Introduction
The monetary policy of an economy plays a huge role in presenting crucial information that influences its day-to-day business operations. These financial guidelines allow governments to regulate their liquidity, credit, interest, and inflation levels, among other economic components, with a view to ensuring sustainable financial growth. In this paper, the application of the monetary policy to the UAE and Egypt is found to depict similarities and differences. Economic growth is found to be steady in the UAE, as opposed to Egypt, thanks to the contribution of the tourism and hospitality sectors.
Differences
Inflation is one of the elements of monetary policies. This component indicates how loose or tight the respective monetary policy is to the prevailing business operations. According to a 2017 report by the Central Bank of Egypt, this country’s yearly inflation rate was on an upward trend since mid-2016. The corresponding negative effects were addressed via the annual NEER depreciation implemented during the second quarter of 2016. This situation led to an elevated price rise discrepancies between Egypt and its trading allies (see fig. 1).
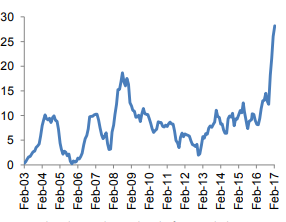
On the contrary, although Egypt’s inflation has been fluctuating in the recent past, resulting in an increased cost of goods and services and, consequently, joblessness, it has continued to be consistent in the UAE for the last three years, ranging from 3.0% to 3.7% (Gukasyan et al. 1535). As a result, the predictable increase in inflation in the UAE has been accompanied by stable commodity prices and reduced unemployment rates.
This difference results from the UAE’s move to execute measures that are meant to trigger the demand and supply patterns while at the same time, ensuring that commodity costs and inflation remain constant. Hence, while Egypt records significant detrimental effects associated with the observed inflation differential, Khan and Derhally reveal the extent to which the UAE’s Central Bank is reporting positive outcomes, which boost its competitiveness due to the corresponding rise in the demand for various goods and services.
Interest rates form another component of countries’ monetary policies. According to Khan and Derhally, interest rate charges are usually adjusted to reflect the prevailing levels set by the central government. Any review determines the performance of various rate-reliant industries, including car-manufacturing and real-estate sectors. When the Fed rate increases, countries, including Egypt and the UAE, are forced to adjust their interest rates accordingly in line with the existing business environment.
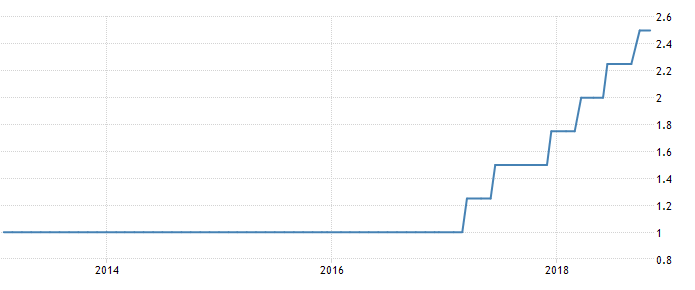
Particularly, the move to increase Fed rates in September 2018 forced the UAE’s Central Bank to elevate benchmark interest charges by 25 bps, which corresponded to 2.5% (Khan and Derhally). This adjustment indicated the onset of tougher economic times throughout the UAE, although unfavorable market conditions had been observed since 2014. See fig. 2 below, which illustrates the status of interest rates in the UAE from 2014 to 2018.
On the other hand, data published by the Central Bank of Egypt indicates the Monetary Policy Committee’s efforts to retain interest rates constant for three consecutive times in 2018. For instance, while the UAE raised its rates to 2.5% in September 2018, the Central Bank of Egypt set its values constant at 16.75% during the same period (Egypt Interest Rate). See fig. 3 shows the extent of fluctuations in interest rates in Egypt from 2014 to 2018.
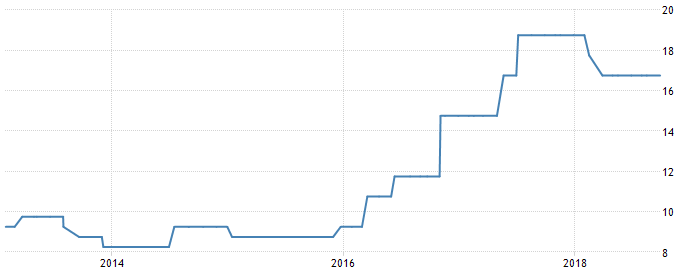
Interest rates in Egypt have been higher compared to the situation in the UAE (see table 1). For instance, while Egypt has recorded highs of 21.4% and lows of 8.25% (Egypt Interest Rate), its counterpart reported 4.75% and 1% as its largest and smallest interest rate charges, respectively (UAE Interest Rate). Hence, doing business in Egypt requires more capital investments compared to the United Arab Emirates.
Table 1. Interest Rate Differences Between the UAE and Egypt.
Similarities
The Central Bank of Egypt (CBE) and the Central Bank of the UAE have managed to formulate and implement effective monetary policies. For instance, in both countries, commodity prices have remained stable in the past three years to attract investors and foster economic growth (Mohamed). Monetary policies in the two countries have also utilized interest rate adjustment mechanisms to regulate the cost of goods and services. This approach has contributed to reduced inflation levels in both economies.
Monetary policies in Egypt and the UAE are executed based on the prevailing market conditions. In 2018, the CBE reduced major interest charges by 100 bps as a strategy for stabilizing commodity prices (Mohamed). Similarly, the decision to adjust interest rates by 25bps in the UAE was in line with the prevailing market expectations (Khan and Derhally). Both economies regulate three elements, namely overnight deposit levels, overnight lending charges, and the main operation rate as provided for by the IMF and the World Bank.
The UAE is a developed economy. Its government employs expansionary monetary policies similar to those adopted in Egypt to ensure stable economic growth (Gukasyan et al. 1534). According to the IMF Country Report, the Central Bank of the UAE applies financial guidelines that guarantee a sustainable money supply to reduce inflation rates. The CBE also utilizes analogous policies. The IMF monitors the GDP growth rates of various economies, including Egypt and the UAE (IMF Country Report; (International Monetary Fund). In addition, monetary policies in both the UAE and Egypt play crucial roles in ensuring that their currencies remain steady in the foreign exchange market.
Conclusion
Monetary policies entail decisions and measures taken by the respective financial institutions such as central banks to ensure that money allowed to circulate is adequate to facilitate the achievement of the laid down price and development goals. Modifying monetary policies in response to forces such as Fed adjustments may produce similar impacts, such as increasing inflation levels. However, the actual figures representing interest rates, price rise, employment levels, and overnight lending charges, among other components of monetary policies, are different in the UAE and Egypt.
Works Cited
Central Bank of Egypt. Monetary Policy Report. 2017. Web.
“Egypt Interest Rate.” Trading Economics, 2018. Web.
IMF Country Report. “United Arab Emirates.” International Monetary Fund. 2014. Web.
International Monetary Fund. “Egypt: The Economy is Gathering Strength.” IMF News. 2017. Web.
Gukasyan, Gurgen L. et al. “State Economic Policy and Reform in the Oil-Exporting Countries on the Example of Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Iraq.” International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, vol. 6, no. 4, 2016, pp. 1534-1541.
Khan, Sarmad, and Massoud A. Derhally. “UAE Raises Benchmark Rate by 25 Basis Points Following Fed Increase.” The National. 2018. Web.
Mohamed, Hanan. “CBE Keeps Interest Rates Unchanged for 3rd Time in 2018.” egypttoday. 2018. Web.
“UAE Interest Rate.” Trading Economics, 2018. Web.