Executive Summary
This report provides an analysis of current issues related to medical assistance programs. Attention is mostly devoted to factors that have led to an increase in spending. Scholarly sources will be examined to collect the data on this subject matter. A set of recommendations that should be considered by policymakers will also be provided. All of the findings will be summarized in the final section of the paper.
Spending
One of the core factors that lead to an increase in Medicaid spending is caused by changes in policy. The Affordable Care Act has had an enormous influence in this case, and the number of enrollees has increased dramatically. It is possible to identify a particular connection with the approach that has been utilized in China. The government has recognized that individuals that are most vulnerable cannot gain access to necessary services, and have tried to remove barriers that were present (Wagstaff, Lindelow, Wang, and Zhang 38). However, the initiative has led to many complications in the United States.
Researchers found that expenses have grown by eighteen percent in the states that expanded, and only by six percent in the rest (Galewitz par. 2). This difference is quite significant and should be acknowledged. It would be reasonable to examine enrollment and spending data to get a better understanding of the issue. It is possible to state that the figures seem reasonable, but the number of enrollees is quite intriguing (“Policy Basics: Introduction to Medicaid” par. 3). Close to fifty percent of them are children, and only eight percent are elderly (see Table 1).
Table 1. Medicaid enrollment and spending in 2012.
The data is quite outdated, but should be analyzed when developing a strategy that would help to decrease budget shortages. The government has to provide full support for individuals that enrolled recently throughout the whole year, according to the health law. However, close to ten percent of the costs have to be picked up by the states. The process is rather gradual, but the impact on the budget is enormous (see fig. 1).
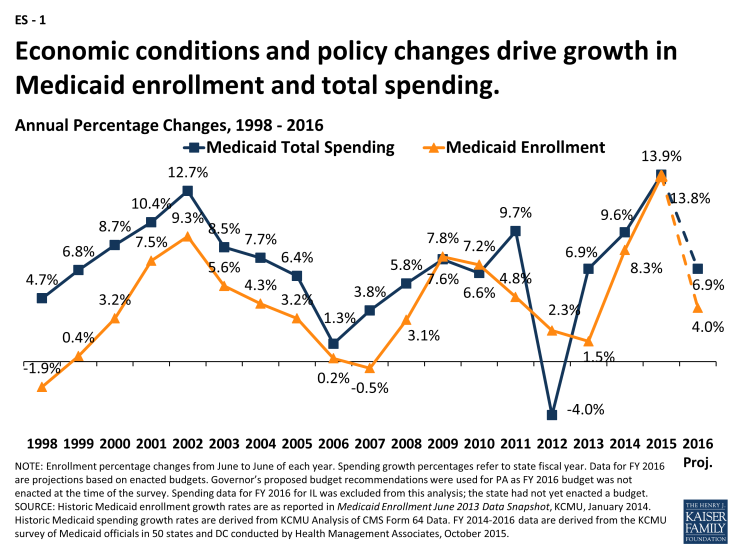
It should be noted that such changes are hard to predict because of numerous economic and political factors. Moreover, the situation is likely to be complicated by the presidential election in 2016, and changes in the policies could be enormous. Another factor that has led to an increase in spending is online insurance. The process became much easier, and eligible individuals could enroll without having to worry about difficulties they had to deal with previously (Galewitz par. 9).
Possible Solutions
Pratt is a certified professional and is quite experienced in this area. She suggests that it would be beneficial to consider a replacement for Medicaid because the program has numerous issues that are hard to resolve (Pratt 12). This approach may be viewed as questionable, but should be taken into consideration because some of the ideas suggested are quite comprehensive. Changes to the expansion should also be considered because the increase in expenses associated with this initiative has been dramatic. Markel, Sauer, and Blasier state that the introduction of additional taxes may be helpful, but the situation will not be improved until the causes of budget shortfalls are addressed (261).
Conclusion
In summary, it is an enormous issue that should not be overlooked because spending is growing at rapid rates, and a financial crisis may follow because the current debt is tremendous, and it could damage the economy in the long-term. The introduction of new policies and an increase in enrollment that followed were determined as the primary causes of the problem. It is quite evident that approaches need to be changed at this point, and it is possible to resolve the situation that has occurred if necessary measures are taken.
Works Cited
“Causes of Enrollment and Spending Growth” n.d. Web.
Galewitz, Phil. “Medicaid Spending Soars – Mostly In Expansion States.” Kaiser Health News. Kaiser Family Foundation. 2015. Web.
Markel, David C., Peter J. Sauer, and Ralph B. Blasier. “Is a Physician “Provider Tax” the Solution to Michigan’s Medicaid Woes?” HSS Journal: The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery 9.3 (2013): 257-263. Print.
Policy Basics: Introduction to Medicaid 2015. Web.
Pratt, Lindsay L. Let’s Fix Medicare, Replace Medicaid, and Repealthe affordable Care Act: Here is Why and How. Sun City Center, FL: Author House, 2012. Print.
Wagstaff, Adam, Magnus Lindelow, Shiyong Wang, and Shuo Zhang. Reforming China’s Rural Health System. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications, 2009. Print.