Introduction
Breakeven analysis is an analytical tool that used for study the relationship that exists between fixed costs, variable costs and profits. It also is used to determine the point at which sales cover up the total costs of an organization. The breakeven point is the point that crosses across the total cost line.
Main text
The formula of breakeven point:
Break-even units = Average Annual fixed cost/Average per unit sale price – Average per unit available cost
Break-even sales = Annual fixed cost/1-(Average per unit variable cost/Average per unit sales price)
The break-even chart is a chart that shows the graphical representation of costs at various levels of activity as shown on the same chart, it is also the variation in income (sales or volume) within the same variation in activity of an organization. The break-even point on the chart is the point where there is neither profit nor loss. The fixed costs are the costs that are not directly related to the level of production or output that is they remain constant whether the business has output or no output, but in the long term the fixed costs can change due to introduction of new investments into an organization for example addition of a new factory unit or through the growth of overheads that support larger business activities.
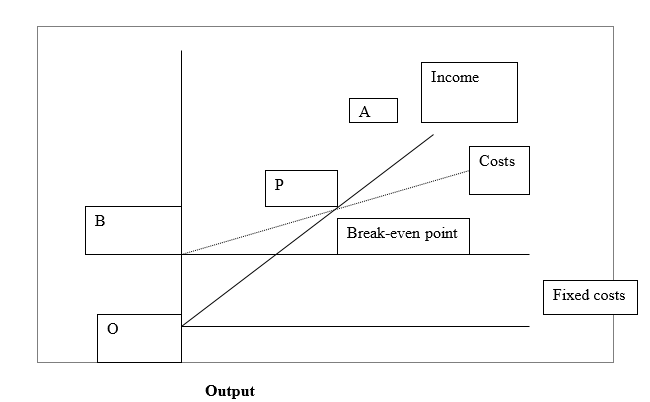
The OA line represents the variation of income at varying levels of production.
The OB line represents the total fixed costs in the business.
As the level of output increases the variable costs are incurred this means that the total costs (fixed and variable costs) also increase at the same rate. At the low levels of output, the costs are greater than income and this leads to losses in an organization. At point P where costs exactly intersect with neither income this is the breakeven point since neither costs nor income are earned or incurred ,the values on the chart that are above the breakeven point are profits of an organizations products.
The variable costs are the costs that vary directly with the level of output of an organization. They represent the payment of the output related outputs as the raw materials, direct labor and the revenue related costs such as the commission costs
The fixed break-even level of output = Average Annual fixed cost/Average per unit sales price – Average price per unit variable cost
£25,000 p.a/Selling price – Variable cost
£25,000/14-10* 2500/ 4= 6250
The margin of safety is a measure that is used to indicate percentage or the amount of cost by which the planned sales exceed the break-even point.
The margin of safety equals budgeted sales minus the break-even sales
The break-even sales = Annual fixed costs/1- (Average per unit variable cost ÷ Average per unit sales price)
Variable cost =10
Selling price = 14
25,000/1(10÷14) 25,000/1-(0.7143)
Margin of safety =
- Budgeted sales 509
- Breakeven sales (87,412.59)
- Margin of safety 421587.41
Percentage margin of safety:
- Margin of safety 421,587.41 x 100
- Budgeted sales 509,000…………………82.83%
The margin of safety is used by the accountants to determine the number of the planned sales that may decline before the losses are incurred in an organization. When an organization has a low margin of safety it indicates that it should attempt to increase the sales volume, increase selling prices or to reduce costs.The extent to which breakeven analysis is a realistic technique for decision making process in an organization is that it can be used by the management to help quantify the level of production that is needed for a new business or a new product that is being introduced in an organization that the management of a firm can determine the costs and revenue that are related to the production of a product.
The product cost center
The cost centers are organizational segments or the areas of activity for which the organization sees it necessary to accumulate costs. They involve companies as a whole. Corporate division’s specific operating plants, departments and machines used to enable work activities to be carried out effectively.
The contribution pricing basis: It is a pricing method of a product which is based on its variable cost of production. It is the amount by which price exceeds the production cost of an organization. The contribution margin pricing
The allocated overheads: they are the inputs that are used for production purposes of the goods and services of an organization, the overheads are labor, taxes and insurance costs, machinery cost and the opportunity costs for the unpaid labor and or land costs.
The cash budget is a budget that is prepared to show the expected cash intake and the rate of spending cash in an organization. It is used to determine the company’s or the organizations’ future ability to pay up its debts as well as its expenses as they arise. The monthly cash budget shows the estimated cash balances at the end of each month, incase the management of a company foresee the short term cash shortfalls then corrective measures are taken into account so that the activities of an organization are carried out effectively.
Sales were 25% high from April to September inclusive October to march
Sales = 98,000
25% x 98,000 = 24,500
98,000 + 24,500 = 122,500
Sales Budget
It is a budget that is used to indicate the estimated amount of anticipated sales that are allocated by product, territory or by a person. It is prepared on weekly, monthly or annually basis according to the management’s strategies. It is expressed in terms of sales volume and the selling price for each class of product or service
Master budget
It is a budget that shows a summary of the company’s plans in which the specific targets are set for sales, production, distribution and the financing activities of an organization. The budget is developed from the cash budget, budgeted income statements and the budgeted balance sheet.
Production budget
It is the budget that shows a detailed plan of how the numbers of units are going to be produced within a given period in order to meet the sales and inventory needs of an organization. It is used for determining how much money is to be spent on a project. It is derived by adding the ending inventory to planned sales and then subtracted with the beginning inventory.
Administrative Budget
It is a budget that highlights the anticipated administration expenses from the sales and inventory cost of goods manufactured budgets. It includes the budgets of various individuals or groups that are involved in administration. It may be derived by combining the selling expenses budget and the administrative expenses portion that contains fixed items such as executive salaries and the depreciation of the company offices.
NB
- The rent is paid on quarterly at the end of each quarter
- The heat and light is paid quarterly at end of each quarter
- The salaries are paid monthly and they include National insurance contribution
- The insurance premiums are payable in January. The fuel is spread evenly across the year at £6600 p.a. its services occurs at April and September at cost of £350 per service
- Frank took dividends totaling £20,000 in March and September.