Executive Summary
The report aims to assess and characterize Meriton Suites’ risks that may develop throughout business activities. A risk report will help better understand the business, social, political, and economic situation and offer recommendations on risk management. The overall findings include stakeholder analysis, business philosophy overview, business risk register, business policies and procedures, and risk radar diagram. Such tools as risk register and templates, namely risk policy and risk procedure examples, will help shareholders assess and evaluate current risks. Risk methodology includes identifying significant risks, using the PESOTEL framework via the business risk register, and adding risks specific to Meriton Suites’ company. According to the risk registry, the Meriton Suites’ total risk score is 65 percent.
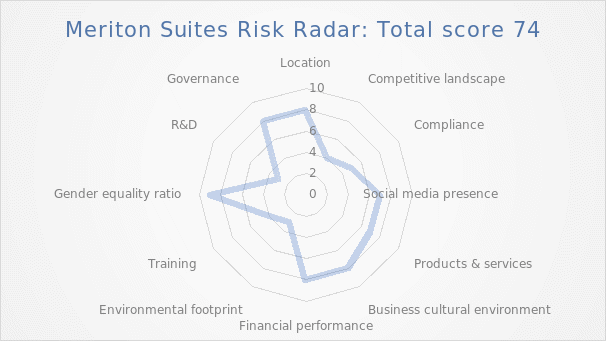
Based on the risk radar diagram, the most critical risks are R&D, competitive landscape, environmental footprint, and training; the overall risk score is 74%. The risk approach in assessing the business from seven risk categories using the “risk register” excel spreadsheet included a systematic literature review, peer-evaluated papers, articles, and governmental policies. The primary recommendation for shareholders is to invest in training to overcome intense competition in the hotel business and provide high-quality services. Furthermore, technological and digital advancements may improve the whole hotel experience. Personnel should be taught about new technology regularly and informed on health and safety procedures and legislation. The business risk score, the average of the two separate scores from the risk register (65) and risks radar (74), equals 69.5%.
Introduction and Business Overview
The risk plan aims to identify, analyze, and describe possible risks for the selected company that may arise during business operations. The overall structure includes stakeholder analysis, business philosophy overview, business risk register, business policies and procedures, and risk radar diagram. The business’s name is Meriton Suites, and it is located in Australia, with the headquarters in Sydney; the business type is privately held. Meriton Suites was founded in 2003 as Meriton Serviced Apartments and has seen tremendous development in its range of premium apartment-style hotel accommodation (“Your home, away from home,” n.d.). The company has become Australia’s largest owner of hotel rooms and one of the biggest private hotel operators, with nineteen locations and a stunning total of approximately five thousand suites. It offers top-quality, professional services combined with smart and modern amenities (“Your home, away from home,” n.d.). Meriton Suites, a luxury lodging brand, is part of Meriton Group, founded in 1963, Australia’s most prominent privately-owned apartment developer (“About Merton,” n.d.). According to the official company’s LinkedIn page, the company size is 201-501 employees (LinkedIn, n.d.). The head office is located at Meriton Tower, 528 Kent St, Sydney (See Figure 1).
Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder Discussion
The key stakeholders that are critical for the operation and functions of the business are owners, staff, and media. Wijtenburn (2020) states that the deal sponsor heads the ownership group with a joint venture partner or a syndicate of limited partners. The job is similar to any other standard real estate owning group but with a hospitality focus. Owners are accountable for ensuring that the brand and operator have a high-quality asset that commands the maximum feasible income (Wijtenburg, 2020). Owners require a financial investment and the use of resources to present the hotel in the best light possible. Hence, the most significant stakeholders are owners who play the most crucial function in the hotel transaction structure. According to Wijtenburg (2020), the staff monitors the hotel’s day-to-day operations, including guest experience, demand planning, sales, and property maintenance. Media delivers value by increasing sales, advertising, and industry best practices (Wijtenburg, 2020). Additionally, hotel positioning in the market is heavily influenced by guests’ perceptions of the company.
Stakeholder List and Diagram
Table 1. Stakeholders’ list
Business Philosophy
Business Name

Business Vision
The business vision of Meriton Suites is to be regarded as the industry leader in Australian suite-hotel accommodation. Meriton Suites aims to provide outstanding value for money and offer the best service that matches the brand and visitors (“Careers,” n.d.). Additionally, the firm aspires to be renowned for having a diverse and inclusive workforce that appreciates all individuals and provides opportunities for advancement in a fast-paced hospitality sector.
Business Mission
The mission is to provide greater levels of service perfection, create unforgettable moments, and surpass all expectations in order to attract brand ambassadors and visitors for life (“Careers,” n.d.).
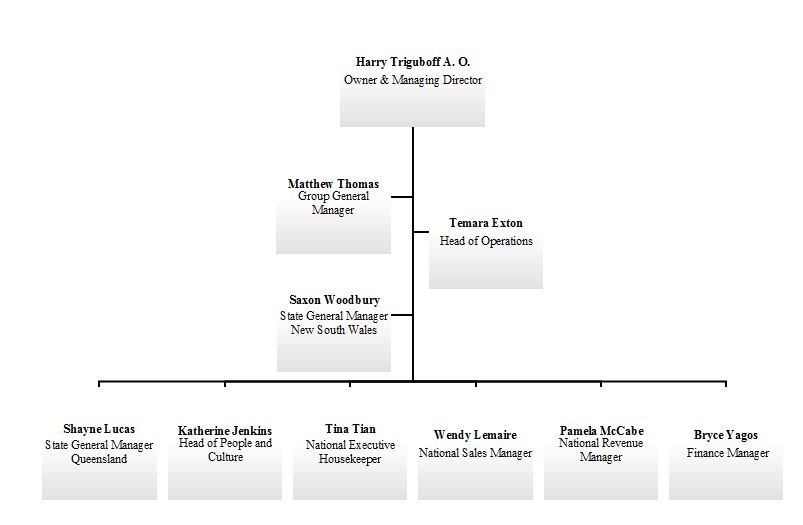
Business Organizational Chart
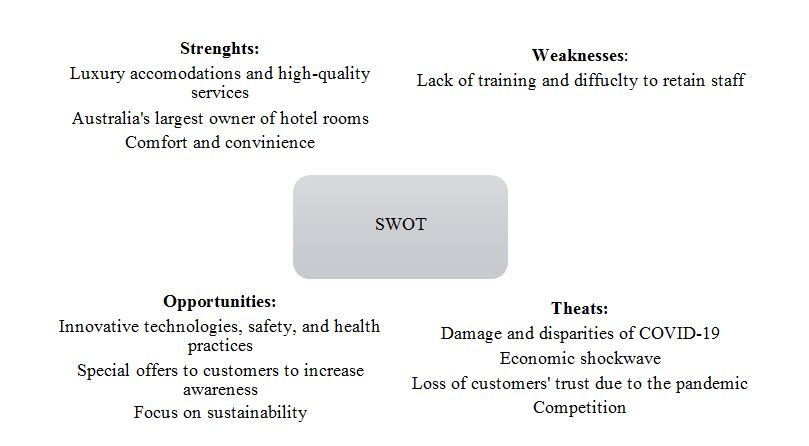
Business SWOT Diagram
The SWOT analysis was prepared as shown in Figure 3. The strengths of the Meriton Suites include luxury accommodations and high-quality services. Moreover, Meriton Suites is Australia’s largest owner of hotel rooms, and it offers comfort and convenience to its guests. Weaknesses include lack of training, especially in crises like COVID-19, and the difficulty of retaining staff. The opportunities are innovative technologies, safety, and health practices to attract more clients and build mutually-trustful relationships. Meriton Suites may also develop special offers to customers to increase awareness and focus on sustainability. Threats are disparities of COVID-19, economic shockwave, loss of customers’ trust due to the pandemic, and the competitive landscape.
Business Risk Register
Risk methodology included identifying the critical risks, applying the PESOTEL framework via the business risk register, and incorporating risks pertaining to Meriton Suites business. Table 2 illustrates the top 10 risks and the degree of influence of each risk incident. The political risk category includes travel restrictions; the closure of state and territorial borders and the prohibition of non-essential travel have a significant influence on the hotel business (Baudille & Rodrigues, 2021). The economic risk category involves fluctuating taxes, whereas the social category includes the following risks: discrimination, layoffs, and lack of skilled staff. For instance, a high incidence of racial discrimination leads to lower job satisfaction in the hospitality sector (Shum et al., 2019). As a result, diversity management and education are critical in the hotel industry.
Notably, the COVID-19 epidemic has substantially impacted the tourist and hospitality industries; hotel managers must deal unpredictably to thrive in this environment. The pandemic’s implications, including travel restrictions, border closures, and quarantine regulations, have resulted in many businesses in the tourist and hospitality industries reducing their operations via layoffs (Japutra & Situmorang, 2021). Employee layoffs are the quickest approach to cutting operational costs. At the same time, hotels should consider workers as intangible assets (Japutra & Situmorang, 2021). Therefore, the necessity of layoffs is a significant risk for both managers and staff.
Operational risks involve misleading or deceptive conduct and workplace injury. Baudille and Rodrigues (2021) claim hotels should not participate in fraudulent or misleading behavior. Reviews, room quality, facilities, rates, and refund rights are examples of representations commonly on complaints and investigations (Baudille & Rodrigues, 2021). Misleading or deceptive conduct is a risk that may negatively impact a hotel’s reputation. Workplace injuries are a crucial risk and may occasionally happen; thus, the personnel should be trained on health and safety measures and regulations. Technological risk is cyber-crime attacks; the managers should ensure to update the software used by the hotel.
The environmental category includes CO2 emissions, and the legal type involves criminal attacks. Owners and shareholders are the most potent influences in the Australian hotel business because their investments prioritize ecologically sustainable policies and practices (ESPPs) (Khatter et al., 2021). CO2 emissions are seen as a critical risk; thus, Meriton takes excellent care and confidence in how the hotel is designed and built to have the least possible environmental footprint (“Sustainable living,” n.d.). Finally, the possibility of criminal attacks should be assessed and investigated because the safety of guests and personnel is the primary responsibility of any hotel, including Meriton Suites.
Table 2. Risk Register (top 10), Meriton Suites, total score = 65%
Business Policy and Procedure Examples
The fundamental purpose of the Risk Management Policy is to provide information and guidance on risk management. Risk is the influence of uncertainty on goals; risk management implements consistent processes within a complete framework to guarantee that risk is handled effectively, promptly, and coherently throughout an organization (Tourism Australia, n.d.). The Risk Management Policy template is attached as Appendix 1. The business is dedicated to identifying, analyzing, and managing risks regularly in the spirit of good governance to maximize the possibility of the hotel reaching its objectives.
A risk management procedure is a systematic method of creating the environment in which the organization, business unit, or project operates and identifying, analyzing, assessing, and treating the risks that may raise doubts about the company’s capacity to fulfill its goals. The Risk Management Procedure template is attached as Appendix 2. A risk management approach also offers a framework for ensuring that identified risks are constantly monitored and evaluated. Communication and feedback are ongoing activities at all phases of the risk management process to deliver, exchange, or collect information and participate in discourse with internal and external stakeholders (Tourism Australia, n.d.). The company has committed to reviewing its risk management framework on an annual basis to ensure that risk management is efficient and continues to promote organizational success.
Risk Radar Diagram
The most crucial risks are R&D, competitive landscape, environmental footprint, and training. COVID-19 has provided the hospitality industry with an unprecedented challenge. Despite being a popular tourist destination globally, Australia was unable to match consumer expectations, especially at its top-tier luxury hotels (Mehta et al., 2021). It also conveys a lack of preparedness and adaptability in the hospitality industry. During COVID-19, Mehta et al. (2021) contend that top leadership in the continent’s hotels is relatively slow in learning and adjusting to altering consumer demands. Thus, it is vital to focus on training to overcome tough competition in the hotel industry and ensure high-quality services at Meriton Suites. Bonfati et al. (2021) claim that technology and digital improvements enhance the whole hotel experience by allowing customers to obtain speedy and effective service. Consequently, according to the World Economic Forum, R&D carries a significant risk of developing new services and receiving positive customer feedback and a high level of service satisfaction. (2021), technology-enabled services may aid in developing new business ecosystems and the advancement of possibilities. Sustainability plays a vital role in modern society; thus, Meriton Suites should assess its sustainability goals and environmental footprint.
Table 3. Risk rating, Meriton Suites
Report Conclusion
The main recommendation for shareholders is to invest in personnel training in order to compete in the hotel industry and deliver high-quality services. Furthermore, technical and digital improvements have the potential to improve the whole hotel experience. Employees should be trained on new technologies regularly and updated on health and safety procedures and regulations. Shareholders should emphasize environmentally sustainable policies and practices. Essentially, the business risk score, the average of the two separate scores from the risk register, namely 65%, and risk radar, 74%, equals 69.5%.
References
About Merton. (n.d.). Meriton. Web.
Baudille, V., & Rodrigues, A. (2021). The international hotel law review: Australia. Web.
Bonfanti, A., Vigolo, V., & Yfantidou, G. (2021). The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on customer experience design: The hotel managers’ perspective.International Journal of Hospitality Management, 94. Web.
Careers. (n.d.). Meriton Suites. Web.
Industry leaders. (n.d.). Meriton Suites. Web.
Japutra, A., & Situmorang, R. (2021). The repercussions and challenges of COVID-19 in the hotel industry: Potential strategies from a case study of Indonesia. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 95. Web.
Khatter, A., White, L., Pyke, J., & McGrath, M. (2021). Stakeholders’ influence on environmental sustainability in the Australian hotel industry.Sustainability, 13(3), 1351. Web.
LinkedIn. (n.d.) Meriton Suites. Web.
Mehta, M. P., Kumar, G., & Ramkumar, M. (2021). Customer expectations in the hotel industry during the COVID-19 pandemic: a global perspective using sentiment analysis.Tourism Recreation Research, 1–18. Web.
Meriton Australia. (n.d.). Corporate office headquarters. Web.
Shum, C., Gatling, A., & Garlington, J. (2019). All people are created equal? Racial discrimination and its impact on hospitality career satisfaction. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 89. Web.
Sustainable living. (n.d.). Meriton Suites. Web.
Tourism Australia. (n.d.). Risk management policy and procedure. Web.
Wijtenburg, J. (2020). 3 major stakeholders and their role in your hotel investment. LinkedIn. Web.
World Economic Forum. (2021). Global risks 2021, 16th edition. Web.
Your home, away from home. (n.d.). Meriton Suites. Web.
Appendix 1: Risk Management Policy Template
Title of policy: Risk Management Policy
Code and Version: F&B000/01-01-2021
Policy Owner: Director of Food and Beverage
Date approved by XXX: 1 January 2021
Schedule review date: 1 January 2023
Related policies and documents:
- Purpose: To ensure that …
- Coverage: This policy applies to all food and beverage operations and personnel.
- Background
- Definitions
- Policy: All food and beverage personnel must ensure that…
- Legal compliance documents and related legislation
Appendix 2: Risk Management Procedure Template
RMP Procedure Template
Title of procedure…
Code and Version: F&B000/01-01-2021
Policy Owner: Director of Food and Beverage
Date approved by XXX: 1 January 2021
Schedule review date: 1 January 2023
Related policies and documents:
- Purpose: To ensure that …
- Coverage: This policy applies to all food and beverage operations and personnel.
- Procedure: Outline and describe the steps involved in this procedure. Ensure that the procedure is unambiguous, clear, and logical in the way it is presented.
- Related documents, legislation, and information regarding this procedure