Current Marketing Situation
Current marketing situation is characterized by rising demand for the microchip particularly in the medical industry. The demand for the product is exponential given a statistical demand analysis for the product. However, it’s worth noting that most of the products are produced by well positioned companies in the market and the ability to penetrate the market may be met with such intense rivalry that it may be difficult to penetrate the market (Douglas, & Craig, 2007).
A responsive marketing analysis reveals that a number of patients who see the use of the microchip as an option in treating their ailments constitute the greatest percentage. That implies demand is directly related to the number of patients in need of the microchip.
In addition to that, an analytical evaluation of the marketing situation reveals that anticipated demand is on the rise. That is strongly correlated to the modern day living conditions and medical predicaments many people encounter due to rising levels of diseases associated with the living style of many people.
Hypothetically, modern day living and lifestyle bears a strong relationship to the development of a number of medical complications in many people today. However, a critical evaluation of the market situation indicates without doubt that the concept of need shaping market has not yet held ground or anywhere near in the same market or industry (Granzin & Painter, 2001).
Therefore, the need to conduct a market driven analysis to identify customer needs and expectations and to tailor the product towards their needs and application in diverse areas is of vital importance. A market driven analysis not only enable the Microchip Company to tailor its products towards customer needs, but will enable the company identify points in need of improvements and wider areas of application for the MC microchip (Insch & McBride, 2004).
Further analysis of the marketing situation reveals that the production cost of the microchip has to be evacuated to determine the most cost effective strategy to employ in manufacturing the chip. Each of the production steps consumes skill, time, labor, and materials which accumulate to the cost of production of the device. If the cost of production goes too high, the production methods may be tagged as costly and inefficient hence the final cost of the product may be too high. The manufacturing company may not eventually benefit and may be in danger of losing business due to the fact that customers can opt for cheaper products with similar features (Cutura, 2006).
According to the market survey and analysis, it is worth noting that production levels have experienced an upward trend in the recent past and the level of consumption has indicated a significant rise (Jo, Nakamoto & Nelson, 2003).
The table below show annual production levels based on specific regions.
Marketing Constraints
Marketing constraints include competition from manufactures of similar devices, ability to inform the market or consumers about the product, and product features that might not meet customer needs and expectations (Dmitrović, & Vida, 2007).
Despite the fact that there is an increased pace with which electronic devices are getting under the skins of individuals, problems caused by their use are worth to contemplate. These problems range from medical to ethical issues, cultural to religious concerns and an abridgement of fundamental human rights to privacy.
Benefits from the Product
The supply chain of drugs can be enhanced by use of these chips on caps and other sealing or enclosing mechanisms for drugs. That increases their reliability and the integrity of drugs consumed by the patient (Lovelock, 1991). In addition to that, research shows that pharmaceutical products have a very long shelf life and are of a high value.
Implying that the use of microchips can enhance knowledge about the shelf life of a drug and these drugs can be sorted to ensure none is in store that has expired. That ends protecting the patient as the ultimate consumer (Josassen, & Richard, 2010).
There is the perception that the chip can cause adverse health conditions on the patient. These health conditions include the threat that cancer can result from the use of the device. Cancer is one of the problems that have been identified to be scientifically associated with the implantation of the chip under the skins of human beings.
In addition to that, dogs and other animals used in the research with the chip have been identified to develop cancer (Dow, 2006).
Market Description
Market description constitutes the sources of market opportunities, abilities to supply the microchip with superior features and abilities, and the unique identity associated with the supply of the new product. It starts with strategic means and ways to stimulate demand for the product.
Among the means of stimulating demand include market penetration capabilities of the new company to target the market population demanding the product, geographic distribution of customers and their demographic trends, access to new types of customers in the regions identified above and other new markets, and tailoring the product features to accommodate customer needs and expectations (Josassen & Richard, 2010).
Other market description elements include understanding inherent regulatory controls for products in the market. In the medical field, these regulations are stringently enforced due to the fact that the health of any customer or individual using the microchip for medical purposes of utmost importance. Each person adversely affected by the microchip implant.
The regulatory requirements for the manufacture of microchips included understanding the most important regulations to be adhered to in order to manufacture products that meet legal and other requirements making them fit for use in the human belong. Moreover, ethical issues should be considered in the process.
Ethical and regulatory requirements are closely related to the following argument. Despite a myriad of benefits that come with the microchip, potential problems have been identified to be inherent in the use of these electronic chips under the skin of an individual.
Among these include the ability to infringe upon the security and privacy of a human being. Several ethical issues are associated with the use of implants in the human body that interfere with the privacy of an individual. It tramples upon the fundamental human right to privacy of life, thus demeaning human dignity, the fundamental and exclusive right to the right of personal integrity, exposure of individual data to persons and institutions which could otherwise not access that information were it not for the device, and the free movement of individual data and information.
These problems doubtlessly interference on individual privacy and protection and openly bridge an individual’s private life, therefore fundamental human rights (Josassen & Richard, 2010).
Product Review
The product is shaped in capsule form and is usually implanted under the skin of an individual. In addition to that, it can be implanted to aid the functionality of the heart, a medical condition that comes with modern day lifestyle. It costs up to three thousand dollars less the cost of implanting these devices by specialized personnel.
Different firms try to tailor the product by making them as small, as possible and incorporate features that help in its functionality and in making the user as comfortable as possible. Different companies have identified the great potential in terms of profits that can be realized from investing in this field. Therefore completion demands that product be continuously improved to meet changing customer needs and expectations and satisfy the ever increasing demands (Kim, & Thorndike, 2000).
Competitive Review
To make the product competitive, the company has taken bold steps in incorporating various competitive mechanisms to ensure the microchip gains a strong market position on entry into the new market.
Distribution Review
A product distribution review indicates that distribution channels will have to be established by identifying and linking with hospitals and other medical facilities that offer medical services for implanting the device. These cannels have to be characterized by efficiency in delivering the product to the target destination without delays.
The distribution channel will also be tailored to provide efficient deliveries particularly at times when need for the product is urgent. Therefore, air courier services will form an integral part of the distribution channel.
The channel will also be characterized by efficient tools since these devices are expensive and fragile; the need to securely deliver them is of utmost importance.
SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis constitutes the strengths that characterize the company in terms of product position in the market, the weaknesses of the company in the market, opportunities that are available in the market and threats that may exist for the product. These opportunities are tabulated below.
Objectives and issues
The marketing objectives of the new product are outlined below.
First fear objectives include:
- To penetrate the market
- To gain a market share of 10 percent within the first one year
- To identify the product brand with the market
- To create a sustainable market within the first one year
- To create a strong brand name for the product within the first year of entry into the market.
- To create a strong customer base and strong customer relations
- To create a strategy for stimulating market growth in the first one year
Issues
- Business issues related to the new business include ethical issues related to the practice of using the human microchip in other contentious areas.
- Monopolistic issues of current leaders in the microchip market in relation to the competition and for the new entrant.
- The integrity of the sale and marketing department
- Fair business practices between competitors in the same field.
- The extent to which the product could be perceived to be safe for use in the human body.
- Religious and other cultural issues.
- Legal issues associated with the use of the device in tracking human beings.
- Fair treatment of target customers.
- Bribery and other practices that may be deemed unfair.
2nd year objectives
- To strategically maintain the current business position for sustainability.
- To increase market share from the current 10 percent to 25 percent.
- To continuously identify the brand name with the market.
- To integrate continuous quality improvement strategies in product improvement.
- To enhance customer relations and sustainably maintain the current level of customer relations.
- To take the product brand into new levels through strong marketing strategies.
- To facilitate the growth of profits from their current level to 35 percent.
Issues
- Evaluate competitor business practices and counter them with fair business practices.
- Establish clear product pricing policies
- Identify the need to employ disable people within the business organization.
- Strategies to avoid unethical business practice such offering bribes for specific favors.
Marketing strategy
The marketing strategy is characterized by efficient resource utilization, enable the marketing managers to identify target opportunities within the market, enable organizational managers identify marketing methods to sustainably generate profits from the sale of the microchip for the company to gain and retain a competitive advantage and a strong market position.
The business strategy is tailored at making customers satisfied by meeting their expectations and needs. In addition to that, the strategy is characterized by a strategic plan of entering the market and gaining a market share that could enable the company to generate sufficient profits for sustainability.
Therefore the marketing strategy is to identify cost effective methods of product development, to penetrate the market with a an initial 10 percent target share, to continuously endeavor to increase the market share through efficient and competitive pricing mechanisms, identify and target a specific market segment, and identify efficient distribution channels through the market (Durvasula, Andrews, & Netemeyer, 1997).
Positioning
The microchip positioning strategy in the market will be characterized by a differentiation mechanism targeting specific customer needs and expectations. The microchip will be address the customer buying behavior and address such needs. With specific customer needs and expectations identified in the process, the microchip will be kept at the top of their thoughts. The microchip positioning strategy will be characterized by clarity and target specific customer needs.
The strategy will be characterized by a strong position against competitors in the market. The microchip is characterized by miniaturized size compared with similar products in the market, durability in its usage, spans all users that are affected by heart related problems (Cicic, Brkic, & Praso-Krupalija, 2003).
Product strategy
The microchip strategy reflects the engineering genius and technology of the manufacturing company. To enter the market and stir profits for the company, the market plan integrates the element of a reliable supply chain, competitor abilities, efficient coordination between organizational departments focused at entering and gaining a strong initial market position, and efficient market analysis techniques.
Pricing strategy
The pricing strategy reflects the uniqueness of the microchip and the specific industry of application. It will be characterized by a pricing mechanism targeted at entering the market, referred to as penetration pricing. However, it is worth to note that the pricing mechanism and strategy shall shift with shifting market needs and demand levels. The pricing strategy will incorporate other pricing techniques such as psychological pricing and shall be continuously tailored to address the ever dynamic market forces. Each of the economy, premium, penetration, and skimming strategies will be critically evaluated and adopted as need arises.
Distribution strategy
The microchip distribution strategy will include establishing target markets and points of sale to reach the specific customer. Other distribution channels will include using the emailing system, the e-commerce strategy, and other direct selling methods. Target customers are usually in the medical fraternity, therefore strategic methods such as telephone calls and real time microchip deliveries methods in the event of an emergency. In essence, the use of the e-market will disinter-mediate between the customer and the manufacturer to reduce prices and directly access the customer (Burnett, 1996).
Marketing communication strategy
The marketing communication strategy will integrate values and beliefs of the target market as identified above. The main problems targeted to be solved by the use of the microchip are specific medical problems that need electronic devices specifically the microchip to address. These include heart problems that are solved through the use of the microchip by implants it into the heart of a patient by specialized personnel. Specialized personnel identify the need for an artificial device to boost the functionality of the heart.
Marketing research
The marketing research will include indentifying the current market position and the need for the device, competitors, projected profits, sales volumes, and current marketing technologies. Information gathered will be analyzed and the probability of success and associated risks identified in the process.
Marketing organization
Marketing organizations will include a partnership with experienced marketing agencies such as e-marketing agencies and organizations.
Action plan by month for the first six months
Action plan for the first month will include, identifying techniques of targeting specific customers with specific needs, establishing contacts with medical facilities and specialized personnel who provide such services. All strategic objectives are clarified in the process, establish specific plans to reach target customers, and continually review achievements due to the target plan.
For the first six months it is projected that the company will have gained at least a 5 percent market share and will have started to earn profits (Bilkey & Nes, 1982).
Budget for the first year
Controls including gap analysis
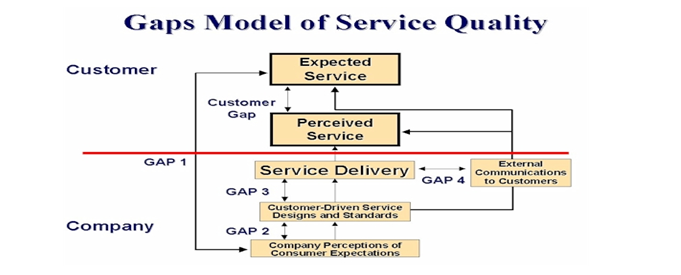
From: Journal of Service Marketing.
The gap model will be used to identify the existence of a gap between what the customer expected and perceived services. According to the case study, all the departments ought to identify the gaps that exist between them and close them in relation to the customer and the consumer.
A good communication link should exist between the customer driven service designs and standards and company perceptions and consumer expectations (Balabanis, & Diamantopoulos, 2004).
References
Balabanis, G. & Diamantopoulos, A. (2004). Domestic country bias, country-of-origin effects, and consumer ethnocentrism: a multidimensional unfolding approach, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 32 (1) 80-95.
Bilkey, W. J. & Nes, E. (1982). Country-of-origin effects on consumer evaluations, Journal of International Business Studies, 8(1) 89-99.
Burnett, J. J. (1996). What service marketers need to know about the mobility-disabled consumer. Journal of Service Marketing. 10(3)3-20.
Cicic, M., Brkic, N., & Praso-Krupalija, M. (2003).Consumer animosity and ethnocentrism in Bosnia and Herzegovina: The Case of a developing country in a post-war time, Akademija MM – Slovenian Marketing Research Journal, 6(10 ) 59-73.
Cutura, M. (2006). The impacts of ethnocentrism on consumer evaluation processes and willingness to buy domestic vs. imported good in the case of Bosnia and Herzegovina. South East European Journal of Economics and Business, 1,254-63. Web.
Douglas, S. P. & Craig, S. C. (2007). Collaborative and iterative translation: An alternative to back translation. International Journal of International Marketing, 15(1)20-43.
Dow, D. (2006). Adaptation and performance in foreign markets: evidence of systematic under-adaptation, Journal of International Business Studies, 37(2 ) 212-226.
Dmitrović, T. & Vida, I. (2007). An examination of cross-border shopping behaviour in South-East Europe, European Journal of Marketing, 41(3/4) 382 – 395.
Durvasula, S., Andrews, C. J. & Netemeyer, R.G. (1997). A cross-cultural comparison of consumer ethnocentrism in the United States and Russia. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 9(4) 73-84.
Granzin, K. L. & Painter, J. J. (2001). Motivational influences on “Buy Domestic” purchasing: Marketing management implications from a study of two nations, Journal of International Marketing, 9(2) 73-96.
Insch, G.S. & McBride, J.B. (2004). The impact of country-of-origin cues on Consumer perceptions of product quality: A binational test of the decomposed country-of-origin construct, Journal of Business Research, 57, 256-265.
Josassen, A., & Richard, F. (2010). Looking at Bothe sides of the coin. Revisiting the role of a country of origin in International Business. Journal of Business systems, Governance and Ethics. Web.
Jo, M. S., Nakamoto & Nelson, E. J. (2003). The shielding effects of brand image against lower quality countries-of-origin in global manufacturing, Journal of Business Research, 56, 637 – 646.
Kim, S. & Thorndike, P. D. (2000). Predicting purchase intentions for uni-national and bi-national products, International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 28.6, 280-291.
Lovelock, C. H. (1991). Services marketing (2nd ed).Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.