Executive summary
This paper examines the marketing strategies employed by two electronic companies Sony and Samsung. The industry background gives an overview of the electronics industry in terns of market segment and regional stakeholders in manufacturing. Both companies background are summarised and an insight about their areas of operations and size of their businesses in terms of sales and product development is given.
An analysis on strategic marketing and planning on both companies follows with a somewhat in-depth analysis of macro and micro environmental factor such as competition and economic factors being tackled. There is a SWOT analysis on each company highlighting their strengths, opportunities, weaknesses and threats based on their operations and positions in different markets.
Additionally there is an analysis on target marketing, segmentation and position generally and as applied to each company. Finally, there are recommendations on the way forward for the companies and those that deal in the same products.
Introduction
The 21st century has been characterised by unprecedented advances in technology. The global electronic industry is so dynamic to an extent that technologies become “obsolete” even before they penetrate all the market segments that they were initially meant for. American and Japanese had for a long time dominated the global technology sector. However, companies from rising economies such as China and Korea have perfected the technologies that exist while coming up with innovative electronic products.
The result has been increased competition and saturation of the market that has seen technology pioneers like Hewlet Packard pushed from the top spot. To compete for and maintain the market niches, companies have had to come up with innovative marketing ways that in order to ensure long-term market survival.
This paper will analyse marketing theory and practice as applied today through a comparison of two electronic companies; Sony and Samsung. There will be in-depth analysis on the ways the two companies have integrated marketing theory with company activities to curve new market niches while maintaining current ones the backdrop of increased competition globally.
The Samsung group of companies is among the largest electronics corporations that has a global consumer base and numerous affiliate businesses. Since its first investment initiative in 1939, the company has transcended various industries in search of an effective and market aggressive industry. The electronics initiative came in late 1960s with several related branches in electronic devises mechanics and telecommunication devices.
The Sony Corporation on the other hand is a conglomerate of several media and electronic companies that specialize in the electronic business unit and the entertainment industry as a whole. Since the 1945 initiative following the invention of the transistor the company has diversified its investments it both mechanical and telecommunication sub segments (Chang, 2011, 90).
Industry background
The global electronic industry is vibrant with a growth rate matched by only a few sectors. In 2008, the industry was estimated to be worth 1.2 trillion Euros. The world production per application sector in the industry by the same year included 6% for home appliances, 15% for audio video, 23% for data processing, 25% for telecoms, 7% for aerospace and defence, 8% for automotive and 16% for industrial and mechanical.
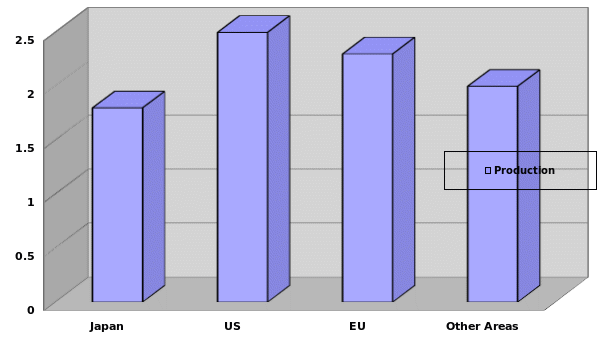
In terms of world production per region, china was ranked the highest with 27%, followed by Europe with 21%, North America with 20%, other Asia Pacific with 15%, Japan with 13% and the rest of the world with 4% (Drummond, et al. 2007, p. 67). The above figures are represented in a graphical format below.
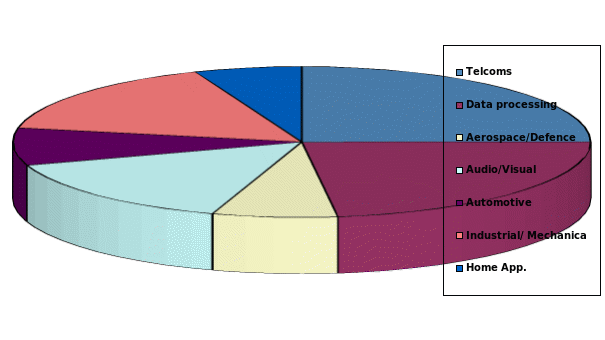
World production per application sector
Source: Sony Vs Samsung: The Inside Story of the Electronics Giants. London: Mcmillan Publishers.
World production per region 2008
Source: Sony Vs Samsung: The Inside Story of the Electronics Giants. London: McMillan Publishers.
The industry like any other has been affected by the global financial crisis through financial instability in terms of currency fluctuation and the credit crunch. There is also growing competition from China whose products are perceived by consumers to be affordable compared to any other in the world.
Company background
Sony Corporation is part of the world’s fifth largest media conglomerate Sony Group with total assets worth over $86billion and headquartered in Minato Japan. Sony Group operates six business segments including consumer products and services group, financial services, music and picture, professional and Sony Ericsson which the cell phone unit of the group. The group is also involved in financial and internet services.
The group has manufacturing and operations network serving the world market. According to (Chang, 2011, 78), almost half of the company’s annual production takes place in Japan. Computers, digital cameras, television sets and memory sticks are among the products manufactured in Japan. It’s important to note that over 60% of all the production that took place in Japan was destined for other regional markets worldwide. The rest of Asia excluding China and Japan, Europe and Americas accounted for slightly over 35% in annual production. The graph below shows the total annual sales and distribution by geographical regions in the year 2009.
Sales and distribution in 2009 (sales in 000,000)
Source: Sony Vs Samsung: The Inside Story of the Electronics Giants. London: Mcmillan Publishers.
Samsung on the other hand is a conglomerate like Sony Group but headquartered in Samsung Town in Seoul South Korea. The multinational conglomerate operates a series of affiliated business touching on industries such as electronics, ship building and engineering, insurance and hospitality.
However, Samsung is known more for its electronic products which include the cell phones and television sets, smart phones, home appliances, slimmer panels and 3D experience. In the year 2010, the company posted a net income of $13 billion. The table below shows some of the company’s electronic products and market share.
Source: Chang, S. (2011). Sony Vs Samsung: The Inside Story of the Electronics Giants. London: Mcmillan Publishers.
Strategic marketing and planning
Both companies fall belong to the category of multinational corporations. In there level strategic marketing and planning must incorporate the elements of hierarchical or enterprise strategy. The hierarchical structure incorporates the corporate level, business unit level and the functional or departmental levels of enterprise strategy.
Both companies display a highly defined corporate hierarchical structure that is very specific and that is aimed at dealing with prevailing market competition.
Microenvironment forces
The technology industry in which Samsung and Sony Operate in is competitive and only innovative marketing can guarantee long-term survival. Marketing of the electronic products produced by both companies is shaped by demographics, economic and political factors.
In demographic factors, the companies have to consider the demographic trends of the target markets they want to venture into. The size, density, location, gender and occupations of the target markets affect the marketing of electronic products.
For instance, the gadgets like the Samsung Galaxy tab can only be marketed to young people and people in business. It’s highly unlikely that older people say baby boomers are likely to buy the product. Additionally, different sections of the population have different occupations which dictate their income and way of life. People in business are likely to buy the Galaxy tab compared to farmers.
While marketing, the companies consider the economic factor which more or less refers to the economic strength of the target market. Further to that marketing managers of the two companies will likely consider the purchasing power of the people in potential markets. For instance the gadgets are likely to do better in the US, Europe and Japan and some parts of Asia owing to the high purchasing power of their populations.
Furthermore, the above markets are more industrialised unlike sections of the developing world where the populations still practice subsistence economy. The above conditions dictate how people spend their money which in turn influences marketing decisions of the electronic companies.
Political forces include all government policies and legislations that regulate business transactions in particular territory. In some territories, some gadgets which may be manufactured by the above electronic companies may not be sold to some sections of the population. Additionally, different governments have different policies for instance on taxation which may affect pricing of electronic gadgets.
The marketing of both the Sony Bravia KDL-40W4000 LCD TV and the Samsung LE40A656 LCD TV can be affected by the above factors.
These are the internal forces that affect the marketing of the electronic companies above. They are forces that the companies can easily alter to suit their marketing approaches (Wilson, S. & Gilliga, 2005, p. 88). Both Sony and Samsung have diverse ranges of products that are much differentiated.
Though they are both located in Asia, some microenvironment forces under which they operate dictate their marketing approaches that are unique in their own ways. This section will analyse both companies in relation to competition, consumer bases and market intermediaries.
Competition is a big factor in marketing of electronics. The intensity of the competition determines the amount of resources and tactics used. Despite Samsung’s success in producing LCD panels, it faces competition from Sony and more closely LG, another Korean electronics maker.
In 2008 fro instance, LG had a market share of 25.8% compared to 26.2% of Samsung in the same year. Sony Bravia is currently the top selling LCD television brand in the US. However, it faces growing competition form Samsung and LG which have the majority global market share.
Another factor that influences the marketing approaches of the two companies has been the consumer bases. In their marketing the companies have concentrated on reinforcing the value of their products to the consumers. The assumption among the electronics makers has been that the skinny the TV is the more appealing it is to consumers.
In 2009, Sony fronted the Bravia to the consumers as the world’s skinniest TV in an apparent challenge to Samsung and JVC’s models that were skinnier. Since then the competition between the two has shifted to picture quality and visual characteristics like 3D images that consumers value more.
Both Sony and Samsung have adapted different marketing approaches as far as market intermediaries are concerned. Market intermediaries’ help in product penetration where the company is unlikely to achieve its targets in the short tem were it to do it alone.
Sony has been the market longer than Samsung and has therefore managed to establish a wider network of regional offices that spearhead marketing compared to Samsung. Though Samsung is adopting the same approach, it has a large network of intermediaries who aid in its marketing.
Swot Analysis
Sony has dominated the electronics industry for a long time. Samsung has however matched the innovation and marketing strategies of the Japanese rival by exploiting its competitor’s weaknesses. A swot analysis of both companies puts into perspective the position they are in right now.
In terms of strengths Sony has a diversified business operations machine that guarantees stable revenue. Additionally, it has a strong brand that has played a crucial role in its gaining acceptance. Furthermore, it has a diversified client base spanning many geographical places effectively reducing business risks.
In terms of opportunities, the company has undertaken reorganization, which is likely to contribute to its savings. Also, there has been a focus on emerging economies which is likely to contribute to long-term growth of the company. The partnership with FIFA is another opportunity if well utilised will enhance corporate value.
The company experiences weaknesses in the high cost of manufacturing that in the long-run will lead to lower margins.
The threats to its progress include the unstable international exchange rates that may affect its margins and the long-lasting impacts of the economic slowdown.
Samsung on the other hand has a very strong advantage when it comes to technology. The company’s investment in advanced technology has enabled it crush competition from market leaders. Additionally, its investment in human resources and product design also form part of its strengths.
Samsung has however not created niche markets like its rival Sony Corp. Its target on the mass market and the low pricing strategy can be considered a weakness because customers are likely to consider them low quality. Furthermore, some of the company’s products have been reviewed as not being user friendly.
There are however many opportunities the company can exploit. The company has a head start in the mobile telephony through the introduction of low priced and user friendly cell phones. Further variation of its products is also another opportunity that Samsung can exploit to increase its market share.
The biggest threat the company is facing is competition from other electronic manufacturers like Sony and LG, and Panasonic and Nokia.
Market segmentation
Effective marketing takes into account different segmentation variables when dividing the market into target segments (Reed, 2006, p. 43). There may be many segments depending on the nature of the market and the products on offer. However, the most common variables include benefit variable and demographic variable.
Benefit variable deal with the needs and benefits expected by customers. Demographic variables on the other hand define the characteristics of the target customers and potential clients. Variables like gender, age and occupation are critical in market segmentation.
Sony and Samsung have numerous products that are suited for different markets based on their use and need. In terms of the market segments the products under discussion from both companies are targeted at the same markets. The Sony Brava KDL-40W4000 LCD TV and the Samsung LE40A656 LCD TV are both targeted at middle class and high end customers in the regions where the two companies operate.
Target Markets
Both the Sony Brava KDL-40W4000 LCD TV and the Samsung LE40A656 LCD TV are targeted at the upper middle class and upper class signets of the population in the areas where the two companies operate. Also targeted, are working male and female consumers, men and women in their late twenties and seniors. They above groups are the only ones likely to afford the prices imposed on the products. The above characteristics fit into the variables that were discussed earlier as shown in the table below.
Targeting strategy
Targeting strategies can be classified as differentiated, undifferentiated and concentrated (Palley, 2000, p. 54). Differentiated targeting strategies include different promotional messages each conveying different product benefits. Undifferentiated targeting strategies on the other hand involve sending of one promotional message to about the benefits of the product to the market.
Concentrated targeting strategies on their part carry messages that communicate product benefits to specific segments of the consumer base. Many businesses choose a target strategy based on the benefits they expect from the market, the market segment they are tying to reach and the costs of the passing the message to the target market.
Sony Corp. uses all the above targeting strategies because compared to Samsung; it has curved clear market niches. Samsung on the other hand mostly uses differentiated targeting because its marketing mostly targets the mass market. Samsung is yet to carve its niche market hence the need for concentrated targeting is low.
Positioning strategy
In the market, different companies use different positioning strategies. They include, price and quality, use or application of the product, product class, competitors (McDonald & Wilson, 2011, p. 90).
In product attributes, business use one or few of the products attributes through which they popularise it to the consumers. In pricing and quality, companies use varying prices and qualities to attract different classes of consumers. The quality can be superior or lower quality both of which will cost differently.
The use or application on the other is used when companies position their products to suit the habits and chores that the target population engages in. in competitor positioning, some companies engage in direct and purposeful comparison of their products to similar ones in the market to gain entry.
Samsung has engaged in the pricing positioning where its products including the Samsung LE40A656 LCD TV are low costing compared to similar products from Sony. Both firms have however perfected the quality positioning strategy where every time they emphasise every little modification that adds to the comfort that consumers are interested.
Recommendations
- Given the dynamism in the electronic technology, companies are only assured of survival through investment in research and technology.
- There is need to focus on diversification because there are all indications that gadgets market may be saturated given the fast development of electronic products.
References
Chang, S. (2011). Sony Vs Samsung: The Inside Story of the Electronics Giants. London: McMillan Publishers.
McDonald, M. & Wilson, H. (2011). Marketing Plans: How to Prepare Them, How to Use Them. NY: Infobase Publications.
Palley, N. (2000). How to develop a strategic marketing plan: a step by step guide. NY: McGraw Hill.
Reed, P. (2006). Strategic Marketing Planning. London: Sage Publications.
Wilson, S. & Gilliga, C. (2005). Strategic marketing management: planning, implementation and control. NY: Jones & Bartlette Publishers.