Introduction
The video streaming industry is comprised of a variety of internet-based platforms, hosted and managed by different companies, for the purposes of providing the general public with access to educational and entertainment content. With a variety of service providers having emerged in the recent years, it can be said that the industry has been experiencing rapid growth and development. With a number of specific brands, namely Youtube, Netflix, Prime Video and Hulu dominating the market, newer sources of video streaming are still created rapidly, giving people access to various types of content on a subscription basis.
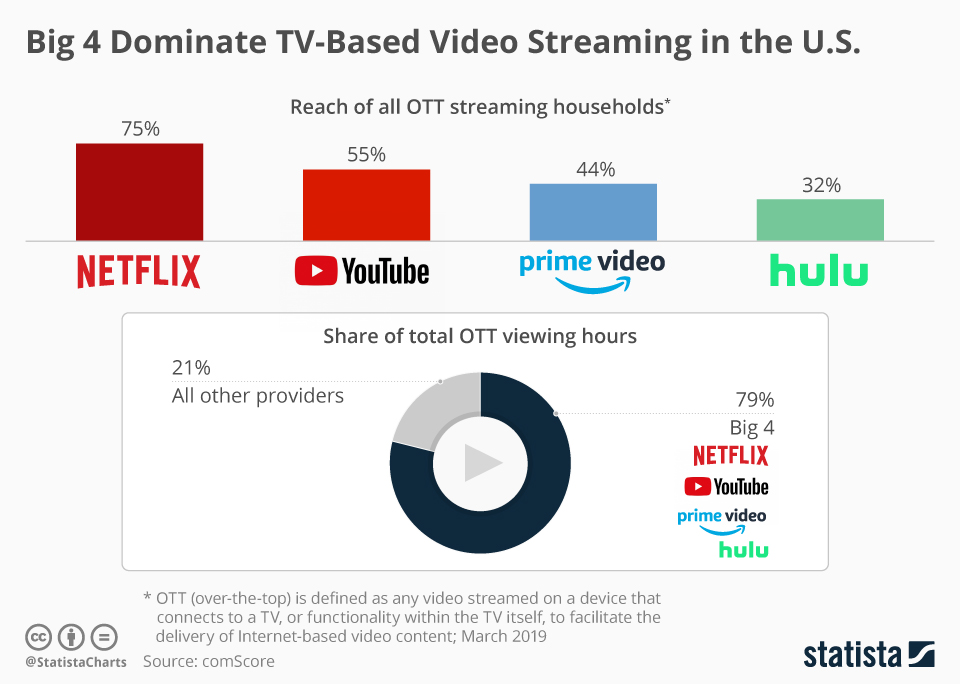
With the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, this part of the global market has enjoyed an unprecedented boom in popularity, with many people needing access to entertainment. The increase in popularity, mainstream awareness and profits is what has contributed to the interest investors and regular people have in this industry. In the light of this, the present report seeks to review and discuss some of the major trends in the video streaming industry. A discussion of some of the current developments will be presented, supported by relevant and contemporary research present on the topic.
Background
With the emergence of internet and the increasing availability of personal computers, people have gained an ability of using the internet for entertainment. Before the advent of streaming as it is known today, people mainly either downloaded films off the internet, bought hard-copy versions, or rented them from specific stores. The internet technology was in its infancy, barely managing to load internet pages and images, or download content. Computer drives and hardware was extremely limited as well, in its space, speed and processing power. This meant that the process of watching a movie using the internet or one’s computer would most likely be either impossible or tedious for an average consumer. That meant that the main way of consuming media was to rent or buy either disks or cassette tapes, or go to the cinema for a screening. With the development of internet as a medium, as well as the advancement of technology, however, new opportunities for content distribution and acquisition became available. People have gained an ability to watch pre-uploaded videos online, download bigger files at faster speeds, as well as buy digital copies of films. In a few years, internet connection and transmission technologies have improved even further, giving both an average user an tech companies a new avenue for exploration. With the popularization of a service-based entertainment system, many companies saw an opportunity to create a convenient and profitable way to share content. No longer were people expected to pay for a singular purchase of a film or a TV show, now consumers were expected to pay for access to a wide selection of media for a specific period of time. The fast internet connections and the emergence of Smart TV’s has allowed this model to thrive, adapting to various internet-connected devices and quickly coming into the mainstream.
Methodology
This work seeks to examine the relevant articles on the development and current status of video streaming services, as well as the video streaming industry as a whole. The review will be performed manually, by accessing the credibility of each source and reviewing its contents in relation to the topic of this report. A total of 4 articles will be discussed, each focusing on a different aspect of video steaming, including the quality of delivery, global development, current trends, and the state of the industry as a whole.
Analysis
To begin the analysis, the quality of adaptive streaming technology, as it is used by the video streaming industry will be analyzed. As stated in various sources on the topic, most streaming platforms use the same method for distributing content, called HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) (Petrangeli et al., 2018). This delivery method is mainly characterized by an ability to maintain a high standard of image quality, regardless of delay or transmission losses. However, it is also noted that this technology is prone to buffering, “jerky” playback and changes in a video’s temporal structure (Petrangeli et al., 2018). The authors of research state that such a method of content delivery can negatively affect customer satisfaction, and decrease the general quality of experience. It is also noted that there is a significant difficulty in presenting a solution to this problem, as well as finding a uniform way to address the problem. Client-based solutions are said to not guarantee solid performance, while network and server- assisted solutions can have some influence on improving video streaming. Both of these works hint at the fact that the method of content delivery can be further improved, optimized and changed to guarantee better customer satisfaction, engagement and retention.
The second consideration refers to the place streaming platforms have made on the market, as well as their current status as a way of content delivery. The review focuses on examining how different streaming platforms approach content distribution and delivery, noting that while all of them operate in the same market, the fundamental aspects of each service are unique to it. The author notes that it might be incorrect to group all streaming platforms into a single category, due to the overwhelming differences in their internal operation (Fagerjord & Kueng, 2019). This work effectively highlights two important aspects of this industry – a lack of scientific research and high variety among each individual company. This is important to consider when thinking about possible ways of growth in this industry, as well for discussing future trends. Another researcher, notably, argues that this industry is still in its development phase, and has not fully matured (Snyman & Gilliard, 2019). This assertion is made using paid subscriber data and materials on the life cycle of an industry, which are used in tandem to surmise that video streaming is not yet fully realizing its full potential.
The last piece of research that is interesting to discuss for the sake of this report is the state of streaming outside of western countries. Notably, some sources have discussed the development of the industry in China, which has been described as fundamentally different from the known cases of media streaming platform development. The authors of the study note the role of personalized experiences, individual recommendation and other highly variable factors in western streaming services, as they have been for a significant amount of time regarding as an inseparable part of streaming and one of its main features (Wang & Lobato, 2019). The ability for customized experience for a particular individual is often seen as the main avenue of improvement in well-known streaming services, which, significantly differs from the realities of the Chinese streaming platform iQiyi. The main difference between the two is shown to be the need for the iQiyi to abide by the regulations and restrictions of the Chinese government much more strictly than western counterparts, changing the way in which it exists as a platform (Wang & Lobato, 2019). The example of China as a country with a different fundamental approach to content delivery is important to note, as the international spread of streaming services creates the need to adapt for different markets, cultures, and political backgrounds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be noted that the streaming platform industry still requires more research to be truly understood and contextualized within the western and other markets. It is a developing industry, one that has had the ability to gain traction with the spread of new technology around the world. However, there are still avenues for development, improvement and growth. In particular, the usage of HAS for content delivery still leaves much to be desired, and needs to be improved in an effort to maximize customer satisfaction. Additionally, the number of active streaming platform users and subscribers is yet to reach its full potential. For future improvement and development, the industry must realize, take into account, and use the differences in international markets to its advantage. Only by understanding how the view of streaming ranges in different countries can this field truly grow in the future.
References
Petrangeli, S., Hooft, J. V., Wauters, T., & Turck, F. D. (2018). Quality of Experience-Centric management of adaptive video streaming services.ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 14(2s), 1–29.
Fagerjord, A., & Kueng, L. (2019). Mapping the core actors and flows in streaming VIDEO services: What Netflix can tell us about these new media networks. Journal of Media Business Studies, 16(3), 166–181.
Snyman, J. H., & Gilliard, D. J. (2019). The streaming Television Industry: Mature or still growing?Journal of Marketing Development and Competitiveness, 13(4).
Wang, W. Y., & Lobato, R. (2019). Chinese video streaming services in the context of global platform studies. Chinese Journal of Communication, 12(3), 356–371.