Define and explain information system as an organizational and management solution
Information system is defined as a consistent, coordinated set of mechanisms acting together with the objective of production, distribution and or processing of information. By using this definition, precision for generality is ignored but in doing so, an emphasis is laid on computer information systems, networked information systems, biological information systems among other various contexts (Ratzan 2004 p.1).
In this context, a system is taken to refer to a consistent, coordinated set of modules working in unity toward achieving a common objective. These mechanisms of a system must work together. When referring to a system, it could either be adaptive or non-adaptive.
Adaptive system has a capability to modify itself to suit in the environment. On the other hand, a non-adaptive system does not need to modify itself to fit in the environment it operates in; instead, it operates independent of its external environment.
Information can be hard to define unless we do so in terms of its characteristics-information is objective, subjective, temporal, ephemeral, and fungible, not reduced by giving it away, not always additive, both a process and a commodity, and is measurable.
Increasing complexity in information and technological solutions have resulted in the rise of e-commerce, the automated office, teleworking and the information ‘super highway’ all forming the facts of organizational life (Perry 2008 p. 3). As a result of these changes, information technology and information systems have become vital aspects in the management of modern organization.
Unless we appreciate how information technologies are used and the numerous ways in which they are structured to form a system, it may be difficult to understand how information systems operate within organizations.
The computer
Understanding computer system configuration is essential in relating how they can be used to support organization’s information communication requirements. A computer system is made up of number components which include the hardware and the software.
The hardware components of a computer include the central processing unit, screen, a printer, a keyboard, a mouse, and a scanner (Lucey 2005 p.24).
The CPU is the heart of a computer system. The CPU comprises of three different elements;
The control unit-this part directs the operations of the entire computer system. It is in the form of instructions that are made up of codes identifying the operation to be performed.
It also contains the data to be to be utilized in the operation which is copied from the main storage to the control unit. In general, the control unit; reads and interprets program instructions, directs operations, and controls the flow of operations and data in and out of the memory.
The arithmetic logic unit-implements operations identified by the control unit.
Main storage- provides a storage place for instructions and provides area for storing data processed by the program.
Input devices are the communication link between the computer and the user. This are regarded as the main aspects of the human/computer interface. These devices include the keyboard, mouse and trackball devices, voice data entry, and light pen and touch screens.
Data capture devices allow input of large volumes of routine data, they are; optical character recognition, optical mark recognition, scanners, magnet ink character recognition, bar code readers, and digital cameras.
These whole ranges of these devices have particular importance in solving management and organizational problems. Optical character readers are used in pre-printed fuel billing whereas optical mark readers can be used in multiple choice marking on a questionnaire during staff selection process.
Scanners find an application in web page creation and desktop publishing. On the other hand, magnetic ink character readers are essential in banking documents and in chequebooks. Digital cameras are applied in new paper or corporate documentation photography.
Output devices -hard copy devices-printers and plotters-are the commonest forms of output devices. Audio output devices such as speakers provide sound output often from CD-ROM or other voice recording (Reilly 2004 p.4).
Storage devices- majority of computers have two types of storage-main memory and the backing storage. Backing memories include the CDs, flash drives and DVDs.
Software components of a computer system are mainly concerned with the hardware (output speed, storage capacity, speed and cost of processing) software component of the computer brings the hardware to life; it controls the hardware. Additionally, software determines the ultimate characteristics of a system and its successful operations.
Software falls into two broad categories-systems software (provide basic operations services) and applications software (carries out specific user requirements). The system software constitutes operations system, utility programs, and communications software.
Applications software performs specific personal, business or scientific processing tasks like word processing, sales invoice processing, tax planning, product design, desktop publishing, financial planning and entertainment.
Computer networks
Computer networks star networks, ring networks and tree networks. Network components include the local area networks which has five components such as network hub, work station, a file server, print server and a communications server.
The internet- this is a public and global communications network that provides direct connection to users over a local area network. Anyone has an access to the internet. This has resulted in
unruly propagation of information. Some common internet tools are the e-mail, world-wide-web (WWW), social networking (Facebook, twitter, LinkedIn, and blogs), newsgroups, chatting, e-conferencing and file transfer protocol. Some benefits of the internet to the organizational management include:
- Online surveys.
- Access to competitors information.
- enhanced communication.
- improved relations with business partners.
- Potential access to prospective customers and markets.
- Innovation in new products and services.
- Business platform (e-commerce).
- Online business contracting.
- Virtual organizational development.
Intranet, which is an organizational network, allows confidential internal information sharing. This may include corporate policy, document sharing, telephone directories, training programs, and so on. Other importance of intranet entails the facilitation of intrabusiness commerce such as internal buying and selling and internal recharging (Perry 11$$).
Extranets are extended intranet of an organization that links to its business partners such as suppliers, customers. The extranet enhances inter-organizational communication, facilitates electronic data interchange and e-procurement (Owens & Abel par 2).
Automation of the office and the workplace has affected how and where employees work. Computers, communication and network technology has revolutionized organizational operations. Data, text, image and sound have been combined into office build multimedia systems.
Teleconferencing and videoconferencing
Organizations are now able to conduct meetings, business negotiations and presentations without its participants having to be at the same location.
This saves organizations money as it does not have to move participants to the venue of the meeting. Videoconferencing overcomes the setback of lack of identification and recognition experienced in teleconferencing. The message saves on time and cost for the participants thus ensuring timelier decision making.
Businesses are using the internet to advertise, trade, and search for information about competitors, customers and suppliers. The use of electronic mails has become a primary form of communication for organizations. The method is easy to comprehend, is speedier, versatile, and eliminates the issue of distance and has a potential for immediate response.
In addition, e-mails reduce the volume of paper movement through the electronic transfer of graphical and textual information. Some organizations still use the facsimile machine due to security reasons.
Terms such as e-commerce, e-business, digital economy have transformed organizational aspirations as they seek to join the global marketplace. By using the internet, companies have an opportunity to gain competitive advantage by creating business models and in finding new ways of doing things. In general, advancement in information systems has led to the death of distance as an impediment to communication; businesses make savings and operate differently due to the reality of virtual organizations; and financial planning, control and evaluation have all been eased.
Environmental and industrial analysis
Organizations’ environment includes both the internal and the external. Internal environment refers to those internal factors that influence an organization from within its boundaries.
Externally, there are three layers of influence; competitors and markets, industry or sector, and the macro environment that comprises of the political, social cultural, technological, legal, and environmental. In the organizational sense, environment will be defined as those elements existing outside
The firm is going to operate in an uncertain external environment. The only way we can survive as a consulting and accounting firm is by continuing to grow through improvements in service delivery. Unless we tailor our services that suit our clients, then, the huge investment that we have made will not pay off. We must be in a position to quickly adapt to shift in the environment, changing consumer interests and innovative technologies.
As it is hard for us to avoid the external shock, we have to strive to be flexible and well-structured to emerge unscathed from the turbulence. These threats will impose significant constraints on the choices we have to make as an organization.
The creation of the internet and its related technologies has sunk the barriers of inter-organizational collaboration. The result of this move is the emergence of virtual enterprises network (VENs), which are consortiums of enterprises that bring together their skills and resources-under the support of computer networks.
The internet has enabled companies to share information in the process improving their agility and broadening their possibility to better reaction to market changes. However, organizations have a choice to make, they can either be VEN or not. Organizations within VEN face multiple challenges in addition to those other independent organizations face.
This is because individual firms have their core competencies, aims and resources different from those of its partners. Majority of firms ignore this arrangement due to the associated challenges (Filipe& Cordeiro 2011 p.49).
In the changing IT world, traditional information specialists are currently playing a decreasing role in information dissemination. Majority of organizations now have IT personnel who are tasked with storage and retrieval of information. To be successful, senior staff is now taking information management issues on board.
Internally generated information has gained more emphasis especially on leading firms as competitors are expected to follow on their suit. Organizational models have developed interconnected variables such as the external and internal organizational factors that influence business success and execution of successful information systems as shown in the diagram below.
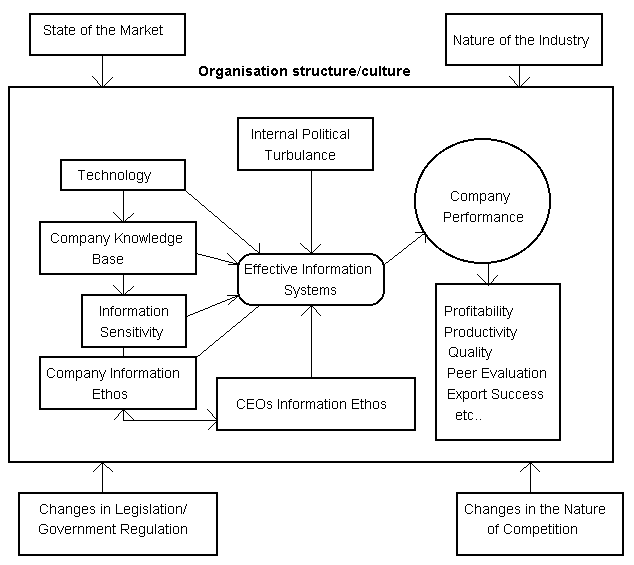
In this model, unlike the traditional model, encompasses aspects such as; the state of the market, the nature of the industry, changes in government legislation, fluctuations in the form of competition. Because these factors are external to the organization, they are crucial in the organization’s internal structure and on its success.
In today’s world, organizations are operating in an environment that lay emphasis on “empowerment”, “learning organizations” and that thrive on chaos. There are numerous calls for organizations to downsize, be focused, emphasize on total quality, quality teams, and supplier partnerships. Today’s organizations are networked and apply performance-based pay.
They also exhibit local autonomy. As an example, modern manufacturing firms are highly complementary. They also have a tendency to alter organizational qualities one at a time thus making the transformation from one model to another difficult and complicated.
A Common view is that change must occur simultaneously with several other related dimensions if organizations are to be successful. Adopting one or two components of the new model make organizations fall due to lack of complementarity. The new organizational model is linked with the structure of firm’s information systems.
Unlike in the traditional models where organizations were governed by relatively unbending functional structure, the separation intertwined with modern organizational paradigms emphasizes on well-defined organizational units that economize on information and communication requirements. This requirement of functional units of information and communications lowers costs and complexity considerably.
The growing use of IT and the move towards networking have had an impact on organizational transformation. The cost of horizontal communication has been cut whereas team working has been enhanced. Additionally, flexible service delivery and provision of information support for management of time have been made possible. All these have enhanced service delivery (Daft 1998 p.45).
Recommend information system for the firm
A variety of information systems exists; these are-
- Office information system-uses hardware, software and networks to improve work flow and enable communication among the employees. In this system, also termed as office automation, workers perform their tasks electronically with the help of computers and other electronic devices.
- Transaction information system- captures and processes data produced during a firm’s day to day transactions such as recording business activity, confirming actions and maintaining data.
- Management information system- generates accurate, timely and organized information so that users can make important decisions, solve problems, and control and track activity progress.
- Decision support system-are designed assist users make decision when situations demand so. This system utilizes data from internal and external sources.
- An expert system captures and stores knowledge of human experts, emulates human thinking and decision making processes for the less knowledgeable. These systems have two main parts; knowledge and inference components.
- Integrated information system-is a combination of all the above systems to meet various needs of the users.
Integrated information system (OIS)-the Accounting Information system (AIS)
An accounting information system processes financial and non-financial transaction that impact on the processing of financial transactions (Cashman par 1). Accounting information system has three vital subsystems;
- The Transaction processing system-this supports the daily business operations of an organization that handles many reports, documents and messages.
- The general ledger/financial reporting system-generates the traditional financial statements such as income statements, cash flow statements, tax returns and so on.
- The management reporting system- provides the internal management with special purpose financial reports and other vital information necessary for decision making.
Management information system enables a complex and specialized organizations in making decisions. Our firm requires additional information to be used in consulting, planning and in control.
Transaction processing system- this will form the mainstay of the organization information system. The system will assist in converting economic events into financial transactions, record financial transactions and distribute important financial operations to daily functioning.
As an accounting firm dealing with thousands of financial and income statements, the transaction processing system will enable our firm deal with such volumes efficiently. Operations of similar nature could be bundled together into transaction cycles. In essence, transaction processing system has three cycle; the revenue cycle, the expenditure cycle and the conversion cycle.
The general ledger/Financial reporting system- these are two closely related subsystems. However, these two systems operate interdependently making it necessary to combine them. The general ledger processes the summaries of the transaction processing system. On the other hand, the financial reporting system (FRS) reports the status of the financial resources.
This is the system that communicates the information generated to the external users. This will be a very vital system of the firm as it provides traditional financial statements, tax returns and a variety of other legal documents necessary for both our accounting and consulting domains (OZ 2000 p. 34).
Management reporting system (MRS)-this system will be of crucial importance for the management’s internal financial information necessary to the management of the firm. The system will assist the managers to deal with day to day business problems and also plan and control their operations.
It will act as a source of information from where the managers and user will base their decisions and therefore their consulting resource. Using this system will enable the generation of budgets, variance reports, cost volume profit analysis and other reports made using the current data. The system is subject to the user’s choice as one can choose the information to report and how to present it.
The general model of accounting information system
AIS have several elements which include the end users, data sources, data collection, data processing, database management, information generation and feedback.
End users
These could either be external or internal. The external users include the creditors, stakeholders, potential investors, regulatory agencies, suppliers and of course our esteemed clients.
Internally, the end users will include the management at all levels, operations personnel and other employees. Internal reporting using the integrated reporting system will be governed by what gets the job done. It will be less structured than external reporting.
Data sources
These are financial transactions that will enter the information system from either the external or the internal sources. The external financial transactions will form the majority of the data that the firm will handle.
These will entail the economic changes within other businesses that our firm will be handling during its day-to-day transactions. Internal financial transactions will entail those financial transactions occurring within the organization.
Data collection
Data collection forms the initial operational stage in information systems. The objective of data collection is to ensure that only valid data enters the system. This data should be error free and complete. Data collection procedures are governed by two vital rules; relevance and efficiency. This is because the information system must only capture relevant data.
Otherwise, the firm will disappoint and lose its clients if erroneous reporting is done or when a client is wrongly advised. The task of analyzing what is and what is not relevant falls on the hands of the system designer. The designer can only do this by analyzing the needs of the user of the data.
Because only relevant data results in relevant information, the firm should use this system to ensure that data collection stage is designed properly to filter irrelevance from the system.
Data processing
This is yet another important element of AIS that ensures timely delivery of correct and consistent information. Upon the collection of data, processing is essential for information to be generated. The tasks in this stage range from simple to complex.
Example of data processing tasks are mathematical algorithms, that are applied in scheduling applications, statistical techniques and other summarizing procedures necessary in accounting applications.
Data management
Accounting is all about data management and data processing. Data is stored in an organization’s database which is a physical repository for financial and non-financial data.in modern information age, data bases are mostly computer disks.
Data attributes
By utilizing the AIS, the firm will be in a position to ensure that data stored in its repositories is logical and relevant. If the firm is working on the account receivable of its clients, the data it has must possess the correct attributes.
The attributes relevance is mirrored in the information content of the whole data set. This is important because the firm will be able to report to its clients on the basis of attributes of the data it worked on. The absence of a single data attribute destroys the information content of the data set (Stair 2002 p.5).
Recording
This is another essential element of AIS. Record is defined as a complete set of attributes for a single occurrence within an entire class. To maintain proper records, the firm must record customers’ names, address and other details to avoid mix up. For proper recording, AIS maintains a unique attribute for every record for ease of retrieval.
Data management task
Managing customer’s data entails three basic tasks; storage, retrieval and deletion. AIS storage tasks assigns keys to new records which are then stored in their proper location in the database. The same system makes locating and retrieval of this data from the database for processing very simple.
Once processing is complete, the same storage task updates the data and restores it to its original database or a different one depending on user’s choice. The user can use this very system to delete obsolete or redundant records from the repository. Such is the ease with which the firm will find data management on using the IIS.
Information generation
This refers to the process of compiling, arranging, formatting and presenting information to the clients. This information could be in the form of sales orders, reports, or even messages. By using IIS, the firm will enhance the relevance, timeliness, accuracy, completeness and summarization of the data presented to the clients.
Objectives of the AIS
There are three fundamental objectives of any information system;
- Supporting the stewardship of the firm.
- Support the management decision making.
- Support the firm’s day to day operations.
Acquisition of IIS
The firm can acquire its IIS in two easy ways;
- Developing customized systems from scratch.
- Purchasing programmed commercial systems (turkey systems, backbone systems, vendor supported system).
Because this firm is large and unique, I suggest that we engage in in-house development.
The accounting function of the AIS will enhance the management of the financial information resource of the firm. It will play two important roles; it will capture and record the financial effect of the firm’s transaction and then distribute the transaction information to the operations personnel. The whole range of the system will assist in presenting relevant, complete, and error-free information
Conclusion
Information system is defined as a consistent, coordinated set of mechanisms acting together with the objective of production, distribution and or processing of information. The computer is the mainstay of information systems. Understanding the various components of a computer is essential if one is to understand information systems. Computers have the ability to network with others and share information.
The internet has profound benefits to the firm in modern information world. Organizations’ environment includes both the internal and the external. Internal environment refers to those internal factors that influence an organization from within its boundaries. Firms have to adapt to their external environment in order to survive the turbulence. Various information systems do exist.
The best system for a consulting firm is the integrated information system. This system helps managers in running firms, support decision making and assist in day to day running of the firm.
Reference list
Cashman, S., n.d. Types Of Information Systems. Web.
Daft, R. L. 1998. Organization Theory And Design (6th ed.). Cincinnati, Ohio: South Western College Pub.
Filipe, J., & Cordeiro, J., 2011. Enterprise Information Systems 12th International Conference, ICEIS 2010, Funchal-Madeira, Portugal, June 8-12, 2010, Revised Selected Papers. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Lucey, T., 2005. Management Information Systems (9th ed.). London: Thomson Learning.
Owens, I., Williams, T., & Abel, A. n.d. Information And Business Performance: A Study Of Information Systems And Services In High-Performing Companies. Information Research: An International Electronic Journal. Information Science, Information Management, Information Systems, Information Retrieval, Digital Libraries, Information Seeking Behaviour, Information Seeking Behavior. Web.
Oz, E., 2000. Management information systems (3rd ed.). Boston, MA: Course Technology.
Perry, B., 2008. Organisational management and information systems (5th ed.). Oxford: CIMA.
Ratzan, L., 2004. Understanding information systems what they do and why we need them. Chicago: American Library Association.
Reilly, R. T., 2004. The handbook of office automation. New York: IUniverse.
Stair, R. M., 2002. Principles of information systems: a managerial approach. Boston, MA: Boyd & Fraser Pub. Co.