Background of the company
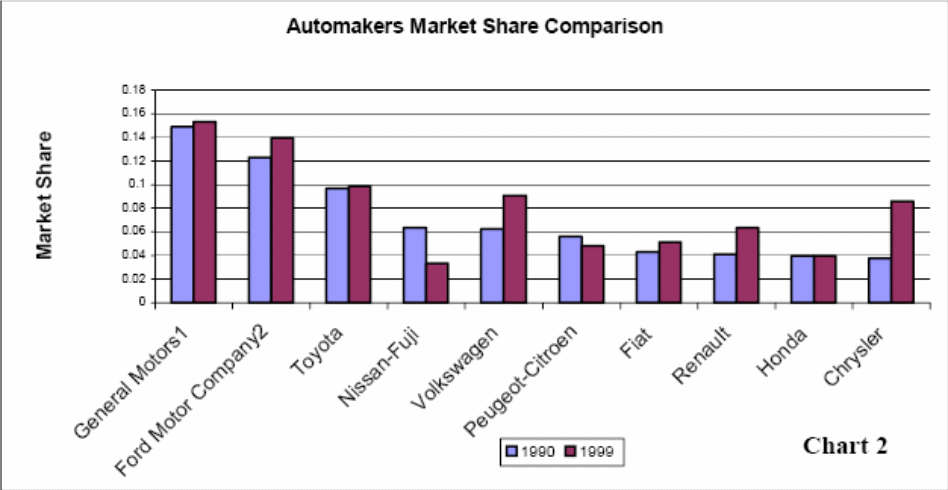
Toyota is the leading automotive manufacturer in Japan and Ian Rowley stated that Toyota has successfully captured 50% of the total market share in Japan (Rowley, 2007) while the company was in the third position in the global market (Ghadar and Ghemawat, 2001). However, the following table demonstrates the market share of Toyota in Japan –
Table 1: Market share of Toyota in Japan. Source: PSA (2005).
Presently, the company is the legal owner of various globally branded cars including Lexus, Scion, Isuzu, Yamaha, and Mitsubishi Aircraft Co with about 522 subsidiaries; the company had been able for making an access into a Formula 1 functionality group through the inauguration of joint-ownership with Citroen and Peugeot (French Vehicle Company) for the creation of speed vehicles up there (Reuters, 2011)(One of the Largest international multimedia news agency in the World).
Toyota closely observes environmental sustainability, and maintenance of its such philosophical view requires obligation of environmental laws for upholding atmospheric safeguard, concerned with production of outstanding low hydrocarbon emitting cars environmentally friendly hybrid-engines for individual markets; it experimented with Brazilian and European markets along with further innovative proceedings for enhancing vehicle-capacity by lowering weight and size (Financial Times, 2011).
Chang-Ran Kim the Asia autos correspondent reported in Reuters that Toyota faced some uncertain events during its entire journey, for example, because of global financial crisis; the company had to sacrifice its continuous record of global profits margin in 2008 by first yearly loss within last 70 years (Kim, 2008) but in 2010, the company’s market share seemed to be far better than the previous year’s.
The following figure shows Toyota’s market share in the context of global automotive industry (Ghadar and Ghemawat, 2001):
PEST analysis
This segment is going to analyze political, economical, Socio- cultural and technological factors of Toyota Motor Corporation in terms of present global market condition (Johnson, Scholes & Whittington, 2008) (Writer’s Full name Prof Gerry Johnson (Author), Prof Kevan Scholes (Author)), for example-
Political factors
Hurley, Norton & Quiroga (2005) stated that foreign direct invest policy of overseas government has major impact on the company, for instance, the Chinese regulation is not easy to follow in case of joint venture (full name of Author John Hurley, Dennis Norton, and Pablo Quiroga). On the other hand, some other government initiatives and policies influence the business operation, such as, tax exemption, tax credit of automobile pool lanes for plug- in hybrid proprietors, financial package, loan facilities for the customers, and volatile exchange rate has both negative and positive impact on its operation (Hurley, Norton & Quiroga, 2005).
However, aggressive approach of the government in Nigeria and socialist government in Venezuela, instable environment in Middle East countries (Iraq, Iran, Egypt, Libya, Israel- Palestine) are posing major influence and Toyota faced legal problem in Nigeria (Ofose, 2011). For instance, Toyota have been suffered legal problem in 2008 due to trade a defective Toyota Corolla 2008 model
Economic factors
Since 1992 to 2007, this company has invested more than 7.75 billion Euro throughout Europe to meet the customer demand in this region and increase profit as well (Arashima, 2007, p.3). Automobile industry seriously affected by the global financial downturn, particularly, this impact was serious in the developing countries (Wad, 2009) and In 2009, Total car production reduced to 55.3% than previous year’s production in UK (BBC News, 2009).
On the other hand, unstable oil and gasoline price, fluctuated international demand of car, rising competitive pressure, increase operating costs, reduce sales revenue, decline the purchasing power of the customer were the major problems for the car manufacturing companies (Wearden, 2010).
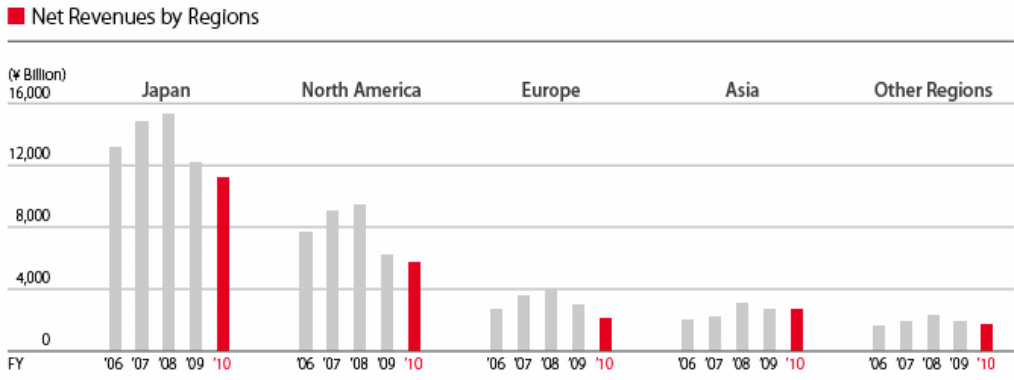
According to the annual report 2009 of Toyota, this company faced direct impact on the US, Japanese, and other Asian Countries, for instance, Toyota has to change its selling vision as its net revenues declined 21.9%, evidenced an operating loss of ¥461 bn, and increases operating costs of ¥491.30 bn (Toyota Corporation, 2009). However, the company is try to recover its market leading and the following figure demonstrates that it share price is increasing after large fall –
Socio- cultural factors
Toyota has operation in more than 140 countries, as a result, it has to emphasis on the socio- cultural factors in order to increase employee retention rate, and manage the customers as well (Toyota Corporation, 2010). The management of this company follows the discloser rules, code of conducts, Sarbanes-Oxley Act, Exchange Law of Japan, and publishes CSR report, business and financial information, and audit report each year for the convenience of the stakeholders (Toyoda, 2010). In 1999, Toyota and its suppliers donated more than US$1,000,000 to 63 NGOs (non-profit organizations) in supplier cities across the US market (vBulletin Solutions, 2010);
Technological environment
Adoption of advance technology is one of the most important factors for the car manufacturing company, as they has to concern about the safety of the passengers by minimizing the risk of accidents (Thompson, et al, 2007). However, the vision of this company is to offer environment friendly cars to reach the aim of zero emission of carbon, as a result, it has introduced next-generation hybrid power cars VSC (“Vehicle Stability Control”), ABS (Anti- Lock Brake System) and Brake Assist, ITS, and so on (Toyota Corporation, 2010). In addition, the philosophy of this company is to think customer first, so, it needs to offer cars at competitive price and concentrates on the innovation where technology play vital role (Toyota Corporation, 2010).
Sustainable aspects of Toyota
From the beginning of its operation, both Toyota and its subsidiaries are taking part in positive sustainable development plan specially seeking harmony among people, society, the global environment, safety, personnel development, and so on (Toyota Global, 2010, p.3).
The government body US Environmental Protection Agency (1999) depicted the scenario of environment pollution due to Hydrocarbon, and this agency graphically represented that cars and motor cycles are the main cause of Air pollution by 55%. However, famous author Daniel C. Esty & Andrew S. Winston concentrated on the fuel efficiency issues in order to meet target market but they also gave importance on the environment challenges (Esty & Winston, 2009, p.133).
Corporate Social Responsibility
As a result, the management team of this company has taken some strict ethical rules to comply with the domestic, national, and global laws for following the selected codes of conduct and CSR commitments (Toyota Global, 2010, p.3). according to the annual report 2010 of Toyota, this company focusing on the basic philosophy of “Customer First”, and developed a number of creative, safe, and standard products to the target customers for enhancing their standard of living, and achieved numerous awards like the House of the Year in Electric 2009 Awards in Japan (Toyota Corporation, 2010, p.16). However, Subhabrata Bobby Banerjee stated that Toyota’s green image is based on its hybrid car Prius and gas-guzzling SUVs (Banerjee, 2009, p.88);
Company’s ethics
According to the annual report 2010 of Toyota, it has already established a CSR Committee through amalgamating the Corporate Ethics Committee to hold regular meetings for the reason of preparation, internal controls, reporting, measurement, response to the biodiversity issues, and ensure strict compliance on the code of ethics (Toyota Global, 2010, p.3). Toyota main aim to protect the environment from the pollution, such as, it has taken Toyota Environmental Activities Grant Program to stop marine pollution, global worming, deforestation and air pollution (Toyota Global, 2010, p.3).
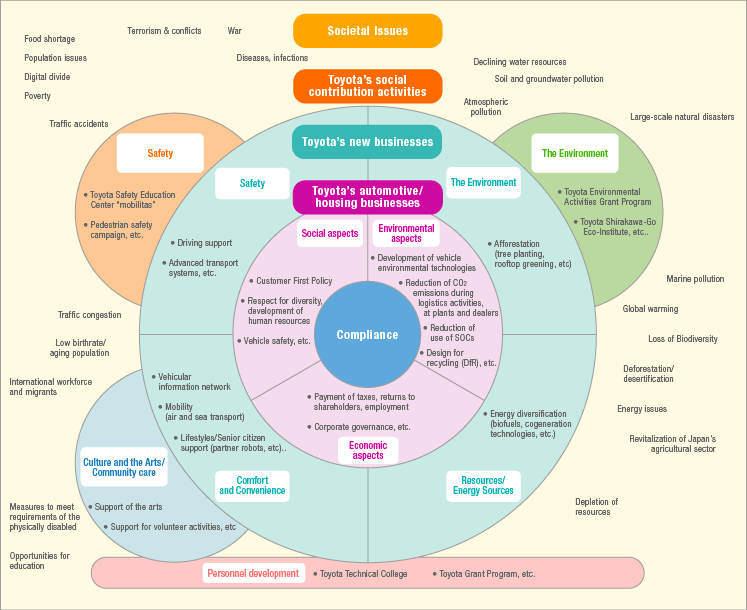
Environmental policy
Toyota has already achieved ISO (International Organization for Standardization) 14000 certification due to keeping track in the root of sustainable growth of the company by decreasing negative impact on natural environment by its business functions, for instance, it has introduced Toyota Prius and the Fuel Cell Electric vehicle to reduce environment pollution (Maybaum, 1999)(full name of writer Mary Ann Maybaum). In addition, the CEO of Toyota would like to implementation of its future vision “Global Vision 2020,” so it promotes different technological experiments for adopting environmental harmony (Toyota Global, 2010, p.3).
However, Toyota Global (2010) reported that innovative mode for initializing clean, safer, and better quality cars, protection of illegal monetary exchange in terms of any corporate partner, public agency or authority with integral honesty are also important parts of its future vision;
However, the following two figures provide the information related with reduction in water consumption and carbon dioxide emissions of Toyota –
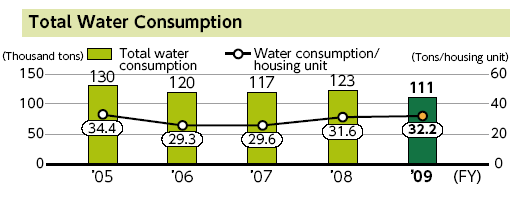
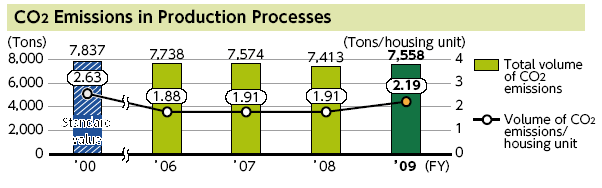
Workplace
All the employees are important to the company, so all get proper respect with unbiased employment scopes, bonus facilities, pension fund, reasonable employment conditions, protection of human rights, incentives, and favourable working condition, equal opportunity irrespective of cultural groups, and so on (Toyota Corporation, 2010).
Benchmarks and good practice of Toyota
Lutsey and Monte (2010) pointed out that the greenhouse gas emissions from automobiles has been accounted as ~20% in this planet which is a major threat to the sustainability and environmental hazards of this era. Thus, it is essential for the global automakers to bring quick improvement in the technological aspects in regards to eco-friendly vehicles and the question of such good practice required to benchmarking.
Henning Lohse-Busch, Ph.D. Argonne National Laboratory (2010) has conducted a benchmarking comparison among Toyota’s Prius model against Honda’ Insight model and Nissan’s the Nissan Leaf model, BMW’s Mini E BEV, and TADA Ford and presented the following competitive benchmarks –
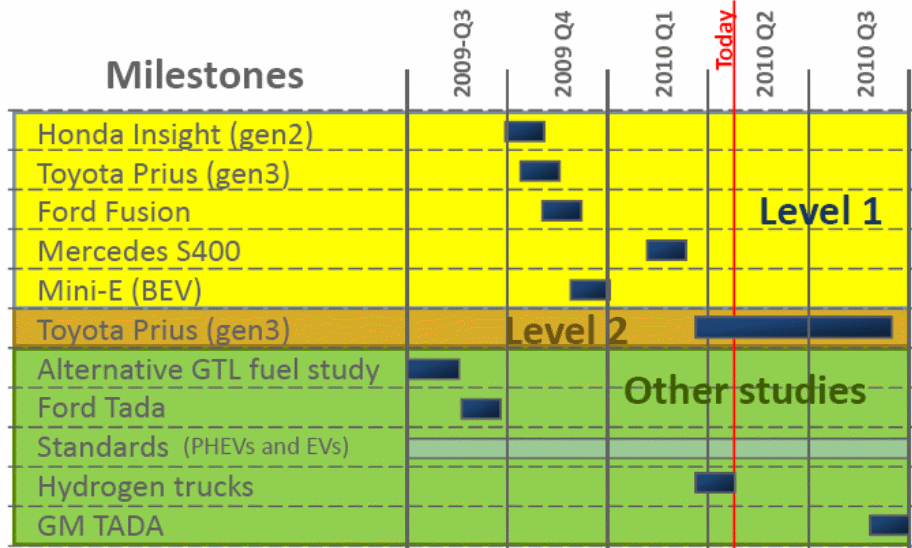
Within the benchmarking process Nissan Leaf and Honda’ Insight placed at the primary level (first round) where it is necessary to bring more modification but Toyota’s Prius model has reached at advanced level with benchmarking indication (Lohse-Busch, 2010).
Iida (2010) determined that the Nissan Leaf is an electric automobile while the Toyota Prius, and Honda Insight are Hybrid Vehicles but all the three autos have identified as next generation vehicles for environmental friendly and low energy costs. Though all the three automakers are from Japan, but only Toyota has jointed to establishing ‘Japan Smart Community Alliance’ where most of the technology giants of Japan in power, oil gas and IT sector including academia and media have gathered under one umbrella to face the challenges of coming era (Iida, 2010).
Author Ann Rodriguez and Chris Page mentioned that to respond to the market needs for economy cars with low fuel consumption and to decreasing carbon emission, Toyota and Honda have simultaneously launched hybrid cars in US market while the Toyota Prius came in the market 2000, Honda Insight started its journey in 1999 as a hybrid car with only two seat (Rodriguez and Page, 2004). Rodriguez and Page (2004) also noted that the hybrid vehicle industry has evidenced a growth of more than 570% while the hybrids have just 1% market share in the US total auto market taking into account of the mentioned three Japanese automakers.
Table 1: Comparison among environmental friendly car shares in the US market. Source- Self generated from Rodriguez & Page (2004, p.1).
Analysis: Effects of sustainable investment by Toyota
Innovation
Being an Asian manufacturer Toyota is a pioneer of automobile manufacturing since its high concern on future development (Asian Leaders Cars, 2011)(the Asian Leader is a member of the Johnston Press group plc). Alternatively, rather than manufacturing traditional cars in recent years Toyota has more concentrate on innovating environment friendly Eco-cars along with alternative energy car resource. Moreover, Toyota’s safety technologies in order to mitigate road accident occurrences as well as superior quality give them the status of pioneer of affordable new technologies. (Toyota Global, 2011)
Brand Reputation
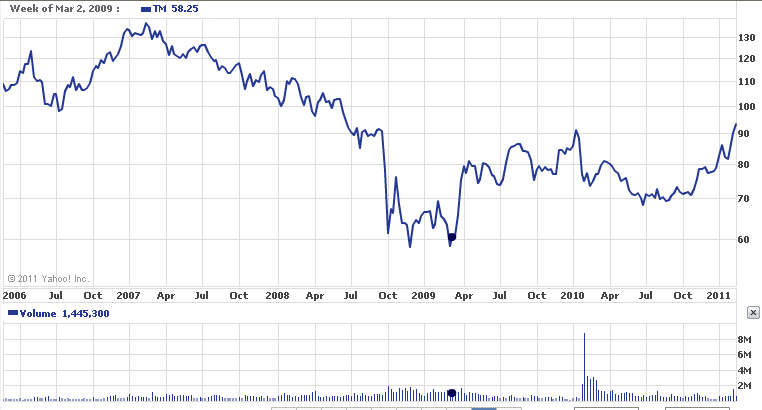
Due to global economic recession, not only in domestic market but also in USA has suffered from massive recalls of stock price fall in the global market for last two years. However, the positive news is that still now Toyota is the most demanded car brand in Japan. Compare to previous years brand value currently their price has decrease by 16.0 % that amounted USD $25.66 billion and in addition, their present stock price is USD $ 82.18. for more clarification in following graph, most recent stock profile is plotted (Stocks and Shares, 2011).
Communities’ Engagement
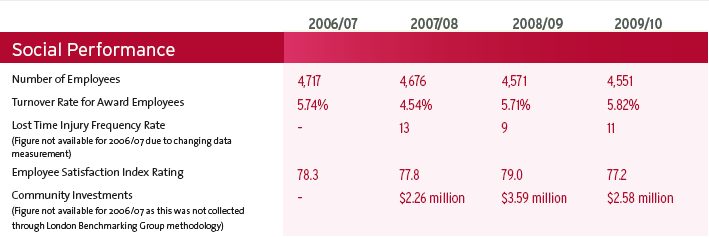
Toyota’s community engagement aimed to contribute society by manufacturing automobiles and additionally, local communities of their global operations have engaged through investments. During the fiscal year 2009–10, Toyota globally invested approximately USD $ 2.58 million in accordance with their community investment program (Toyota Corporation, 2010). Alternatively, in Australia, Toyota participated the National Tree Day 2009 for encouraging peoples to plan more trees and their global philosophy is worked for efficient employee management (implementing health, safety, the environment, equal opportunities and quality control training for manufacturing employees) confirming stable as well as secure though tough global economic recession. (Toyota Australia, 2010)
New markets
Reuters (2011) (one of the Largest international multimedia news agency in the World) reported that, Toyota is going to launch Home Batter Chargers for the environmental friendly electric cars in the beginning of 2012 that has remarkable competency with the non-Toyota cars. The innovation of Toyota has expected to creating a new market of Japan, USA and Europe by selling 20, 000–30, 000 units of battery during opening year of launch and additionally, in domestic market target to sell of 50, 000 units of battery over a year having production cost of USD $ 2, 405 or ¥ 200, 000 (USD $1 = Yen ¥ 83.16) each (Reuters, 2011).
Strategic ignorance of sustainable issues of Toyota
Stakeholder Analysis
Business profile of Toyota has not limited on automobile car manufacturing though they are the world’s second largest car producer. Besides car production, Toyota has involved in multilateral business operations (financial services, telecommunications, prefabricated housing, and leisure boats) as well as enough dynamic to reporting their stakeholders about public response towards their products and services (One World Trust, 2006). But the key problem is that external stakeholders of Toyota has not any unambiguous policy to engaging external stakeholders though the entity has always listen and appreciate any criticism of stakeholders in improving their product quality (One World Trust, 2006). Currently, stakeholders of Toyota have demanded compliances to participating in corporate decision making as well as an outline of their involvement policies (One World Trust, 2006).
Recommendations
The report has considered a number of external factors and strategic issues of Toyota, which helps to identify many global challenges and competitive pressures; so, the following recommendation will lessen those dilemmas, for instance-
- Global automotive industry is becoming highly competitive within very short period considering the quality, features of the product, shorter innovative and development cycle, technological adoption, reliability, safety, price, fuel consumption, environmental reflection, customer relationship and finance. In this context, Toyota Motor Corporation needs to be more responsive in meeting above requirements to regain its market leading position around its national and international market;
- However, Toyota Motor should identify the nature of volatility of global automotive market because increased demand depends on the political, social, economic, and technological factors of the serving market, so this company should apply satisfactory forecasting methods in order to predict these uncertainties;
- Furthermore, it is not always possible to reduce all external forces; therefore, Toyota can try to handle some of them to reduce adverse impact, for instance, Toyota can use advance software to keep a good relationship with overseas suppliers and customer;
- To increase sales profit in this recessionary period, Toyota can introduce few low cost model like Tata Nano for the customer of both develop and developing countries. In addition, Toyota Motor should can increase incentives, rewards and other facilities in order to formulate a better incentive plan, which will encourage the employees;
- In order to be the market leader in global automotive market, Toyota should provide special offer for the loyal customers and it should concentrate more on the marketing activities to boost sales revenue from Asian and Middle- East markets. However, Toyota always takes advantages of the technological development, for instance, use powerful media for selling of various items or advertising, but it should develop database with such files which would be easy to access for all customers;
- Finally, Toyota Motor needs to be more alert in developing and maintaining proper co- ordination within its global distribution channel with proper monitoring system as lack of collaboration and control can increase the operating costs and other non- monetary costs for the company, particularly in the developing countries.
Conclusion
Toyota Motor Corporation one if the huge auto manufacturers in the world that incorporates and independently practices many strategic appraisals; it has supposed that such appraisals are essentially not restricted in a particular field of discussion rather than an integrated implementation over contemplation. Toyota’s target marketing strategy offers a greater portion of superiority within its overall functional background; from that point of view, it can idealize that Toyota manufactures a wide extent of differentiated motor cars and additionally, the company undertakes various marketing strategies for locating and satisfying their target customer needs. Toyota it tries to maximize revenues by the application of efficient manufacturing technique in terms of TQM (Total Quality Management); moreover, its brand name is also powerful enough to make positive image in customer’s mind.
Presently, Toyota is not merely a Japanese carmaker; it has multi-faceted contributions internationally in terms of carrying out massive globalization-manoeuvres, which has given some additional value to the company itself; subsequently, combining with several internally acquired and externally posed wide-ranging and notable distinctiveness, it has been running a giant and integrated business organization for more than 70 years.
Within this extensive range of time, it has notified and placed a specific position in not only the hearts of the global customers but also to the non- buyers’ mind by implementing a intricate-web of strategic-framework, highly-recognized strategies, and adoption of TQM, lean and JIT strategies at different sectors of production, marketing, HR, leadership, technology and even supply chain network.
Even though execution of contemporary methods have resulted into a long-standing success for Toyota, some pessimistic influences of global economic downturn have forced the business in forgoing larger fractions of revenues and market share in 2009; nevertheless, that situation would not affect this firm for a longer period of time if would take some preventive measures to respond that crisis. As a result, it has anticipated that appliance of relevant and effectual series of professional, economic, and other levels of tactical resolutions, inspection and continuous modernization could grant the corporation with such types of influences in order that it would preserve and get back to its high market revenues internationally in the automobile industry in near future.
Reference List
Arashima, T. (2010) Toyota in Europe. Web.
Asian Leaders Cars (2011) Toyota Cars Continue to Be Market Leaders. Web.
Banerjee, B. S. (2009) Corporate Social Responsibility: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. New Delhi: Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd.
BBC News (2009) Car production down 55% in April. Web.
Esty, D. C. & Winston, A. S. (2009) Green to Gold: How Smart Companies Use Environmental Strategy to Innovate, Create Value, and Build a Competitive Advantage. Manhattan: Yale University Press.
Financial Times (2011). Toyota Motor Corp. Web.
Ghadar, F., & Ghemawat. P. (2011) The Three Myths of Globalization. Web.
Hurley, J. Norton, D. & Quiroga, P. (2005) Toyota. Web.
Iida, Y. (2010) Japan’s Policy for next Generation Vehicles. Web.
Johnson, G., Scholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2008) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. 5th ed. Prentice Hall.
Kim, C. (2008) Toyota sees first operating loss. Web.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2006) Marketing Management. 11th ed. Prentice Hall.
Lohse-Busch, H. (2010) Advanced Technology Vehicle Benchmark and Assessment 2010. Web.
Lutsey, N. & Monte, E. (2010) Technologies and Trends for Reducing Automobile Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the 2025 Timeframe. Web.
Maybaum, M. A. (1999) Toyota Motor Corporation: Adult Award Winner in 1999. Web.
Ofose, G. (2011) Nigeria: RT Briscoe Sued for Selling Faulty Toyota Car. Web.
One World Trust (2006) Global Accountability Report (GAR) Accountability Profile–Toyota. Web.
PSA (2005) Market overview: Japan. Web.
Reuters (2011). Toyota Motor Corp (Tm). Web.
Reuters (2011) Toyota to launch home electric car chargers in 2012. Web.
Rodriguez, A. & Page. C. (2004) A Comparison of Toyota and Honda Hybrid Vehicle Marketing Strategies. Web.
Rowley, I. (2007) Toyota set to top 50% market share in Japan. Web.
Stocks and Shares (2011) Can Toyota Motor Corporation (NYSE:TM)’s Image Bounce Back? Web.
Thompson, A. et al (2007) Strategic Management. 13th ed. New Delhi: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited.
Toyoda, A. (2010) Toyota Motor Corporation. Web.
Toyota Australia (2010) Tree Day Home. Web.
Toyota Corporation (2009) Annual Report 2009: The Right Way Forward. Web.
Toyota Corporation (2010) Annual Report 2010: The Right Way Forward. Web.
Toyota Corporation. (2010) Highlights from Toyota Australia’s 2010: Sustainability Report. Web.
Toyota Global (2010) Corporate Philosophy and Structure: Sustainability Report 2010. Web.
Toyota Global (2011) Innovation. Web.
Toyota Motors (2010) Sustainability Reports 2010. Web.
Toyota Motors (2011) Overview of Toyota’s CSR Activities. Web.
US Environmental Protection Agency (1999) Mobile Source Emissions – Past, Present, and Future. Web.
vBulletin Solutions (2010) Pest Analysis On Adidas. Web.
Wad, P. (2009) Impact of the Global Economic and Financial Crisis over the Automotive Industry in Developing Countries. Web.
Watanabe, K. (2008) Toyota Business Strategy Meeting 2008. Web.
Wearden, G. (2010) SMMT says car industry faces bad year. (2010). Web.
Yahoo Finance. (2011) Basic Chart of Toyota Motors Corporation for 2006 to 2011. Web.
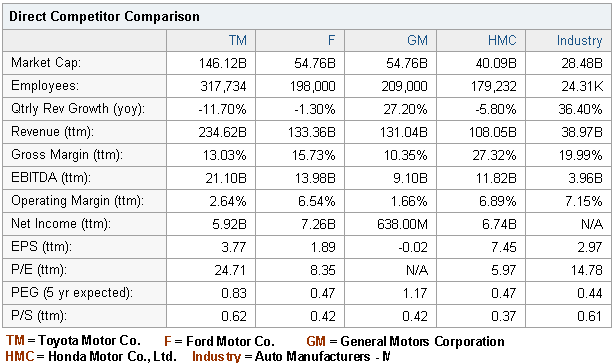
Yahoo Finance. (2011) Direct Competitor Comparison Toyota Motors Corporation. Web.