Functional Performance
A multinational company is one that has several branches in different countries around the globe. Examples of such companies are Toyota, Sony, and General Motors. However, this paper analyses the performance of Japan’s Toyota Motor Corporation.
Firm’s Background
The Toyota Motor Corporation (Toyota) was founded by Toyoda Kiichiro of Japan in 1937. It is a multinational corporation with its headquarters located in Japan, and the larges automaker by sales. In Japan, Toyota is also the largest manufacture with a current market share of 50% (Rowley, 2007). In the global market, however, the motor corporation holds a third position in the market share. The market share of Toyota in Japan is as shown in the table 1.0.
Table 1.0: Market share of Toyota in Japan. Source: PSA (2005).
The logo of Toyota Motor Corporation is shown in the figure below.

Introduction to International Accounting System
International accounting is a broad topic that generally focuses on issues relating to multinational companies. In addition to that, the topic also deals with the study of various functional areas of accounting in a global perspective. International accounting tries to provide solutions to the issues facing multicultural companies when engaging in foreign direct investment and international trade.
The world economic situation is quickly changing momentum and more exporting and importing companies being incorporated into the system. This trend appears to move in the direction of normalising international trade as much smaller firms are now participating in the trade as well.
Within the last 20 years, there has been substantial growth in the foreign direct investments which is attributed to globalization effects that encouraged countries to liberalize investment laws.
With such investment capabilities, countries and multinational countries have to employ better ways of ensuring profit maximization and value is attained. Therefore, special accounting systems that can help in achieving such goals have to be developed and applied in their models.
Type of Accounting System Used by Toyota
Toyota Motor Corporation utilizes the Just-in-time (JIT) model of accounting system in running its businesses worldwide. “In this approach, companies attempt to modify the process of manufacturing so that the non-value-added activities are completely removed fro the process” (“Just-in-Time, n.d”).
By doing this, companies are in a position to determine weather the cost involved is high or low. Therefore, this provides a company with the benefit of monitoring itself. The JIT evolves as a result of the need to meet demand just in time rather than having inventory at hand just in case.
“The characteristics of this system include: Minimization of defects in goods; minimization of raw material; simplification of the process of production; and the creation of timely multi-skilled workforce” (“Just-in-Time, n.d”).
Impact of the Accounting System
Other than having a number of positive implications, the JIT also has some negative implications on a business. Below are the advantages and disadvantages of using the JIT accounting system in a multinational company.
Advantages
- The use of JIT helps in lowering costs that would come as a result of space needed for inventories and production;
- It reduces costs that would arise from inventories being obsolete.
- It leads to reduction in handling and transporting inventories.
- It lowers the cost of investing in inventories.
- It leads to less paperwork as records of purchase, storage, and used inventories are cut low.
- Finally, it leads to reductions in the total costs of manufacturing goods that would be compromised by better coordination required between departments to achieve run at limited levels of inventories (“Just-in-Time, n.d”).
Disadvantages
- The introduction and actualization of a serious Just-in-time procedure can prove to be very difficult and expensive for a start.
- Furthermore, JIT exposes a business into more risks with regard to the business’ supply chain. “A production line can quickly come to a halt if essential parts are unavailable” (Shawn, 1994).
Justification of the System – Dell Computer Case Analysis
Del Computer Corporation is a multinational company which utilizes the Just-in-Time system in it operation. At the moment, the JIT system in Del has been improved to a level that a delivery for a customized computer can be made 12 hours after customer places his or her order via the internet (Shawn, 1994).
Application of this system has led to the reduction in production cost of Dell computers by a significant factor. The low production costs has since enabled Dell to maintain a competitive edge since it values its products 10-15% lesser than its business rivals. In addition, the effectiveness of the JIT system has led to an increased growth rate of Dell at 5 times more than the average growth rate of that industry (Shawn, 1994). The lower costs are achieved in a very simple manner.
“While machines from Compaq and IBM can languish on dealer shelves for two months Dell does not start ordering components and assembling computers until an order is booked.” (Shawn, 1994). This works effectively for Dell since the price of computer parts can take a very short period to drop by significant figures. This mean while other manufactures will be making losses due to lower prices, Dell does not participate in such losses.
Basing on the case of Dell, it is evident that the benefits of the Just-in-Time system are much more than the possible disadvantages. This is true because by implementing the JIT system; Dell has experienced lower production costs, more sales, minimal losses, production efficiency, and general growth of the company. Therefore, the Just-in-Time system is very effective and should be adapted by other multinational companies for better results.
Recommendations for Improvement of Accounting System
Judging from the Dell case, it is conclusive to say that the JIT system is more effective in maximizing a firm’s productivity as compared to other accounting systems. This is due to many benefits that it yields for a business as compared to the risks. It is a recommendation that more multinational companies should implement the system so as to enjoy the same benefits. However, companies engaging in the implementation should be aware of the accompanying risk and work against it.
Business Performance
Toyota is a major car manufacture with its headquarters in Japan. Therefore, it is purely a product-based company manufacturing various types of cars. The vast variety of automobiles produced by the multi-national ranges from mini-vehicles to huge transport trucks.
Apart from the common brand (Toyota), several other brands are produced such as Lexux, Hino, and Daihatsu. In the year 2005 alone, these brands sold over 6 million units in almost all parts of the world. Apart from manufacturing millions of cars to meet the local and global demand, Toyota has values that guide its service to customers.
These values are in line with their mission to serve ethically, uphold quality, and create an eco-friendly company in harmony with nature and society. In order to meet their mission and goals, Toyota has adapted a favouring marketing mix as described below.
Marketing Mix
The 4Ps marketing mix blending for Toyota; product strategy, pricing strategy, promotion strategy, and places strategy are discussed under the subtitles below.
Product Strategy
Anything that can be offered in a market with an aim of satisfying a particular need or want is referred to as a product. Toyota has used various brands like name, sign, symbol, term or design to identify and differentiate the finished goods from their competitors.
For example, the well known brand in Japan is TOYOTA which also sells and is known in various parts of the world. Also, labeling has been used by the company by creating simple tags that are attached to the finished product. The mark containing the three ovals (as shown in figure 2) is identified as the label or logo for the company.

Price Strategy
Generally, companies adapt their pricing strategies and change them depending on the conditions of the market. In the international market, a new marketing strategy through collective action is being organized by emergence of commodity marketing organization.
However, Toyota employs a value-driven pricing method for its commodities. With this method, value is given to the customers in terms of quality, warranty, and customer support. Therefore, the company wins loyal customers by providing an affordable price quotation for a quality product. This process enables the company to reinvest in its operations making it a low-cost manufacturer without sacrificing the quality of offerings. This process results in attraction of more value-conscious customers.
Depending on the region, Toyota cars will be sold at different prices. Therefore, a differentiated pricing is also adapted. This is referred to as location pricing where different states get the same model for different prices. This is due to different insurance rates and road taxes from one state or country to another.
Promotion Strategy
Generally, Toyota uses various techniques to advertise its products because most of the printed adverts are usually individually targeted. These promotions are usually customized according to factors like power, comfort, driving pleasure, performance and leg room. Toyota conducts its product promotions through various methods such as advertising, brochures, bill boards, display signs, bulletins and television broadcast.
As such, advertising is a type of communication which has the intention and effect of convincing an individual into purchasing a certain product. In this type of promotion, for example, Toyota uses pictures of models posing next to best selling brands so that one may be easily interested in the brand. Also, brochures, leaflets, and posters are produced with picture of brands like Prado, Innova, and Toyota Corolla on them so as to attract more influence.
In India, Toyota uses billboards at various expressway and highways to advertise Innova and Toyota Corolla. Other methods that are used by the company in promotion include; sales promotion, public relation, personal selling, direct marketing and over the internet/Pioneer Toyota website.
Place (Distribution) Strategy
This involves the selection and management of channels and product flow to customers. It represents the pre-determined locations where a company’s products can be bought. This may refer to the physical location such as showrooms or actual geographical locations where one can place a purchase order.
The figures below show a sample picture of a showroom and a map showing various destinations for purchasing Toyota cars.

The company employs a vertical marketing system in its distribution process as indicated in the figure 3 below.
Competitive Analysis/PEST Analysis
In this section, an analysis of the political, economical, Socio- cultural and technological factors affecting Toyota Motor Corporation in relation to the current global market condition shall be conducted.
Political factors
Foreign direct investment policy in foreign governments has major impact on the company; for instance, the Chinese regulation is not easy to follow in case of a joint venture (Hurley, Norton & Quiroga, 2005). On the other hand, some government initiatives and policies influence the business operations: These include; tax exemption, tax credit of automobile proprietors, financial package, loan facilities for the customers, and volatile exchange rates (Hurley, Norton & Quiroga, 2005).
However, the aggressive approach by the government of Nigeria and socialist government in Venezuela, in conjunction with the instable environment in the Middle East countries are causing a major influence (Ofose, 2011). For example, Toyota suffered a legal issue in 2008 due to trading a defective Toyota Corolla 2008 model.
Economic factors
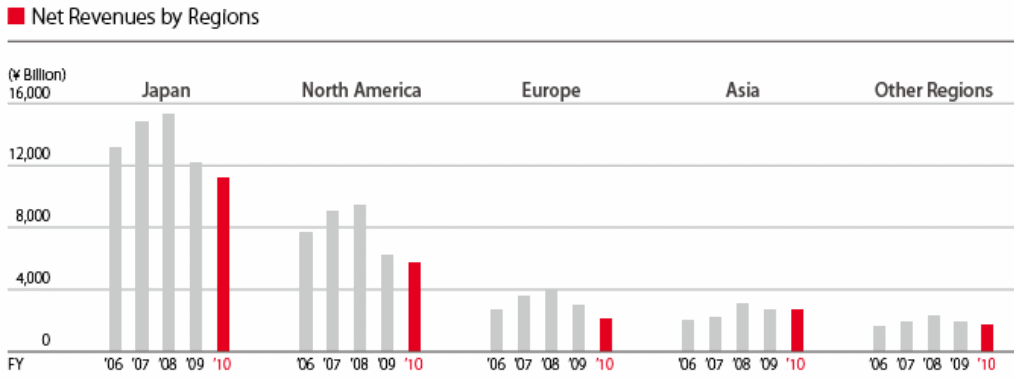
Between 1992 and 2007, Toyota invested more than 7.75 billion Euros throughout Europe to meet the customer demand in the region and increase profit as well (Toyota Corporation, 2009). The automobile industry was seriously affected by the global financial downturn; particularly, this impact was serious in the developing countries (Toyota Corporation, 2009).
In 2009, total car production reduced by 55.3% less than the previous year’s production in the UK. On the other hand, unstable oil and gasoline price, fluctuated international demand for cars, rising competitive pressure, increase operating costs, reduce sales revenue, and decline in the purchasing power of the customer were major problems for car manufacturing companies.
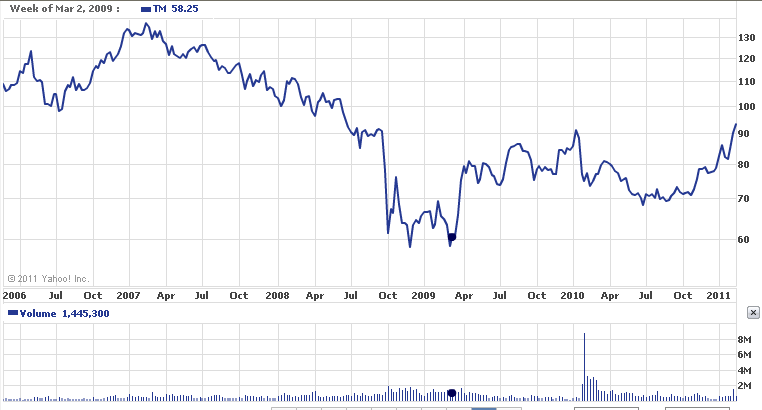
According to Toyota’s annual report of 2009, this company faced a direct impact on the US, Japanese, and other Asian Countries; for instance, Toyota has to change its selling vision as its net revenues declined 21.9%, which resulted in operating losses of ¥461 bn, and increases in operating costs of ¥491.30 bn (Toyota Corporation, 2009). The company is trying to recover its market position. The following figure shows the companies share price increasing after a large fall.
Socio-cultural factors
Toyota Motor Company operates in more than 140 countries, as a result, it has to emphasis on the socio- cultural factors in order to increase employee retention rate, and manage the customers as well (Toyota Corporation, 2010).
“The management of this company follows the discloser rules, code of conducts, Sarbanes-Oxley Act, Exchange Law of Japan, and publishes CSR report, business and financial information, and audit report each year for the convenience of the stakeholders” (Toyoda, 2010). In 1999, Toyota and its suppliers donated more than US$1,000,000 to 63 NGOs in supplier cities across the US market (Toyoda, 2010).
Technological environment
The Adoption of advanced technology is one of the most important factors undertaken by the manufacturing company, as it has to be concerned about the safety of passengers by minimizing risk of accidents (Toyota Corporation, 2010). However, the vision of the company is to offer environment friendly cars; thus, it has introduced next-generation hybrid power cars with VSC (“Vehicle Stability Control”), ABS (Anti- Lock Brake System) and Brake Assist, ITS, and so on (Toyota Corporation, 2010).
In addition, the philosophy of the company is to put the customer first; therefore, it needs to offer cars at competitive prices and concentrate on latest innovations (Toyota Corporation, 2010). Table 1.1 shows how Toyota Motor Corporations competes with its market competitors; Ford Motor Company, General Motors Company, and Honda Motor Co. Limited in relation to the Auto Manufacturers Industry.
Table 1.1: Competitor Comparison Toyota Motors Corporation. Source: Yahoo Finance (2011).
Reference List
Hurley, J. Norton, D. & Quiroga, P. (2005). Toyota. Web.
Just In Time. Web.
Ofose, G. (2011). Nigeria: RT Briscoe Sued for Selling Faulty Toyota Car. Web.
Rowley, I. (2007). Toyota set to top 50% market share in Japan. Retrieved from the Bloomberg Businessweek
Shawn T. (1994). Raiding a company’s Hidden Cash. Fortune: PP 82-87.
Toyoda, A. (2010). Toyota Motor Corporation. Web.
Toyota Corporation. (2009). Annual Report 2009: The Right Way Forward. Toyota Co. Web.
Toyota Corporation. (2010). Annual Report 2010: The Right Way Forward. The Toyota Global. Web.
Yahoo Finance. (2011). Basic Chart of Toyota Motors Corporation for 2006 to 2011. Web.
Yahoo Finance. (2011). Direct Competitor Comparison Toyota Motors Corporation. Web.