Introduction
Organizational activities need to be managed and organized in an efficient and effective manner. The managerial tasks vested in the management should be implemented to ensure the organization handles all the issues in an amicable manner. The manner in which this can be achieved can be well explained in an organizational structure the organization follows. An effective and efficient structure facilitate the smooth flow of the organization activities.
Organisation structure
Definitions of organisation structure
Organization culture has over its history encountered numerous definitions with basically try to shed more light on its nature and importance. Organization structure may be defined as follows;
“Kalian-city blog spot.com defined it as Organization structure refers to the network of relationships among individuals and positions in an organization. Scholars have defined organization structure as the formal system of task and reporting relationships that controls, coordinates and motivates employees so that they cooperate and work together to achieve an organization’s goals. In fact organization structure describes the organization framework……..”
Evaluation of organisation structure
The organizations are faced with a great challenge of identifying the levels of power and authority associated with those levels. The work activities and the job descriptions are evaluated for the purposes of enabling the effective job assigning and allotment in the organization. An organization structure is composed of the following aspects as outlined by robbins.
- Strong relationship between the variables evaluated.
- The chain of authority and command.
- Individual tasks allocations.
- Corporate mission, vision and objective statements.
Management is the monitoring and adjusting the se activities in order to achieve the greatest effectiveness and efficiency in achieving the organization goal. It is very important because it involves the planning, organizing, controlling, monitoring, revising and modifying the organization operation to meet the expected objectives and expectations. These roles are integrated in the management and thus enable a firm to effectively coordinate all the resources optimally with the main aim of arriving at the organizations vision, missions and objectives. Performance management is the act of monitoring the progress on the corporate objectives and the ways of achieving them while management control is the process of monitoring these objectives and the adjustment of the organization activities which will facilitate the accomplishment of these corporate objectives. These two aspects have an advantage on the organization at large these advantages include;
- Performance management can build trust and improve the communication in all the areas of an organization, it can also promote similarity in the high level of the management, it can promote equity and recognize quality through financial and non-financial rewards and thus emphasizing on the direction of the organization and the total quality management.
- Management control basically establish the standards, action plans, performance indicators etc thus measure their success and also take corrective actions on the problems identified and thus the overall organization performance is achieved.
Principles of a good Organisation structure
Robbins described them as follows.
- The expectations of each individual is explained with clear guidelines on the job description.
- The flow of power and authority i.e. who is answerable to who?
- Tasks of each position or worker known.
- Managerial functions should be put in place.
- Performance appraisal mechanisms should be in place.
Types of organisation structure
Classical Form of Organization
The Simple Structure
This is a centralized for m of structure which is composed of two to three levels of management.
The Bureaucracy
This structure is characterized by an inflexible structure, highly standardized and an impersonal one. Max Weber (1947), considered it as an ideal form of organization dispensation in the early times. This form of organization is used by state organizations which have the strict following of rules and regulations as their major weakness.
The process of fitting the organizations operational strategy on the organization to make it work is referred to as organization design. It has the following functions in the organization;
- It helps reduce and eliminate the gap between the way the organization works and the strategy itself.
- The organization design sets out the decision making process thus establishing the levels of responsibility and accountability in the organization.
- It is composed of performance indicators which basically aim at achieving the organization’s objectives thus increasing its efficiency in its operations.
- Conflict resolution in the organization is also enhanced by the design since a chain of command is in place and thus accountability is increased.
The Matrix Structure
This type of structure arises where the bosses in the different functional scope can give orders to any employee. The managers are in the same level and the employees in the departments are responsible to any of the managers depending on the tasks being performed. This method can be the best due to its flexibility in the human resources. This approach has three broad types of structural forms are:
- Functional Structure
- Divisional Structure
- Adaptive Structure
Functional Structure
A functional structure is basically structure in the functional areas present in an organization e.g. marketing department, finance department etc. The activities are set in a manner in which they are allocated in similar units. This structure is advantageous since it has a specialization aspect in the organization and thus enabling the organization to attain the operational efficiency in the people. The top management has a link with the lower management in that they basically have the flow of information and authority. This method is usually suited to the small sized enterprises.
Divisional Structure
This applied in cases where the firms have different brands or operating in different locations or regions and the structure is based on these attributes. They are semi autonomous divisions which contribute to the profits of the organization. The division is carried out in the form of departments or product lines. It could also be based on the regions they operate.
In a divisional structure each division operates as an independent organization but contributes to the profit of the organization. The divisional management in this case has the authority to perform the strategy formulation roles in the divisions. It is usually a decentralization mechanism. Thus, it enables prompt decision making in the organization. The matters within the jurisdictions of the managers are well handled since they have the authority to make decisions. This structure is disadvantageous in that it has a huge cost and also it requires able managers to control the organization.
Adaptive Structure
Organization structures are often designed to cope with the changing environmental situations both in the internal and the external environments. This type of structure is referred to as adaptive structure. There are two types in structures.
- Project Organization
- Matrix Organization
Project Organization
The organization stipulates the project to perform without any influence in the normal operations of the business. These systems are normally used in the expansion projects. This type of projects is headed by the project managers and they are basically supposed to report to the chief executives.
This type is advantageous since it leaves the normal business of the organization undisturbed and is basically concerned with the completion of the tasks in time and the conformity with the standards set to achieve the set goals. The major disadvantage is that the functional managers may conflict with the project managers in the project implementation. The frequent shift or transfer of the labor from project to project may also affect its success.
Centralization and decentralization
In centralization little delegation of authority and control of the organizational decision making; power and discretion is based on the top managers who head the organization and they have exclusive authority in the organizational direction in terms of policy and strategy formulation. In small and competitive environments is basically the most efficient model.
Decentralization is the spreading of the decision making roles to the managers and the distribution of the production activities to other regions of the economy. The importance of decentralization is the transference of authority and control from top management to lower level managers. It gives the personnel directly related in the production make decisions and thus they influence the operational efficiency in the organizations.
Span of control and scalar chain of command
The span of control has an effect on a manager’s activities in that the effective coordination of the workforce require an accountability perspective which can only be achieved by the control abilities of the manager. The span of management usually depends on the type of work to be done so that the manager has sufficient time to supervise the workforce. A productive span of management should be dictated by the management and thus the managerial functions would identify the number of workforce under the managers, this is decided by the roles of the organization.
Manager’s ability to manage the workforce also varies from one person to the other and thus they should take responsibility for the more areas and the variety of work in the organization.
The nature of work and the capability of the employees determine the size of the span and thus the span of control vary with the nature of the work and tasks being performed in cases where there are wide levels of supervision and this would be able to facilitate the communication and information flow in the organization. A narrow span requires a large number of supervision levels and thus the flow of communication and information is basically lower.
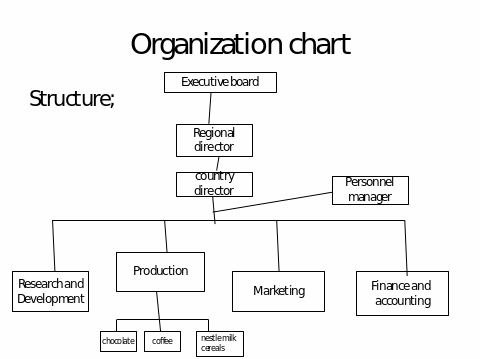
Organisation chart
Organisation charts are graphical representations showing the chain of control or the flow of authority with the specified tasks and functions of every position in the organisation. In most cases it is represented in a hierarchical format as follows;
Organisation culture
Definition of culture
The pressure of adopting a particular leadership style are seen through the effects of corporate culture and peer expectations, organisations usually have their values and they perform their duties in a certain way, this is what is referred to as organisation culture. Organisation culture is influenced by the powers of the managers and this will determine how they behave in the organisation.
Organisation systems can also be important in the influencing of culture in organisations in that for instance the control systems can influence the manner in which certain persons behave in the organisations. In the management of change the organisation needs to act in such a manner that the culture supports their organisation strategy and the leaders therefore have to take into account the different organisational cultures. In practice the organisation has three layers;
- Values; they are written as part of the organisations mission or vision statement establishing the interests of the organisation.
- Beliefs; they are more specific in terms of selection of maybe supplier, creditors etc
- Assumptions; they are unwritten culture but the stakeholders tend to follow them in the organisation e.g. interpersonal relations.
Types of culture
Culture can be seen in different perspectives and thus are classified in terms of their scope. Robbins described them as follows:
- Person culture is basically common in the animal protection organizations. Communes and partnerships.
- task culture is job or project orientated.
- Role culture is sometimes and previously referred to as bureaucracy.
- Power culture; It involves a powerful central character or leader e.g. campaigns groups.
Formation of a culture
Culture is developed or formulated in the initial stages of the organization existence and thus is more related the cultural back ground of the owners. Robbins advised that they can be outlined as:
- Owner/Founder
- The owner’s culture is incorporated in the organization
- Size
- Culture changes as the organization increases in size.
- Organizational Environment
- The environment is changing very fast both in the external and the internal environments and thus the organizations have to be very proactive in dealing with these changes.
- National Culture
- Function and Purpose
- The organization functions and purpose lies in the areas or the opportunity the business needs to exploit
- Goals or Objectives
- The corporate goals and objectives are incorporated in the culture formation to ensure that the organization is able to achieve them.
- Staff
- The staff and culture relation should be harmonious and thus not going against the population’s beliefs and thus should be well worked out.
- Technology
- The technological changes in the environment should be incorporated to the organization culture to ensure a smooth floe of activities in the organization.
Cultural socialization
Organizational culture is ever changing as environmental conditions change and as it expands to regions with different cultures. Culture socialization is evident when an organization is involved in a foreign business and when it has ventured in a region with a different culture and thus the organization has to adopt to the cultural differences and incorporate some of those cultures in its organizational setting.
Managers need to understand the culture to enable them drive the organisation in an amicable manner, this reduces the conflicts with the consumers, workers and governments in the regions of operation.
Behaviour at work
The characteristics of the human resource could influence the organization in a positive or a negative way. These characteristics influence its success or failures in the operations. Behaviour is described in the following aspects:
- Attitudes: they can be seen as favorable and unfavorable behavior towards an organization, department or persons.
- Values: personal values influence ones behavior at work.
- Personality; it’s the manner in which people think eel etc. It could be based on the following;
- Goals.
- Skills.
- Motives.
- Self image; it is the display of ones originality and individuality as it is bases on ones personality and education during his/her younger ages in the human development and growth process.
Team work
Definition of teams and groups
Groups are formed by a group of individuals with the aim of accomplishing certain objectives. A formal group is referred to as a team. A group is characterised with the high level of interaction among the members and their attitude towards accomplishing the particular objectives.
Nature of groups
The size and the composition of the group determine the success of the groups in the corporation and the coordination aspects. A group could be composed of many persons in number, ranging from 4 to several hundreds. An effective number of group members should be kept to maintain harmony among the members. Large groups have been characterized by different varieties of opinions and thus conflicts in the decision making pha
Group dynamics
It involves the relationship between the individual conduct and the attainment of group goals. Their compatibility, diversity, or expertise as the major determinants of the appointment of members to a group the different personalities in the groups should be dealt with in a manner that the harmony among the group members is maintained at a high level.
Tuckman’s role
Groups follow some stages before they attain a maximum performance level. These stages include:
- Forming: also called dependent stage, at this stage the members depend on the outside information and expertise to establish their roles and job descriptions.
- Storming: also called counter dependent stage. At this stage the group is able to formulate its own roles and responsibilities, operational rules and procedures which it will use in the operation of its duties.
- Norming: interdependence, cohesion, and group norms are developed in the members and this will help the organization operate in an amicable way in the future.
- Performing: after all that has been done the organization is positioned in such a way that the goals and the activities or tasks designed to steer the group towards attaining then is established and followed.
- Adjourning: this stage is when the group has completed the tasks assigned and the intended purpose and goal achieved.
Belbin’s role
The team roles are designed to achieve the organisation objectives as outlined by Belbin. Belbin outlined them as follows:
- The Coordinator presides; the coordinating roles are utilized to ensure that the objectives are achieved.
- The Shaper i.e. dominant approach.
- The Plant imaginative and innovation.
- The Monitor evaluator – spots flaws.
- The Resource investigator.
- The Implementer.
- The Team worker.
- The finisher.
Impact of technology in the functioning of the team
The term technology refers to the extent or degree in which an organization transfers its inputs into outputs. The organizations use these knowhow to produce thus using it as a competitive advantage over the other firms in the same or similar industry. It’s basically important in the flow of information and communication especially if the group members are located in different location within the organization. Documentation and the fast dissemination brought about in the group enables it process the results fast. In the event of conflicts the technology aspect can be applied in the conflict resolution mechanism and it would be great since the information got will not be jeopardized.
Organisation structure determines the organisation success and thus an important attribute to consider since it ensures the optimal utilization of the available resources. The macro and the micro factors in the organisations when dealt with in a manner that suit the situation will basically steer the firm towards achieving its corporate objectives.
In this section we will be looking at the organisation approaches with emphasis on the leadership, motivation and their applicability and relevance in today’s management practices. The past management approaches formed the base under which successive theories were developed and through them the management principles have been changing thus making these organisations more and more efficient and effective.
Approaches to management
Scientific management
According to Frederick W. Taylor, who was known as the “father of scientific management,” indicated that managers should follow four scientific management principles, which include:
- The element of work should be studies and the best way to perform the work established.
- The selection, training, teaching and the development of the workers should be of a scientific nature. This for of selection would make them optimally efficient and effective.
- The management functions should be well formulated to ensure an effective and efficient implementation mechanism.
- The division of labor approach should be used to ensure there is responsibility when it comes to accountability in the organization.
Taylor felt these principles could be used to align managers and employees by determining a description of the work and in specified amounts. What an average worker could produce at a reasonable time limits. What management should pay workers for that effort in the production process? He indicated that the incentive were the best way to align the workers to the organization goals and objectives.
Classical approach
Frenchman Henri Fayol’s (1841–1925) work experience significantly shaped his thoughts and ideas about management concepts. His management ideology was formed when he was a managing director in a company in France. Fayol is widely known for developing five functions of managers and 14 principles of management, as well as his belief that management is not a talent and could be thought to others and shape the management field.
Human relations approach
The human relations approach to management focused mainly on the psychological and social aspects of work in the organizations. In this approach the people are treated in a better way and not like machines and thus the organization values them more. The aspects of motivation, effort recognition in the work force made great impact on the production levels of the employees and enhance the relationships with their bosses, co workers and workgroup members. This approach insists that the management approach alone is not enough unless it is coupled with the human resource aspect.
Contingency approach
The contingency approach to management dictates that there is no universal management theories which are affective and efficient and that the most effective management theory or idea depends on the kinds of problems or situations that managers or organizations are facing at a particular time. The major implication of this approach is that management is harder than it looks. It is a complex way of dealing with the organization and the management needs a wide range of skills to enable them deals with the ever changing needs and the different risks facing the organization in particular situations. A second implication of the contingency approach is that managers need to look for key contingencies that differentiate today’s situation or problems from yesterday’s situation or problems. This tests their analytical skills in the analysis of the problems and situation and this will determine the manner in which they successfully solve or fix those problems.
Bureaucratic approach
German sociologist Max Weber (1864–1920) proposed this idea of bureaucratic organizations to the business world. It was basically referred to as red tape in the US. This approach was associated with monarchies and patriarchies, In monarchies, where kings, queens, sultans, and emperors ruled, and patriarchies, where a council of elders, wise men, or male heads of extended families ruled, the top leaders typically achieved their positions by virtue of birthright.
Comparison of the approaches to an organisation indicating the approach they follow
Bureaucracy is probably one of the common approaches used by governments and public enterprises e.g. the military, police etc for instance the military is in today’s management associated with these attributes and due to its nature of operations and the sensitivity of its activities it is probably the best approach to use to ensure that there is high level of discipline and commitment to the organizations.
Managers should be able to apply their managerial skills especially in control and influence the employees in the following of the organization’s procedures, rules and regulations. This approach is said to focus more on the punishment part and not the rewarding side of the coin. This approach makes the employees conscious of the consequences of breaking any of those regulations. This approach is characterized with high level of discipline and the military is the best example of a bureaucratic organization.
Definition of leadership and leaders
Managers as leaders in the organisations in times of change are expected to be proactive and not reactive, Various factors outline their ability to manage effectively and define their individual style of management, their functions can be outlines as; coaching and supervision of personnel, controlling financial and human resources, delegation and organizing of functions and activities, leading others i.e. act as a role model, managing work, planning and scheduling, and motivating and employee appraisal.
The manager’s role must be coupled with the thought that all these functions are influenced by both the internal and external changes. Leaders consider three factors when making decisions in their organizations these factors include;
- He considers his own experience, inclination, confidence, and his background.
- The willingness and the unwillingness of the subordinates to accept responsibility is considered in decision making.
- The situation of the organization in terms of corporate culture, time available, style of work and the tasks to be performed are also important.
The situation in the organization will force the organization adopt to change. The situation comes with other factors i.e. pulling and pushing factors and the organization should position itself to a flexible state where it can accommodate those factors.
Qualities of a good leader
A good leader possesses the following qualities;
- A leader should be trustworthy and commendable to extemporary issues.
- Enthusiasm is one of the traits a good leader should poses to ensure that he maintains the cause of the people.
- He should be disciplined and orderly in nature and should be able to tolerate fellow workmates when they make mistakes.
- He should pose academic skills in logical and analytical aspects.
- Should be goal focused and proactive with high commitment to objective achievement.
- Should be able to manage change and any environmental uncertainty at all times in the organisation.
Approaches to leadership
Scholars in the past have come up with various theories of leadership and management of organization in times of change, they range from traditional views to the relatively new theories which insist on situation to any universally desirable set of attributes, some of these theories include;
Leadership approaches in the past have been developed and can be used in the modern organisational setup. Some of these approaches include;
Situational leadership model
This approach depends on the readiness of others in the performing of the organisations tasks. In this theory the underlying argument is that the managers need to vary their approach too incorporate the needs and expectations of their followers. In this theory the analysis is done on four quadrants which can have the following properties;
- In quadrant 1 the employees are unwilling and resisting any form of direction and control and thus not giving the required productivity or returns. In this stage they should be directed and in any case they should be closely supervised and the negative elements in them eliminated.
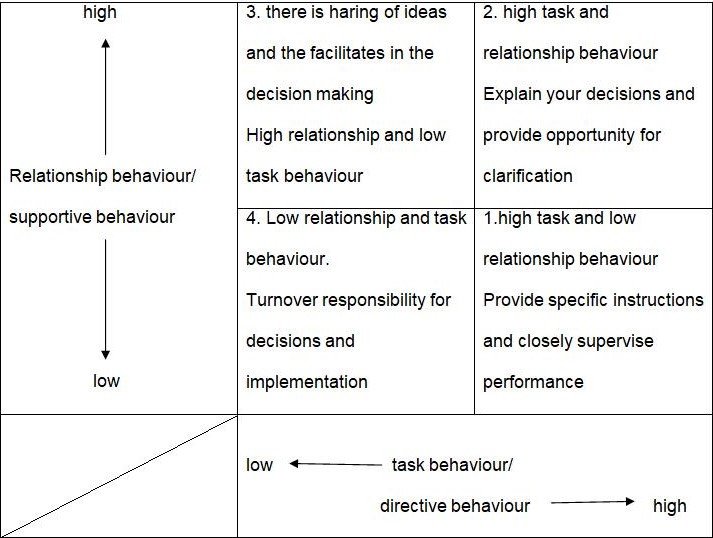
- In quadrant 2 the situation is characterised by high task and relationship behaviour and in this case the leader should explain the decisions and provide the opportunity for any form of clarifications.
- The third quadrant is designed to sharing of ideas and thus facilitate decision making where all the stakeholders views are considered, it is characterised by high relationship behaviour and low task behaviour.
- The last quadrant i.e. 4 is characterised by both low task and relationship behaviours and this section is very efficient since a certain level of delegation is required and can be implemented.
Leaders are supposed to poses the highest degree of versatility and competence to handle the environmental issues. Leaders have a tendency of accepting responsibility for what happens in the organizations in that it’s viewed as an area where hard work and consistency is required in the organization. Since leadership is a function that sets direction and in a changing environment it becomes very essential. Leadership skills enable the management implement their goals, visions, missions and objectives efficiently thus the organization cannot survive without leaders. They include;
- Leader-member Relations: this can be describes as the trust the employees have on their leaders. This is the most important factor in the leader’s effectiveness.
- Task Structure: it measures the degree of procedure stipulations. It measures the complexity and the simplicity of the tasks to be performed in the organization.
- Leaders’ position Power: in this position the ability to control and coordinate the workforce is used.
Managers using situational leadership approach will make conscious decision choices between their use of directive behavior and supportive behavior in the management of the organization.
Management Grid
Leadership is a multidimensional approach, this grid shows the different ranges of management behaviors based on the various ways the task oriented and the employee oriented approaches are interacted together. This grid can be illustrated as follows;
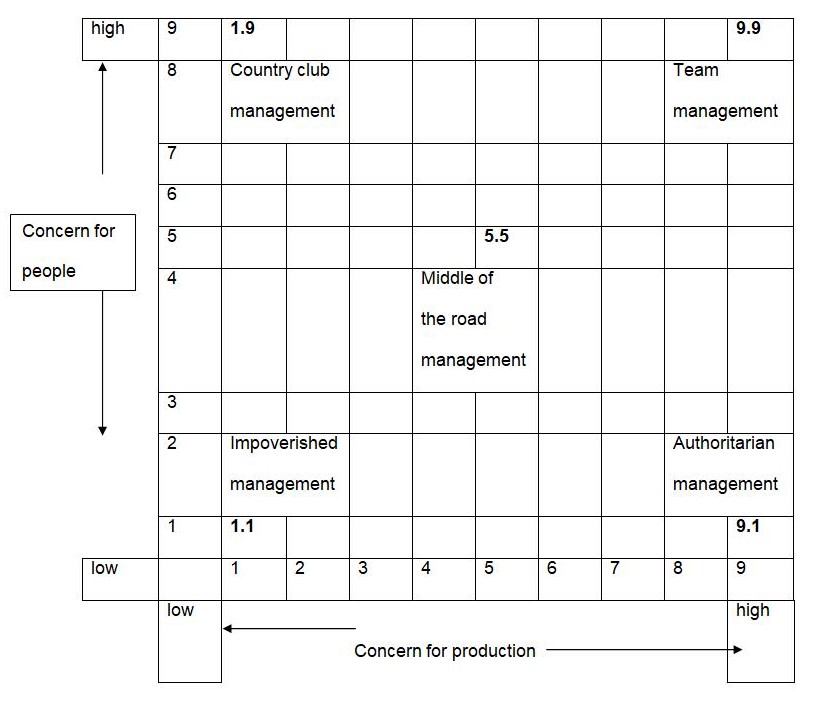
In this grid formulated there are 81 possible outcomes or interactions and there are five extreme positions namely;
- Country club management; this section score the highest on the concern for people or human resources and lowest on the concern for production and production related activities. The level of satisfaction is very high in this section and is appropriate in areas like clubs, voluntary cooperation etc which involves a lot of contact with the people in the operational level. In this combination the member’s satisfaction level is very high and mangers are perceived to be incapable of making decisions.
- Authoritarian management; this combination scores high on the production level and the efficiency and scores low on the concern of the people. It is basically task oriented and insists on the quality of the decision over the wishes of the middle level managers and subordinates. In this level the subordinates perform the assigned tasks and in some cases they may be unable or unwilling to put extra effort as long as they achieve the set limits.
- Impoverished management. This method believes in laissez faire since it does not give leadership in a positive sense.
- Middle of the road management; this combination scores the most moderate amounts of all the aspects of the organization i.e. its concern for both people and production is moderate. Those applying this method believe in compromise since the decisions are only taken when all the stakeholders in the organization endorse them. These managers and leaders may be dependable and supportive but may not be the best in times of innovation and change.
- Team management; the managers believe that the combination of these concerns is the most compatible since they give satisfaction to workforce as well as meeting the production targets.
Contingency approach
The theories of trait and behavioral leadership approaches indicated that the leadership success depend on many variables e.g. personality, attitudes, leadership and management styles etc. Managers will look at the different factors which influence their leadership choice and this is put into consideration in the practical considerations. This theory describes three components in deciding the leadership style;
- Personal forces from within the person in terms of experience, confidence, own back ground and inclination.
- The characteristics of subordinates in terms of accepting the responsibility and decision making ability.
- The situation facing the organization determines the corporate culture, the style of roles and the nature of activities being taken and in the required time frames.
Contingency approach indicates that the manager should consider all the options in the organization to determine the actions to take i.e. the management style demonstrate the self fulfilling prophecy of the extent in which the management style determines the choice of action.
Evaluation of a leadership style with the help of an existing leader
Contingency approach to leadership and management style, organizational culture and the nature of tasks being performed Managers will look at the different factors which influence their leadership choice and this is put into consideration in the practical considerations. At Mc Donald’s the US operation which is headed by Janice L. Fields as its president and the chief executive officer has been applying this approach in her management. She has been applying the contingency approach to her management style in the US.
Since her employment she has been very flexible to the changing needs of both her workers and her consumers and since this is a food company the prospects of quality and marketing are the determinants of the success of the business.
The tasks performed in the over 14000 outlets she manages has enabled her choose this style or approach to manage the organisation and she has received several awards for her extemporary management and leadership style e.g. she was named the Forbes’ 2008 and 2009 etc.
Definition of motivation and motivational theories
Motivation can be referred to as the re-evaluation and the activation of the employee’s morale and attitude towards a specific job by using many ways e.g. giving rewards, promotions etc. Motivation theories are the theories or suggestions by scholars on the best ways to achieve the status of employee satisfaction in an organisation.
Types of motivational theories
Motivational theories are important for the understanding of management since they help the organisation identify the best ways to deal with their employees and the ways to motivate then effectively. Motivational theories enable the organisation utilize its workforce since they are able to formulate strategies which would motivate then thus optimal productivity could be achieved. They include;
Content theories
Maslow (1954) that the theory is designed in sequence from the lowest level to the highest level in the pyramid. In case an employee is satisfied in one level of the hierarchy he moves to the higher level with the change in needs until he reaches a peak level of self actualization.
- Physiological needs.
- Security needs.
- Social needs.
- Self esteem needs.
- Self actualization.
This theory indicate that the employees expect more from their employers in terms of career growth and development and thus this approach has been adopted by many organizations in the promotion processes. Their needs are said to follow the pyramid of needs as shown above and this is assumed to be the trend in all the employees thus this is used as a fair mechanism for promotion purposes. The greatest challenge arises in the part of identifying the stage in which the employees are in the pyramid so as to adequately develop their careers.
The need theories are concerned with the employee needs in the organization setup and how they can be managed to ensure employee satisfaction in the organization. These theories try to explain how the people’s motivation changes over time and attempts to classify the human needs. These theories have an important implication to the managers and give them an opportunity to motivate their employees by different ways like job design, management styles, compensation etc. The following their practical implication;
- Need theories require a satisfaction of the physiological needs and thus the organization should design its programs to try and fulfill these needs e.g. sufficient wages, lunch breaks etc.
- The organization should be able to provide a good working environment which is safe and secure by e.g. proving retirement benefits
- The sense of community in the design by maybe working in teams will fulfill their social needs for instance.
- These theories provide a framework for employee recognition in cases of hard work and extemporal performance and thus their self esteem is boosted. This translates to the huge output.
- The theory outlines the different needs of the employees in the hierarchy and thus the changing needs in the organization’s workforce should not be ignored because they enable the employees perform at their full potential.
Alderfer (1972) in his contribution to motivation theory suggests that individual needs could be summarized and divided into three groups:
- Existence needs; these are the needs necessary for their survival e.g. nutritional and material requirements. And in the case of a working environment could be remuneration and security or safety in their tasks.
- Relatedness needs; these are basically interaction needs which could be with the fellow workers or in relation to their families and thus a work-life balance should be adopted to ensure all these needs are met.
- Growth needs; they may be in form of personal psychological developments, this ensures that the employees are satisfied in their roles and thus this will reduce the conflict between the management and the workers.
Process theories
Adams (1965) and others describe process theories especially equity theory as one of the most useful motivational frameworks ever formulated. Valence, instrumentality and expectancy (VIE) theory was got from Vroom’s (1964) work into motivation theories. He tried to link reward and effort and thus explained the need for effort recognition in organizations and rewards given on the same. The individual’s abilities, traits, role perceptions and opportunities are used as a motivational force towards mobilizing the workforce t produce at optimum levels. The expectancy theory acts as a reward mechanism for the motivation of the employees in the organization. This theory is important in that it identifies which rewards the employees value for particular course of actions and it bases its analysis on the fact that the level of performance vary with the need for achievement and the reward to be given.
The main contribution of both equity theory and Valence, instrumentality and expectancy (VIE) theory is to highlight the major effects of cognitive and perceptual processes on objective work conditions in the organizations. It suggests that subordinate’s perceptions should not be ignored by the managers and thus they should be looked at with more attention:
The past theories of management are still relevant to days managers in that they are the back ground under which the management policies are based and can be useful in following ways;
- They help in the prediction of the organization trends.
- They help in the understanding of the present situation by giving the background for the interpretation of what is happening and why.
- Some theories are based on the research and they are used as a basis for actions in the organization. The understandings of the management theories help the managers predict the relationship between variables.
- They help in the development of the best practices in the management of the organizations in modern society.
Goal setting theory incorporates the notions of the expectancy theories with the other forms of motivations to increase the performance of the employees and is currently the most influential approach. It has the following applications in the organization as indicated by Robbins:
- The broad goals set in the theory will enable the people interprets their performance in against a variety of the indicators thus output is basically increased as the satisfaction increases.
- The STRECH is one of the applications whereby the organization sets up unrealistic targets which may appear to be absolutely impossible to achieve thus influencing the employees thinking by making them work harder thus enabling innovation, asset utilization, performance improvement etc.
- There should be measurable goals i.e. goals whose success can be determined by the organization, this will boost the innovation, asset utilization and performance improvement.
- Goal setting will basically guarantee attainable goals to be attained in reasonable time periods with the consideration of the contingency factors affecting this theory thus enabling it have the best results.
Application of these theories to organisations with emphasis on the theory my organisation follows
Most organisations follow the Maslow hierarchy need theory in the management of their human resources. In the communication giant Vodacom UK this is the approach they use even though it is a modified version of it. The growth of ones career at Vodacom is gradual and they give all their employees the opportunity to achieve the full potential in their areas of expertise. The growth of the employees skills through the frequent training programmes has enabled the company have a workforce which can grow up the ladder and become the leaders of tomorrow thus maintaining the organisations competitiveness in the market.
This approach works well in the motivation of the work force in that it reduced the rate of workers turnover since their needs are met as they grow and change from the lowest level to the highest level in the pyramid. It is evident that most of the employees of Vodacom have been growing in their needs and the organisation has responded effectively and thus enabling it to achieve its corporate objectives.
Recommendation on the suitable theory for my organisation
Valence, instrumentality and expectancy (VIE) theory is the most efficient theory to apply in today’s organizations since it observes the employees abilities and their needs and the ways their needs can be used to influence their performance thus giving the organization optimal productivity. In the theory Vodacom has tried to incorporate or modify its motivation theory with this one and thus the best mix may be achieved in the long run.
Conclusion
These theories imposes the skill variety, task identity and significance of motivation to influence the employees experiences meaningfully and thus increase the personal responsibilities thus the more the satisfying or motivating job the more the productivity. The job designs when incorporated with the motivational and reward theories will come up with the best mix for the organizational success since they are moderated by factors such as the individual differences in personality, confidence levels and ability as well as the presence of quality of the organizational support systems.
References
- L. Mcshane & M Von Glinow, Organizational Behavior, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi (2005).
- M Jennifer, George & G Jones. Understanding and Managing Organizational Behavior, Addisson, Wesley Publishing Company, New York. P. 56.
- M John, Ivancevich & T Matteson, Organizational Behavior and Management, Irwin, Chicago. 2006. p. 77.
- P Robbins, Organization Behavior, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi. 2007.
- R Dwivedi, Human Relations and Organizational Behaviour – A Global Perspective, Macmillan, Delhi. 2004. p. 112.
- W John, Newstrom & K Devis, Organizational Behavior, Tata McGraw, Hill Publishing Company Ltd, New Delhi. 2001.
- Kalian-city blogspot.com. Organization structure. 2010.