Terms of reference
The business plan is to start Acme consulting Services Company that provides consultancy services to companies which deal in the production of hardware and software products to become competitive in the current and new markets by identifying effective distribution channels to reach local and international markets and to increase the market shares.
Executive summary
This is a business plan for Acme consulting Services Company that aims to offer consultancy services to corporate entities like IBM in the computer hardware and software industry. The services include identifying new market opportunities and hardware and software distribution channels that could be cost effective and assure higher returns on investments.
To determine the feasibility of the business plan, the author conducted a comprehensive analysis of the macro and micro business environments, a SWOT and PESTEL analyses to evaluate the different marketing environments. Porter’s five forces were used to determine the role the forces play in the market to help formulate an effective business strategy and the most appropriate approach to control the business and ensure success.
Business Mission
Acme consulting company’s business mission is to provide high quality professional marketing consultancy services for computer hardware and software manufacturers.
Political factors
Here, computer hardware and software and related electronic devices are sold under the “copyright, patent, trademark, and trade secret laws and the licensing of rights in software subject to contract law, bankruptcy law, and antitrust (competition) laws” (Neubauer & Meinhold 2012, p.3).
Economic Factors
Computer technology is one of the largest employers in the UK’s job market that has experienced rapid growth and enables companies to increase productivity in different sector of the economies of many countries (Knox, Agnew & McCarthy 2014).
For instance, Intel’s cumulative economic impact showed an increase of “44,800 jobs in 2008 to 53,200 in 2012, with a $39.4 billion in wages and salaries and benefits and a contribution of $120.7 billion to the GDP of the UK (Knox, Agnew & McCarthy 2014). The direct impact on the economy includes job creation, increase in GDP and availability of labor as shown in figure 1.
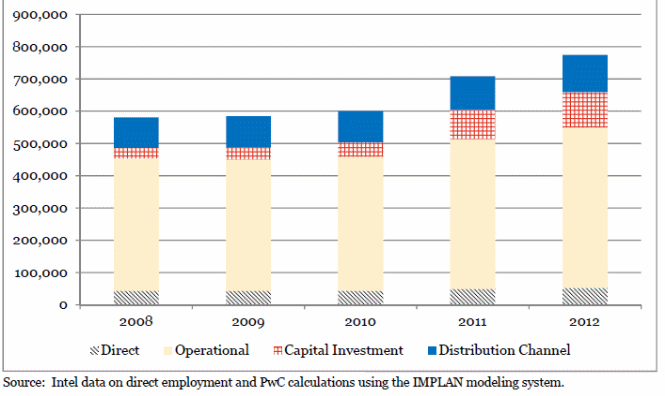
Figure 1: Intel benefits (Keller & Yeaple 2009)
Statics show that the price of computer hardware and software decreased by 67% between 2002 and 2007 and a 40.3% decline in the price of semiconductors” (Keller & Yeaple 2009). However, the current business plan is justified because a decrease in price stimulates demand for hardware and software products in the international market leading to higher profits that translates to increased service turnover.
Microenvironment
Market
According to Duke and Tucker (2007), the consultancy services offered by Acme targets high technology computer hardware and software product manufacturers intending to increase their market shares in the United States and European markets.
The potential customers include executives from large corporations, sales representatives and general managers charged with the responsibility of creating and expanding local and international markets for the software and hardware products (Singh, Veron-Jackson & Cullinane 2008).
Acme provides solutions for market access problems experience by large corporations using the company’s consultancy services by enabling the companies to avoid investing in high risk markets to reduce the cost of hiring new staff (Zou & Cavusgil 2002).
Internal Marketing Audit
The internal market audit was conducted to determine the strengths and resources required to make the company competitive in the market. According to Kotler and Armstrong (2013), skilled manpower is important for a company to be successful and based that argument, Acme has hired 5 skilled personnel with supply chain and marketing management skill and content publishing on the company’s websites.
The new workers have knowledge and contacts of customers across a large network of customers across the world (Wei 2010). Acme consultancy has a disciplined workforce employed on a permanent terms of services. In addition, the company has an efficient marketing team who are well trained marketing strategies and relationship management (Morgan, Vorhies & Mason 2009).
According to Zou and Cavusgil (2002), a critical evaluation of the approaches used to interface with the customers recommends Acme consultancy services to coordinate the communication function to achieve the communication goals effectively (Pride 2008).
When seeking for clarification on issues, the company has specialised personnel who interact with the clients by updating the client on issues that might arise in the market. A critical analysis of the company’s performance between 2010 and 2014 shows a 10% increase of profits in the first year and an increase in demand for the consultancy services (Piercy & Morgan 1994).
The strategic issues that were considered in the study include cost leadership, cost focus, differentiation focus, and differentiation of the services. The cost leadership strategy is based on the lowest prices that Acme offers and uses for competitive advantage in the current market (Helms & Nixon 2010).
Most of the competitors offer high prices as compared with lower prices offered by the Acme consultancy Company. However, by combining good pricing, focus on service provision, and market segmentation and the operational strength of the company in the current market, an overall balance of the generic factors that puts the company in the middle of the rectangle is achieved (Roger 2010).
Operating results
The expected turnover from the consultancy services is expected to increase by 20% in the first year and increase by 20% per year for the next two years before achieving a 50% increase in 5 years. The estimates are based on the size of the market, the company’s competitive advantage over rival companies that offer similar services in the industry.
Strategic Issues analysis
An analysis of the service provision industry shows that most of the industry players lack the competencies of skilled consultants who can advise them in the distribution of software and hardware products in the market (Filip 2012). The gap provides a significant opportunity for Acme to fill by making an investment in the industry to generate revenue by addressing the gap in the industry.
However, Acme faces the challenge of how to brand itself to be viewed as a risk free consultancy service provider to enable the large companies invests in the services and develop a positive risk appetite for the services provided by the company.
Marketing Objectives
- To increase the volume of sales of the computer hardware and software products by 10 per cent in each market segment
- To increase the number of corporate entities seeking for Acme consultancy services on computer hardware and software distribution channels and market growth by 7% in each year’
- To increase the revenue earned from the consultancy services by 5% of the current revenue generation in the next financial year.
- To increase the Internet presence of the Acme consultancy services in the Internet market by 20%.
Market Segmentation
Zou and Cavusgil (2002) contend that segmentation should be a strategic tool that enables a company to focus on the market and specialise in the provision of consultancy services. Here, the strategic market segments are the large corporation in the United Sates that include Apple, Microsoft, IBM and Hewlett-Packard that manufacture specialised computer hardware and software products.
According to Tavitiyaman and Zhang (2011), Acme offers services by identifying the best supply chain channels and alternative companies to use to outsource their services.
Core competencies
The company has employed highly skilled and experienced personnel with over 10 years working experience in the industry. The employees have worked with many clients in the industry and many of their clients always remain loyal to them (Cole, Graves & Cipkowski 2010).
Competitive advantage
The company has a strong brand image and many of the employees are experts with a lot of experience and knowledge in computer hardware, software, and marketing skills as added advantages.
Positioning in the market
The company will conduct a comprehensive market analysis by identifying the target customers who are the manufacturers of computer hardware and software in the UK and create a strong market positioning strategy shown below.
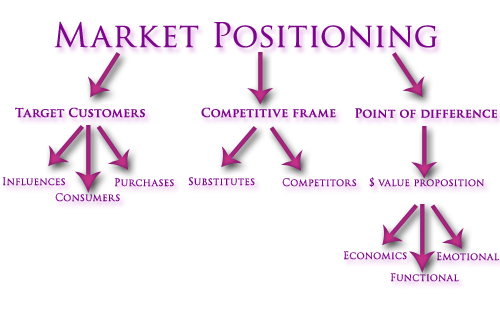
Figure 2: Market positioning (Takano 2009)
The figure shown above provides a market positioning model for the company to use to position itself in the market. The model shows the elements identified by customers, the points of reference, and the competitive frames to focus on when positioning the company ion the market.
Portfolio Analysis
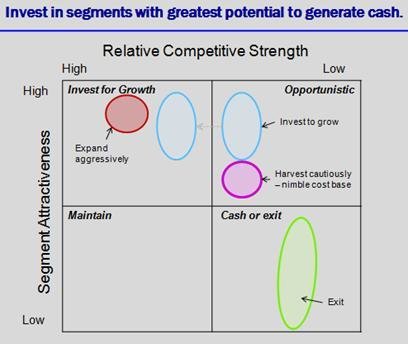
Figure 3: Competitiveness (Sridhar 2010)
The firm proposes to invest in the provision of consultancy services in the computer hardware and software industry to enable the firms benefiting from the services to identify the most profitable markets both locally and internationally.
Marketing mix effectiveness
The marketing mix consists of the product, price, place, and promotion components that are critical for the company’s success because promotions is conducted through social media websites to reach large audience of customers.
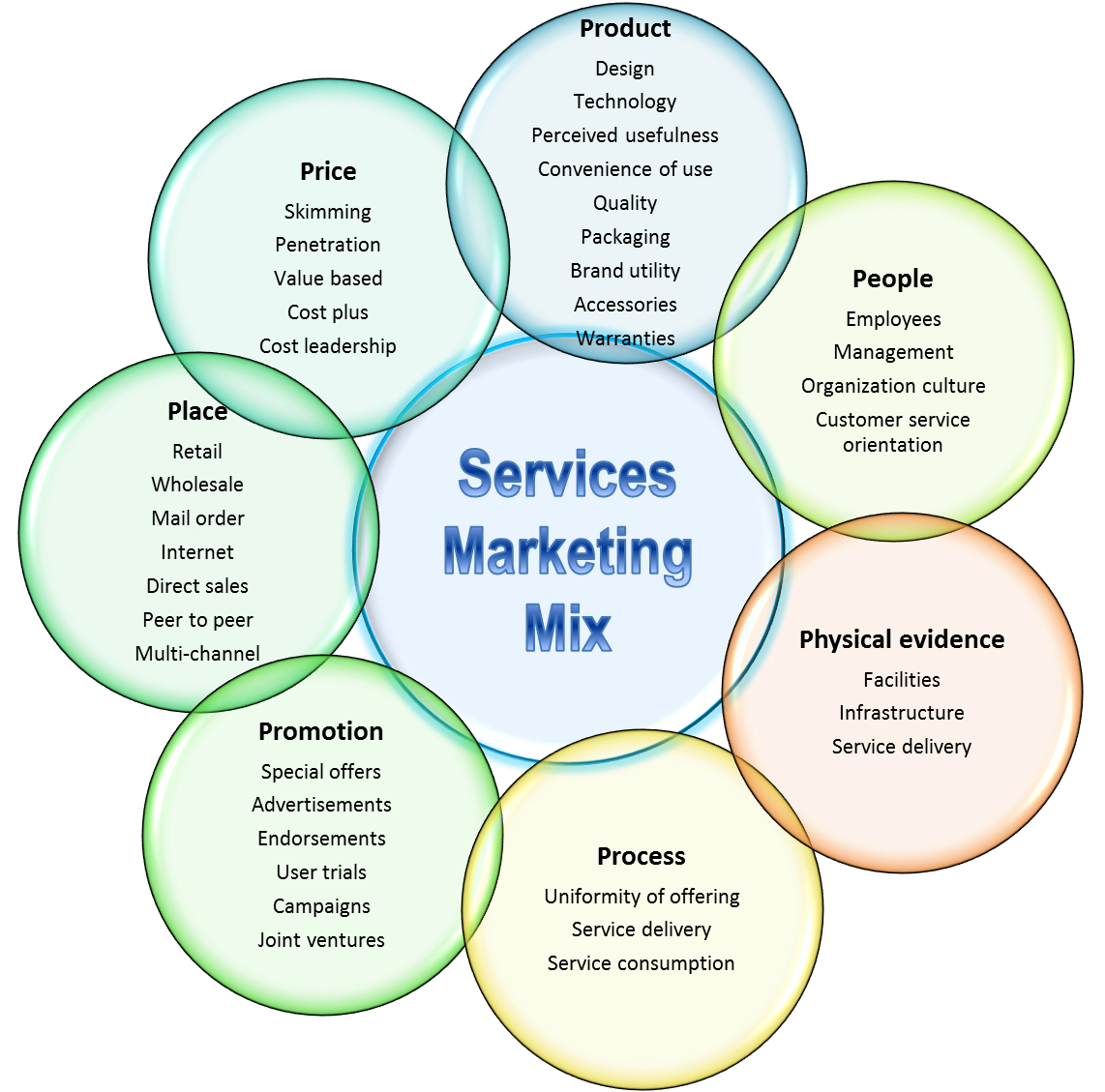
Figure 4: Service marketing mix (Sridhar 2010)
The elements to consider to be effective include processes, physical evidence of the location of the company and its infrastructure, the evidence of the links among different companies, promotional tools such as advertisements on the Internet, the people, the product being offered the services, the pricing, and the place (Internet).
Marketing structures systems
The company has a partnership with three partners who contributed financial resources to start the company. The business was not incorporated entity because the owner decided to have a sole proprietorship, but the terms of the business contract binding the three stakeholders together are drawn in an agreement that shows the binding terms and how to share the profits from the business.
The agreement includes the roles of each stakeholder in the business. The company stakeholders hold monthly meetings to evaluate the performance of the business and create new strategies when necessary.
SWOT Analysis
Table 1: SWOT analysis (Sridhar 2010)
The strengths of Acme consultancy services include effective and efficient distribution channels in existing and emerging markets for the large corporations to optimise to increase revenue, increase market share, and reduce by a significant amount the number of costly distribution channels and markets (Takano 2009).
Marketing Objectives
The objectives are based on the following suggestions:
- Employ a brand positioning strategy for IBM and other computer hardware and software products.
- Provide evidence to the prospective clients of the ability to identify new markets, optimise existing distribution channels, and create cost effective high response channels for their products.
Strategic objectives
An analysis of the current market needs shows that companies are in need of identifying cost effective distribution channels and
Porter’s Five Forces
Sridhar (2010) argues that the five forces model provides the baseline for the management of the company to analyse its business strategy and the level of competition to determine the attractiveness of the business. In context of Porter’s five forces’ framework, Acme applies its core competencies to generate revenue and profits that are above industry profits.
According to Sridhar (2010), the framework is composed of five components which include the bargaining power of the entrants, the threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and the bargaining power of buyers as illustrated in table 1 below.
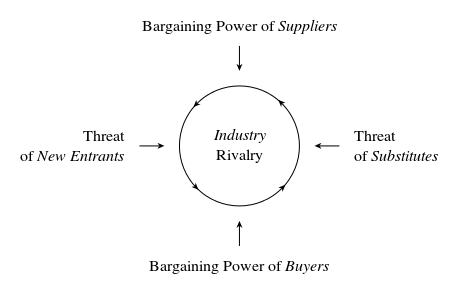
Figure 5: Industry Rivalry (Sridhar 2010)
Bargaining power of suppliers
Roger (2010) maintains that the concept of the bargaining power of suppliers is based on the ability of the customer to exert pressure on Acme consultancy Services Company adjust to prices to the needs of the customers’ buying or consuming the consultancy services. There are competitors that can offer the consultancy services on hardware and software product and identify cost effective distribution lines (Sridhar 2010).
Threat of new entrants
Sridhar (2010) provides a critical analysis of the consultancy industry in the computer software and hardware industry showing that increasing opportunities in the industry are likely to attract new entrants into the computer hardware and software consultancy services industry.
Rao, Agarwal and Dahlhoff (2004) argue that the government policy, customer loyalty, brand equity, capital requirements, absolute cost, economies of scale cost advantage, and access to distribution channels make it more difficult for new entrants into the industry.
Threat of substitutes
In theory, the threat of substitutes revolves around the propensity of the customers to switch to other companies offering similar services. According to Rao, Agarwal and Dahlhoff (2004), the potential factors Acme has evaluated include the switching costs, ease of substitution, quality depreciation, the relative performance of the substitute companies, number of companies offering substitute services in the market, and the perceived level of services differentiation to formulate a strategy to address the threat of substitutes. The overall conclusion is that the threat of substitutes is low.
Bargaining power of buyers
The bargaining power of buyers is based on the concepts of buyer concentration where the number consumers of the services offered by Acme consultancy services determine the degree of dependence of the firm on the buyers.
According to Sridhar (2010), the availability of information of the services and the companies that offer similar services, the price sensitivity of the company that are receiving the services from Acme consultancies, and the buyer bargaining leverage contribute to the strategic approach the company will make to ensure that the company addresses the concern of buyer powers to lock in the customers.
Industry Rivalry
Sridhar (2010) argues that competitive rivalry is a situation where different firms operating in the same industry offering similar services compete for the available market. The degree of transparency in the provision of the consultancy services by other firms is high.
Morgan, Vorhies and Mason (2009) contend that the presence of firms on the Internet is high and that has increased the competition from the firms offering consultancy services. However, to address issues related to industry rivalry, the firm’s strategy is based on the powerful competitive strategy to address the rivalry in the industry (Sridhar 2010).
PESTEL
The Political, Economic, Social and Technological analysis (PESTEL) referred to as PESTEL are macro-economic forces that could have a potential effect on the operations of Acme consultancy Services Company (Tuten 2009).
Political
The company will operate in countries with political stability where copyright laws cannot be violated (Ho 2014).
Economic
The economies of the current and target markets suffered the global economic crisis but they have recovered and the demand for computer hardware and software products is on the rise (Kotabe & Helsen 2014).
Social
The social factors in the current and target markets include the aspects of health, culture, attitude and emphasis on safety, and the market demand for the use of the computer hardware and software products (Yüksel 2012).
Technological
The technological aspect include the rapid changes in technology and the need adapt to the changes. The study shows that the corporate entities in the business are sensitive to the rapid changes in computer technology and the provision of products that are up to date and latest in the market (Yüksel 2012).
Legal environment
The legal environment allows for freedom of association in many countries the company intend to take its operations (Neubauer & Meinhold 2012).
Core strategies
The core business strategy will be based on pricing the services being offered by the company to ensure that the customers are offered services at competitive prices compared to those offered by competing firms. In addition, the market research reports will be priced at $ 5,000 and each consultancy service will be priced at $ 2000 per day and $ 10, 000 per month for the service providers that are retained and giving daily services for a full moth (Kotler 2011).
The sales strategy is defined by information on the project, retailer, market research, and strategy reports. In addition, the core elements that define the strategy include a good pricing mechanism using social media and communication channels for promotional purposes.
According to Thackeray, Neiger, Hanson and McKenzie (2008), the place strategy consists of the use of a website to host details about the services on offer, the people consists of the challenges facing the corporations, the product consists of the services tailored for each company, and the process consists of the procedures necessary to develop excellent consultancy services (Van Zee 2009).
Target markets
The target markets will include the United States, the UK, Latin America, and the third worlds countries markets that are emerging and growing quickly.
Competitor targets
The competitor target is DSofware that is now offering consultancy services at exorbitant prices that has weakened its position in the market, lowering its competitiveness in the market (Uzama 2009).
Competitive advantage use of skilled and experienced staff. Establishment of many links with many companies in the local and international markets.
Marketing Mix Decisions
Table 2: Marketing mix (Kotler & Armstrong 2013)
The table shows the marketing decision mix elements of distribution, price, promotion, people, and product that the company will consider when making the decision to offer consultancy services for the corporate entities in the computer hardware and software industry (Thackeray et al. 2008).
Budget
Table 3: Budget (Author 2014)
The budget is subject to revision depending on changes that might occur in the market and people who may show interest to become share shareholders.
Organisation and Implementation
Regular meetings are held with the employees under the leadership of the organisational manager to on a weekly basis to evaluate the success of the company and the problems and challenges the company faces in the provision of consultancy services (Terrados, Almonacid & Hontoria 2007). In addition, the management evaluates the performance of the employees of the company and to formulate new motivation and strategies to remain competitive in the market.
Control
To determine the success of the marketing plan, the firm will engage in a comprehensive evaluation and control process (Zou & Cavusgil 2002). Various parameters will be utilized in determining the success of the marketing plan.
Firstly, the firm will analyze its sales revenue in order to determine the percentage change. The margin of change obtained from the analysis will enable the firm to determine the effectiveness of its marketing strategies (Goi 2009).
Reflexive Account
Before I wrote this business plan, I used to think that it was an easy task. However, when I started to write the business plan, I realised how important it was to read widely on different areas that contribute to a comprehensive business plan (Westwood 2013).
For the first time I was able to read be informed of the need to identify the core elements of a business plan stating with the mission statement that provides the purpose or the reason for the existence of the company. I came across many business plans that have been prepared by different authors on the Internet and I noted that conducting an audit of the internal and external market environment was a preliminary and important step in the right direction in determining the feasibility of the plan.
The political and economic factors of the macro environment were fundamental in determining the viability of doing business in different environments. A study of the micro environment was done by analysing target market segments to tailor the services according to the needs and expectations of the customers using the business plan.
One of the areas of critical importance to the study is Porter’s five forces in the market. The five forces provide the company with the ability to analyse its business strategy by determining the impact of the five forces on its overall strategy.
I was able to identify the competitors and the effects they could have on the company’s business strategy and that enables me to revise the strategy to ensure that the results were according to the business goals and objectives. The main forces were the rivalry in the services industry that consists of the threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, bargaining power of suppliers, and the bargaining power of the buyers.
The most important element here was to translate the academic practices and knowledge into the real world business environment. As I continued with the study by putting the business plan elements together, I realised that adding a SWOT analysis to the competitive framework of the company, I was able to determine the strengths of the company, its weaknesses, the market opportunities, and the threats from new entrants into the industry and the strategic methods to address the weaknesses and threats of the new entrants.
SWOT was important because I was able to identify the key strengths and optimise them to exploit the weaknesses of the competitors to penetrate the market and increase revenue from the services being offered by the company. Using the SWOT and the PESTEL analyses by combining the results from the study, I was able to decide on the best methods to use to achieve the business objectives I had set down and the core strategies to pursue using the current budget I had drawn.
In conclusion, I have realised the importance of writing a business plan, the important of creating and outline of the control strategy, and need to motivate employees before starting a business.
References
Cole, K., Graves, T & Cipkowski, P 2010, ‘Marketing the library in a digital world’, The Serials Librarian, vol. 4, no. 58, pp. 182
Duke, L M & Tucker, T 2007, ‘How to develop a marketing plan for an academic library’, Technical services quarterly, vol. 1, no. 25, pp. 51-68.
Filip, A 2012, ‘A global analysis of the educational market environment’, Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, vol. 1, no. 46, pp.1552-1556.
Goi, C. L 2009, ‘A review of marketing mix: 4Ps or more?’, International Journal of Marketing Studies, vol. 1, no. 1, pp.2
Helms, M M & Nixon, J 2010, ‘Exploring SWOT analysis–where are we now?’, A review of academic research from the last decade. Journal of Strategy and Management, vol. 3, no.3, pp. 215-251.
Ho, J K K 2014, ‘Formulation of a Systemic PEST Analysis for Strategic Analysis’, European Academic Research, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 6478-492.
Keller, W & Yeaple, S R 2009, ‘Multinational enterprises, international trade, and productivity growth: firm-level evidence from the United States’, The Review of Economics and Statistics, vol. 4, no. 91, pp. 821-831.
Knox, P, Agnew, J & McCarthy, L 2014, The geography of the world economy, Routledge, London.
Kotabe, M M & Helsen, K 2014, Global marketing management, Wiley Global Education, New York.
Kotler, P & Armstrong, G 2013). Principles of Marketing 15th Global Edition, Pearson, London
Kotler, P 2011, ‘Reinventing marketing to manage the environmental imperative’, Journal of Marketing, vol. 4, no. 75, pp. 132-135.
Morgan, N A, Vorhies, D W & Mason, C H 2009, ‘Market orientation, marketing capabilities, and firm performance’, Strategic Management Journal, vol. 8, no.30, pp. 909-920.
Neubauer, D & Meinhold, S 2012, Judicial process: law, courts, and politics in the United States, Cengage Learning, London.
Piercy, N F & Morgan, N A 1994, ‘The marketing planning process: behavioral problems compared to analytical techniques in explaining marketing plan credibility’, Journal of Business Research, vol. 3, no. 29, pp. 167-178
Pride, W 2008, Marketing. Cengage Learning, Boston.
Rao, V. R Agarwal, M. K & Dahlhoff, D 2004, ‘How is manifest branding strategy related to the intangible value of a corporation?’, Journal of Marketing, vol. 4, no. 68, pp. 126-141.
Roger, K 2010, Strategic Marketing Problems: Cases and Comments. Pearson Education, New Jersey.
Singh, T, Veron-Jackson, L & Cullinane, J 2008, ‘Blogging: A new play in your marketing game plan’, Business Horizons, vol. 4, no. 51, pp. 281-292.
Sridhar, K 2010, ‘An incumbent vs. a new entrant: a Porter’s five forces tale of a powerful electricity provider vs. a green energy retailer’, International Journal of Sustainable Strategic Management, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 138-154.
Takano, S E 2009, ‘Application of combined SWOT and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) for tourism revival strategic marketing planning: A Case of Sri Lanka tourism’, Journal of the Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, vol. 1, no. 8, pp.112
Tavitiyaman, P, Qu, H & Zhang, H Q 2011, ‘The impact of industry force factors on resource competitive strategies and hotel performance’, International Journal of Hospitality Management, vol. 3, no. 30, pp. 648-657.
Thackeray, R Neiger, B L, Hanson, C L & McKenzie, J F 2008, ‘Enhancing promotional strategies within social marketing programs: use of Web 2.0 social media’, Health promotion practice, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 338-343.
Terrados, J, Almonacid, G & Hontoria, L 2007, ‘Regional energy planning through SWOT analysis and strategic planning tools.: Impact on renewables development’, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 1275-1287.
Tuten, T 2009, ‘Real world experience, virtual world environment: The design and execution of marketing plans in Second Life’, Marketing Education Review, vol. 1, no. 19, pp. 1-5.
Uzama, A 2009, ‘Marketing Japan’s travel and tourism industry to international tourists’, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, vol. 3, no. 21, pp. 356-365.
Van Zee, A 2009, ‘The promotion and marketing of oxycontin: commercial triumph, public health tragedy’, American Journal of Public Health, vol. 2, no. 99, pp.12-29
Wei, M 2010, ‘Construction of marketing management information system of travel agency based on customer relationship management’, Advanced Materials Research, vol. 1, no. 136, pp. 69-76.
Westwood, J 2013, How to write a marketing plan, Kogan Page Publishers, London
Yüksel, I 2012, ‘Developing a multi-criteria decision making model for PESTEL analysis’, International Journal of Business and Management, vol. 24, no. 7, pp. 52
Zou, S & Cavusgil, S 2002, ‘The GMS: a broad conceptualization of global marketing strategy and its effect on firm performance’, Journal of Marketing, vol. 4, no. 66, pp. 40-56.