the analysis, a multiple regression model will be used to estimate the savings for the United Kingdom. In general, a regression analysis is a statistical tool that develops and approximate linear relationships among various variables. When coming up with the model, it is necessary to separate between dependent and independent variables. Multiple regression analysis focuses on the regression between the dependent variable and several explanatory variables. As mentioned above, the dependent variable is savings. There are a number of macroeconomic factors that affects the national savings of a country. Some of these factors will be the independent variables for the regression model. The selected independent variables are inflation, exchange rate, GDP per capita, and trade openness and policy (Gautam 2006). The regression line will take the form Y = a0 + a1X1 + a2X2 + a3X3 + a4X4
Where
- Y = Savings;
- X1 = Inflation;
- X2 = Exchange rate;
- X3 = GDP per capita;
- X4 = Trade openness and policy.
Savings
In this case, the data for gross national savings will be used. The value of gross national savings is arrived at by taking the total amount of national income less aggregate consumption. The value gives information on the amount of funds that is available for both local and overseas investments. The data on gross savings is reported in current US dollars.
Inflation
Inflation captures the continous rise of prices in the economy. Inflation has a significant impact on most variables in the economy because it creates a lot of uncertainty. Studies that have been carried out shows that there is a negative relationship between inflation and savings. Therefore, a rise in inflation is likely to cause a decline in savings. The GDP deflator will be used to estimate the inflation rate of the country. The values are reported in percentages.
Exchange rate
In this case, the exchange rate between the British Pound and the United States dollar will be used. The exchange rate is expected to have a negative relationship with savings.
GDP per capita
The value of GDP per capita is arrived at by dividing the gross domestic product of a country and total population. It is expected that there is a negative association between GDP per capita and savings. The data on GDP per capital is reported in current US dollars.
Trade openness and policy
Trade openness and policies have a positive impact on national savings. Therefore, it is expected that there will be a positive relationship between these two variables. Further, trade openness also causes an increase in both income and welfare of the community. The data on import, export and GDP is reported in current US dollars Trade openness is often calculated using the formula presented below.
= (Import + Export) / GDP
The ratio gives information on the intensity of trade. Calculations of trade ratio are presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Calculation of trade ratio.
From the above discussion, the theoretical expectation of the coefficients are; a0 can take any value, a1, a2,and a3 < 0 while a4 > 0. However, these expectations can change depending on the country that is being analyzed.
Data collection and analysis
The data of the independent variable are collected from The UK Data Services, Office for National Statistics, International Monetary Fund, Fusion Media Limited, and The World Bank Group (The UK Data Services 2016; Office for National Statistics 2016; International Monetary Fund 2015; Fusion Media Limited 2016, GBP/USD; The World Bank Group 2016). The data are presented in Table 3. Eviews software will be used to estimate the regression equation of the saving model that is discussed above.
Table 3: Data for independent variables.
Regression results
The results of the first regression analysis are presented in Table 4. From the results, the regression equation will take the form presented below. The equation is based on the data for the period 1974 and 2008.
Savings = – 4.77E+11 + 7.19E+09inflation – 5.92E+10exchange rate + 15232870GDP per capita + 2.12E+11trade openness
Table 4: Regression results using entire data.
Diagnostic testing
Inflation, GDP per capita and trade openness have positive coefficients. This implies that there is a positive relationship between these variables and savings. Therefore, an increase in the values of these variables by one unit will cause an increase in the amount of savings by the value of the coefficient. On the other hand, the equation above shows that there is a negative relationship between savings and exchange rate.
T-test
The t-test will be used to evaluate the statistical significance of the explanatory variables. A two tailed t- test is carried out at 95% level of confidence.
- Null hypothesis: Ho: bi = 0
- Alternative hypothesis: Ho: bi ≠ 0
The null hypothesis implies that the variables are not significant determinants of savings. The alternative hypothesis implies that variables are significant determinant of savings. The table below summarizes the results of the t – tests.
Table 5: The results of the t-tests.
In the table above, it can be observed that inflation, exchange rate and GDP per capita are significant determinants of gross saving at the 95% confidence level. However, trade openness is not a significant determinant. Therefore, the last variable can be dropped because it is not statistically significant.
R-square value
Coefficient of determination estimates the amount of variations of the dependent variable explained by the independent variables (Vinod 2008). A high coefficient of determination implies that the explanatory variables adequately explain variations gross savings. For this regression, the value of R2 is 94.37%. This implies that the independent variables explain 93.72% of the variation in gross savings. It is an indication of a strong regression line. Also, the value of adjusted R2 is high at 93.43%.
F – test of the regression models
The overall significance of the regression model can be analyzed using an F – test. The test will be carried out 1% significance level.
- Null hypothesis H0: β0 = β1 =, = βp
- Alternative hypothesis H1: βj ≠ 0, for at least one value of j
The null hypothesis implies that the overall regression line is not significant. The alternative hypothesis implies that overall regression line is significant. The results show that the value of F-calculated is 100.5763 while the value of probability of F-statistics is 0.000. The value is less than the value of alpha (0.05). Thus, the null hypothesis will be rejected and this implies that the overall regression line is significant at the 95% confidence level (Verbeek 2008).
Durbin Watson Test
It is used to evaluate autocorrelation. Autocorrelation is a scenario where the error terms of different periods are related. The null and alternative hypothesis in the Durbin Watson test are shown below:
- Null hypothesis Ho: d = 2 (no autocorrelation)
- Alternative hypothesis H1: d ≠ 2 (There is autocorrelation. It can be positive or negative)
The value of Durbin Watson computed is 1.502602. This clearly implies that the null hypothesis will not be rejected. Thus, there is autocorrelation.
Table 6: Using data for the period between 1974 and 2008.
White test for heteroskedasticity
Heteroskedasticity is a scenario where the error term violates the assumption of constant variance.
- Null hypothesis: There is no heteroskedasticity
- Alternative hypothesis: Heteroskedasticity of unknown general form exists
The results show that the p-value for the f-test and chi-square tests are 0.605829 and 0.529804 respectively. The values are greater than alpha(0.05). Therefore, the null hypothesis will not be rejected at the 95% confidence level. This implies that there is homoscedasticity.
Table 7:Heteroskedasticity test result.
Re-specification of the original model
In the new model, the GDP per capita will be dropped from the regression equation. The results of the new regression model are presented in Tables 8 and 9. The results show that the remaining explanatory variables will be statistically significant as indicated by t-values. Further, the overall regression line will be significant as indicated by the values of f-statistics (Mankiw 2011).
Table 8: Results of the new regression model.
Table 9: Results of heteroskedasticity
Also, there is an improvement in the value of Durbin Watson Statistics. Therefore, the final model that will be used for estimation is presented below.
Savings = -5.02E+11 – 2.16E+10inflation + 2.18E+11exchnage rate + 7.58+11trade openness
Forecasting
The results of the forecast are presented in Figure 2. The graph shows the forecast output and two bands of standard error. A comparison of the trend of actual and forecasted savings shows that there is a slight variation in the two values. The results of forecast evaluation compare the values of forecasted values and the actual data over a similar time period.
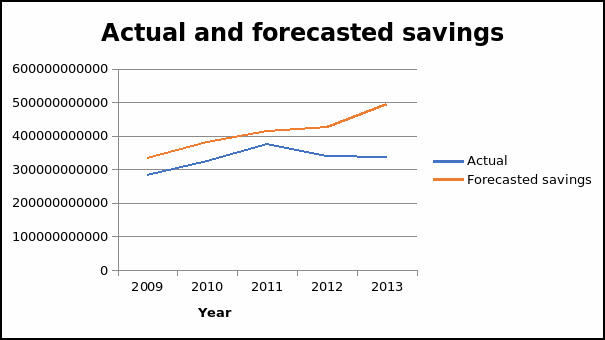
Therefore, the forecast was carried out in-sample. Further, the bias and variance proportion gives information on how far the mean and variance of the forecast are from those of the actual values. The covariance proportion gives information on the random forecasting error. Since the values of bias and variance proportions are high, it indicates that the forecasts are not good.
An evaluation of the residuals and the forecasts shows that the model is not good. This creates the need to revise the regression model so the forecasts can look reasonable. One of the adjustments that can be made is excluding the observations prior to 1985. The second adjustment is by adding a seasonal dummy variables. The final adjustment that can be made is correcting error autocorrelation. These measures are likely to improve the forecasts (Hamilton 2004).
Economic approach to model building and forecasting
The analysis above clearly indicates the importance of the econometric approach to model building and forecasting. The analysis shows that several models can be built using econometric tools. Besides, the econometric approach provides a basis of evaluating the strength of the models built and the suitability of the estimates for the variables being analyzed.
Such models aid in economic planning, policy making and training. Besides, with the enhancements in technology, computer program and modelling techniques, there has been an improved ease in econometric analysis and accuracy in forecasts (Greene 2008).
References
Arnold, R 2011, Economics, Cengage Learning, USA.
Bade, R & Parkin, M 2013, Essential foundations of economics, Pearson, USA.
Baltagi, G 2011, Econometrics, Springer, New York.
Dunn, P 2005, Measurement and data analysis for engineering and science, McGraw–Hill, New York.
Fusion Media Limited 2016, GBP/USD – British pound US dollar historical data. Web.
Gautam, G 2006, Essays: Liquidity, returns autocorrelation, price formation, markets, ProQuest, USA.
Greene, WH 2008, Econometric analysis, Prentice–Hall, UK.
Hamilton, JD 2004, Time series analysis, Princeton University Press, New Jersey.
International Monetary Fund 2015, Data and statistics. Web.
Mankiw, G 2011, Principles of economics, Cengage Learning, USA.
Office for National Statistics 2016, Datasets and reference tables. Web.
The UK Data Services 2016, Open access data. Web.
The World Bank Group 2016, United Kingdom. Web.
Verbeek, M 2008, A Guide to Modern Econometrics. England: John Wiley & Sons.
Vinod, HD 2008, Hands on intermediate econometrics using r: templates for extending dozens of practical examples, World Scientific Publishers, USA.