Introduction
Unlike in early years, financial institutions all over the world are now facing many challenges of managing their operational risks. With the tremendous increase in financial market deregulation and globalization, coupled with the sophisticated financial technology, risk profiles of financial institutions have increased mainly because of the complexity of financial activities (Abkowitz 2008, p. 25). Recently, risk prevention has become a key objective of corporate organizations all over the globe. Andreas (2010, p.3) defines operational risks as, “the risks of losses arising from failed or inadequate internal processes, systems, people, or from external processes”. Operational risks arise from the execution of various functions in a business. In the management of operational risks, the aim is not to generate profit but to eliminate any operational risks that will translate into massive losses for the company (Garrick 2008, p.36). In this regard, organizations must develop risk cultures that mainly focus on the risk management. Managing operational risk should include inspecting various categories of risks, which can occur in a business organization such as legal risks, environmental risks, physical risks, and fraud risks. Consequently, AlphaDelt, a gigantic multinational bank that mainly focuses on personal financial services and products, is prone to many risks, which will lead to loss of reputation or money following the failure to implement proper risk management program. As an operational risk consultant, I take this precious opportunity to table a report for the Executive Board that addresses the key failures within the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt.
People
Based on the behavior of the staff employed AlphaDelt, it suffices to declare people one of the key failures in the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt. Following a keen analysis of AlphaDelt case study, I wish to draw to your attention this failure evident in the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt. Employees of an organization are the chief contributors of the colossal losses incurred by the company. As Graeme (1999, p.43) posits, Operational risk is a broad concept that should focus on all risks arising from all sectors used by an organization in its operations. The company bestows a fair deal of power to the senior managers. As a result, it is impossible for junior staff to question their decisions. This critical problem has created a loophole for the senior staff to engage in dubious activities. For instance, Mark, the director of sales and marketing at this company, has powers to decide which firms to award contracts without consulting anyone else. This comes after Helen, the head of Marketing at AlphaDelt, noticed enormous disparities and unprofessionalism in awarding contracts at her department. Helen questioned Mark why a company named BRN Boards received another marketing contract award despite its poor quality work. What exasperated Helen the most was the fact that BRN Boards lacked expertise and detailed professionalism that marketing contracts demanded. In addition, this Operation Risk Framework lacked balances and internal checks. As evident from the case study, the operational risk framework of AlphaDelt failed to inspect its internal activities that exposed the company to fraud risks from dishonest employees like Mark. As Conklin (1991, p.38) reckons, financial institutions must strive to eliminate loses arising from operational risks by inspecting both external and internal activities executed by the organization. Failure to inspect all the activities performed by employees in the company resulted into a big fraud executed by Mark and his accomplices.
Moreover, inexperienced Employees were another failure in the framework. The Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt has failed to employ people with wide experience and specialized skills to identify operation risks in the company. As Mansell (2004, p.98) posits, the main functions of workers in a department dealing with operational risks is to aid the company areas in identifying, assessing, and managing risks. As evident from the case study, some workers in the operational risk division did not know how to investigate senior employees. This hindered effective elimination of operational risks for the company. Utilizing advantages brought about by advanced technology and globalization aid in hiring competent personnel from any part of the world (Behrens, 2010, p. 51). The framework lacked well-set guidelines on the responsibilities of employees in the department of operational risk. Kelly Feingold working in the department of operational risk had no idea on whether she possessed the mandate to investigate her seniors. Investigating a senior person like an executive director is a strenuous exercise to junior workers, which creates intimidation and fear.
Poor supervision of all employees employed by AlphaDelt was another main failure in this framework. The management employees had great autonomy as no one was inspecting their activities. This enabled Mark to carry out fraud for a long time as no one was inspecting his operations. The excess autonomy given to the employees created a big loophole for them to engage in illegal activities at the expense of the company.
Poor systems
Secondly, the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt has developed poor systems to support various processes within the institution, which have caused a tremendous failure following their inefficiencies. The framework has failed to collect all the data on various operational loses that the company has incurred. This has limited AlphaDelt’s capacity to use the data collected to model operational risks to avoid future losses. As Klein and Sorra (2006, p.49) reckon, “In the current world, principal risks faced by financial institutions include system failure, terrorism, fraud, and claims for compensation by employees”. Thus, the framework for operational risk should utilize all the necessary data to reduce its operational risks. Management of operational risks in an organization involves methods, practices, institutional culture, and polices that enable an organization to understand, control, and prioritize risks (Mendenhall, Punnett & Ricks 1995, p. 37). Failure to eliminate operational risks, as evident in AlphaDelt, will result to elephantine losses, tarnishing the company’s reputation. As Northouse (2010, p.57) reckons, “Operational risks in a company have pernicious effects, as they threaten the well-being of the enterprise, its operating partners, communities living in its operational area, and society” at large. Effective systems are paramount in any organization as they ensure efficient flow of information. The system also enables easy detection of fraud or dubious deals by the employees by detecting any abnormalities. Because of poor processes, AlphaDelt experiences huge losses arising from fraud that has prospered and continued for a long time.
Poor processes
Another failure that I wish to point out in the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt is poor processes that this framework used to execute its operations. They were not effective. In fact, they lacked the capacity to investigate all activities undertaken by the company. As Alexander (2003, p. 125) reckons, investigating potential risks is one of the main activities of such department. Were it not for the intervention of Helen, the fraud committed by Mark would have remained hidden, thus, affecting the company’s performance. As the head of marketing, Helen did not have a wide training in operational risk. Nevertheless, she was able to unravel the enormous fraud, which operational risk employees had not noticed for many years. This depicts the failure of operational risk framework in carrying out extensive investigations of all activities undertaken by the various company departments. Implementing changes in the organizational management in any organization requires a detailed study of the whole organization (Spector 2010, p. 108). As a result, directors like Mark were able to plan and execute fraud for a long time because of the lack of proper investigations. Poor processes will increase financial institution’s risk by creating a vacuum for employees embezzle company’s funds for their own egotistical need. This results into huge losses for the company, which has pernicious effects, as the operations of the company will come to a halt.
Poor departmental coordination also affected the company’s operations and increased risks. The Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt failed to create a strong and effective coordination between various departments in this company (Laura 2008, p. 18). Mark used vastly inflated and duplicated accounts with fragrant disregard of company policies and rules. Complete fabrications utilized by mark and failure of fraud investigators enabled him to amass wealth at the expense of the company. As Adler (2008, p.19) posits, “Undesirable events in an organization will lead to business interruption, fatalities, penalties, environmental degradation, and property loss. As Murray (2006, p.76) reckons, “losses are inevitable in any organization because of imperfect systems, people, and process, which lead to ineffective operations and many errors”. However, working toward mitigating these risks is of paramount essence to any organization.
Ineffective environment
The environment, referring to the diverse external events or work environment within which systems, processes, and people operate was not well organized and conducive. The AlphaDelt’s Operational Risk Framework lacks well-set guidelines that can coordinate and detect any potential threats in the company. As Marshall and Fiore (1994, p. 85) posit, organizations must strive to eliminate all threats that might hinder its operations. Accounts approved by Mark, the Director of Marketing, are dubious. The fraud instigated by the marketing director, enhanced through his close associates and family members, continued for a long time in the presence of the detailed operational risk Framework in AlphaDelt. Failure of the operational risk framework to discover that there was something awry with many of the invoices approved by Mark had irreparable damage on the company’s operations.
In addition, the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt has failed to put workplace safety into consideration. Thus, it exposes its workers to discrimination and intimidation, more so by the senior staff (Flichy 2007, p. 27). The grand autonomy given to the management of this company created a loophole for them to engage in dubious deals with egotistical missions of enriching themselves at the expense of the company and other employees. Keith, the chief internal auditor at this organization, reckons that, as director of sales and marketing, Mark headed the mandate to engage any marketing firm he solely perceives as fit. He can decide the amount of pay the company should receive according to the services delivered. This is against any standards in a professional organization. More than one employee should hand every activity involving money (Carolyn 1998, p.67). Because of the fact that the director at AlphaDelt owns the whole budget of the department under his or her office, the director can approve any amount he or she wants without facing any obstacles. This creates room for frauds that continue for a long time without any detection.
Recommendations
It is imperative for AlphaDelt to come up with effective measures to manage, control and mitigate risks that might occur in the future. Abkowitz (2008, p.47) recommends measures such as using advanced technology, using continuous trends towards litigiousness, tightening margins, thus, reducing the room for errors, and increasing globalization. It is also imperative for the AlphaDelt to create awareness on its employees concerning how to identify and control the diverse operational risks to which it is prone. As diverse expositions discussed in this report indicate, the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt failed because of its failure to create a strong management for its operational risks. The operational risk work requires determined people: undeterred and not easily intimidated (Jack 2001, p.214). Consequently, the situation at AlphaDelt requires a quick adoption of another operational risk framework, which utilizes an effective approach to managing operational risks. The organization should strive to adopt systematic and holistic approach of managing operational risks that will aid it in achieving its objectives and hence eliminating operational losses. The organization needs to execute the creation of a good corporate culture where all employees understand what risks are and how to avoid them, as it is of paramount essence. Moreover, the board of directors, as well as senior management team should involve themselves in the management of operation risks. Eventually, the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt will experience a paradigm shift that will result to efficient management of operation risks, thus, eliminating or mitigating losses that the company might have incurred in the future.
References
Abkowitz, M., 2008.Operational Risk Management: A Case Study Approach to Effective Planning and Response. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. Print.
Adler, N., 2008. International dimensions of organizational behavior. Cincinnati, OH: South-Western College Publishing. Print.
Alexander, C., 2003. Operational Risk: Regulation, Analysis, and Management. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Financial Times Prentice Hall. Print.
Andreas, J., 2010.The Credit and Operational Risk- Implications for Practitioners and Regulators. Journal of Operational Risk, 5(1), pp. 2- 34.
Behrens, H., 2010. Globalization vibrates the 21st century. Lithaus, Berlin: Lithaus Uni-Edition. Print.
Carolyn, M., 1998. When Old Technologies Were New: Thinking about Electric Communication in the Late Nineteenth Century. New York: Oxford University Press. Print.
Conklin. W., 1991. Comparative Economic Systems. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Print.
Flichy, P., 2007. Internet Imaginaire. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Print.
Garrick, B., 2008. Quantifying and Controlling Catastrophic Risks. San Diego, CA: Elsevier. Print.
Graeme, S., 1999. Global Transition: A General Theory. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. Print.
Jack, L., 2001. Operational Risk: Measurement and Modeling. Hoboken: Wiley. Print.
Klein, J., & Sorra S., 2006. The challenge of innovation implementation. Acad Management, 21(4), pp. 1055-1080.
Laura, S., 2008.Speech without Rights: The Status of Public Space on the Internet. The Communication Review, 11(2), pp. 1–23.
Mansell, R., 2004. Political Economy, Power and New Media. New Media & Society, 6(1), pp. 96-105.
Marshall, M., & Fiore Q., 1994. War and Peace in the Global Village. New York: Simon & Schuster, Inc. Print.
Mendenhall, E., Punnett, B., & Ricks D., 1995. Global management. Hoboken: Willey Publishers. Print.
Murray, W., 2006. Geographies of Globalization. New York: Routledge. Print.
Northouse, P., 2010. Leadership: Theory and practice. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc. Print.
Spector, B., 2010. Implementing organizational change: Theory into practice. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall. Print.
Incident Analysis
The supervisor should analyze all incidents or risks to establish specific causes and prevention measures for each incidence. The incident analysis process encompasses operational risk management (ORM) steps, viz. identification of hazards, risk assessment &measurement, risk mitigation and monitoring risk controls and risk reporting.
Mission of the ORM
To identify the key failures of the Operational Risk Framework of AlphaDelt
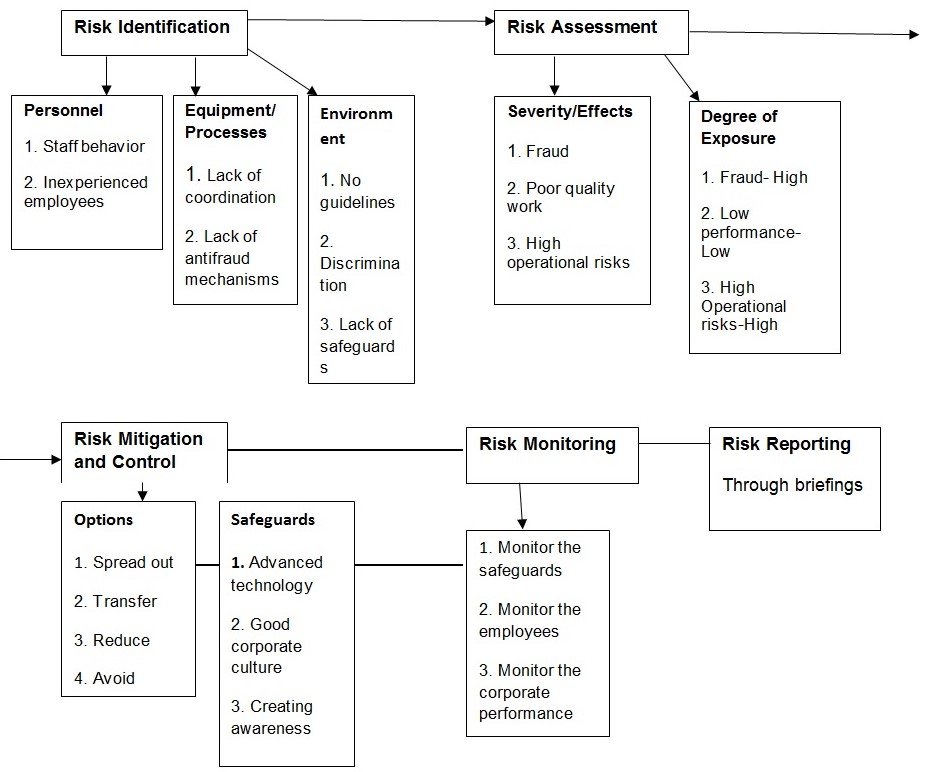
The Operation Risk Management Strategy (ORM) for AlphaDelt
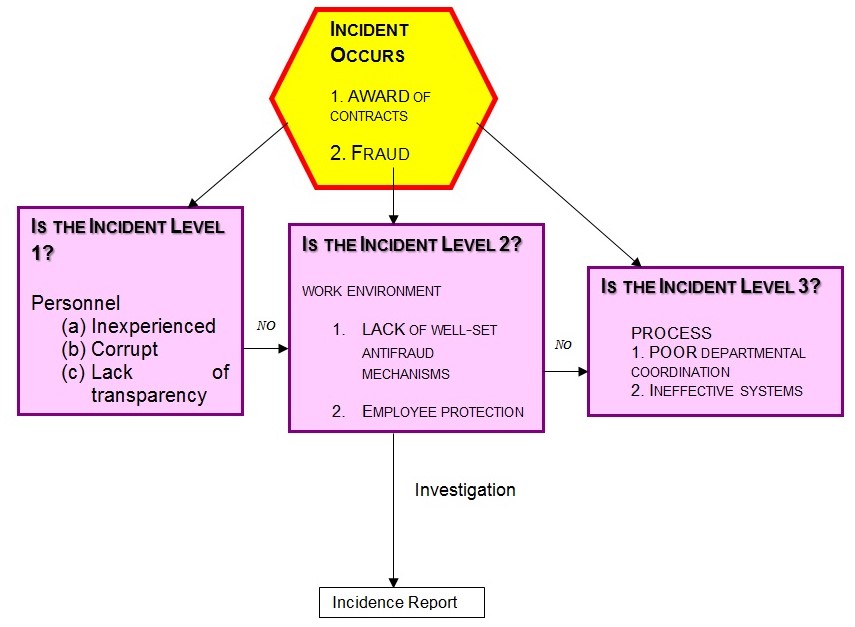
Conclusion
The AlphaDelt ORM strategy had many loopholes that especially in the management. Consequently, the bank should incorporate the ORM concepts into its daily operations including maintenance and support systems. Daily preventive checklists and integrated systems, organizational culture of transparency and adoption of advanced technologies are the ways of mitigating the risks.