Welcome to our essay sample! Here, you will learn all about Toyota globalization strategy. This essay will also discuss Toyota’s rise to success and the effect of globalization on the company’s current situation.
Toyota Globalization Strategy: Introduction
Globalisation and its Driving Forces
In the past two decades, technology has significantly become sophisticated, making it easier and economical for people to carry out business across the world. Two major driving forces for this are advances in telecommunications infrastructure and the rise of the internet. The driving forces have broken down many physical barriers to worldwide communication, which used to limit connectivity between businesses over long distances. Globalization simply refers to the rapid growing interconnectedness between countries. The interconnectedness has been driven by increasing liberalization of international trade in goods and services, capital flow through foreign direct investment (FDI) and short-term flows, growth of multinational enterprises, reorganization of production networks on an international scale, and adoption of new technology including information technology. Globalisation is a multifaceted as it covers both economic as well as social aspect (Audretsch and Thurik, 2000).
Another facet of globalization is the international flow in soft technology – knowledge of management practices and methods of work organization. Countries have been able to exchange good management practices. Further, there has been a free flow of low-cost human capital across borders due to the opening of borders. Advancement of technology (internet and infrastructure) has greatly improved the intensity, velocity, extensity, and impact of globalization (Audretsch and Thurik, 2000).
Globalization has brought about significant changes in the global world. To start with, social, political, and economic activities have obtained a much larger extensity, that is, decisions, events, and activities in one part of the world have signed on people in other parts of the world. Also, globalization has increased the velocity of worldwide interactions and transactions. There have been quick diffusion of ideas, goods, and information, capital, and people across the globe. Finally, globalization has made people more aware of issues such as democracy, human rights, and gender due to greater access to sources of information. The impact of globalization has been felt all over the world (Martens and Raza, 2010).
Globalisation and Foreign Direct Investments
In order to obtain a chance of capturing the potential benefits of globalization, low-income countries need to attract a vigorous flow of foreign direct investment. FDI is usually a commonly used driving force by the less developed countries to attract globalisation for the reason that FDIs bring infrastructural and technological advancement, creation of massive employment, new business ideas, and cultural advancement into the host country. In order to attract FDIs, a low-income country has to set up a special export processing zones or free trade zones. Governments of these countries concentrate on the benefits which accrue from FDIs, ignoring the social cost implications such as pollution. Most export processing centres are characterized by extremely poor working conditions, low wages, and poor disposal of waste, among others (Chudnovsky and López, 1999).
The impact of globalization, as a result of injection of foreign direct investment, on low-income countries has some benefits, for instance, there has been vivid economic growth in host countries as experienced in Mauritius and Madagascar. However, the impact of FDI is not always positive among the countries as such FDI brings hypothetical development rather than real-life scenario (Martens and Raza, 2010). Through FDI flow, the developed countries have been able to transfer environmental hazards and industrial pollution from their home country to the host country. With the recent trends, the developed countries are not interested in compensating host countries for such environmental hazards caused by FDI flow. Also FDIs cause collapse of domestic industries due to unhealthy competition resulting from low cost of production as a result of from duty-free imports (Chudnovsky and López, 1999).
Impact of Globalisation on Automotive Sector
Globalisation has created a wave of mergers and acquisitions in the automotive assembly industry. Various manufacturing and assembling plants are merging so as to be more efficient and survive the face of stiff competition resulting from advanced technology. Further, there has been transformation of the auto parts business into a single industry unlike before where auto spare parts were part of business of parent company. In addition, automobile companies such as Toyota have adopted efficient and less costly methods of stock management such as just-in-time. Due to advancement of technology, global financial crisis and increasing demand for vehicles, automobile companies have to be innovative and be able to produce at minimal costs. This would enable them survive in the global market (Martens and Raza, 2010).
There has been elevation of skills and qualities of employer and employee relations. Technology and internet has made it possible for employers to engage and interact with employees in different parts of the world. Further, many employees have been rendered redundant due to growth of technology. This has raised unemployment level in developed countries and has lead to low wages and poor working conditions within the less developed countries due to FDI inflow.
With lean production and outsourcing, the automobile parts industry is increasingly important for global production chains. Many automobile companies are going over to modular assembly in which the main components manufacturer not only supplies but also coordinates the design manufacture and installation of the major parts or systems of the car or truck. The automobile industry may suffer from competitive pressure resulting from low wages paid in less developed countries having comparatively lower per-capita income. These countries pay low wages leading to low cost of production and are therefore able to sell their automobiles at relatively low price (Martens and Raza, 2010).
Impact of Globalisation on Toyota
Globalization appears to be understood as a continuous process of increasing cross-border economic flows, financial and socio-economic, leading to economic interdependence among formally distinct national economies. Capital flows across borders and organizational structures are created in such a way that companies can respond quickly to changing environment. Toyota Company commenced globalization early in the nineties through FDI flow. This strategy turned out to be very successful because it has experienced growth in production plants and increased profitability. This strategy was characterized by production in other countries rather than home. Toyota introduced its foreign production in 1963 in Australia, 1964 in Thailand, 1966 in New Zealand and 1969 in Peru among others. In addition, by 2006, the company had engaged with other 52 foreign production factories (Toyota Motor, 2003). Generally, Toyota view globalisation as a more efficient way to address future uncertainties in advance and as a way of spreading unpredicted risks and prospects.
Health Issues and Impacts of Globalization on Toyota
The future of a globalized world may not be as bright as its proponents would have people believe. Globalization can be viewed as a double-aged sword, it has its pros and cons. For instance, internet and other means of communication has made it possible to share information on better health across the world, and this can bring positive impact (in terms of improved health) on the world at large. At present, globalization has enhanced the speed of global business transformed the whole mercantile structure. The automobile industry among various other industries has been opened to the whole world and is able to conclude transactions faster and efficiently. As a result, Toyota has been able to grow its international market to a greater extent. More expanded market implies increasing sales thus, higher annual returns for the motor company. Contrarily, globalization has impacted negatively on the environment and on public health (CleanAir Systems, 2010).
Toyota has production plants all over the world. These plants are engaged in constant production so as to meet the constantly growing demand for automobiles. Due to pressure from the market demand, production companies have been engaged in malpractices such as producing low-quality products which emit large amounts of toxic pollutants in form of gases. These cars are sold all over the world and emissions during usage of such cars are responsible for global warming, dreadful diseases such as cancer and respiratory problems. In addition, there is no proper disposal of waste by end users and wastes from such automobile industries. These wastes end up in streams and water bodies which turn out to be harmful to the population. Such pollution are responsible for death of green plants, thus distortion of the ecosystem.
As much as globalization has helped businesses to capture an extensive market, it has exposed companies such as Toyota to stringent rules and regulations regarding reducing the negative impacts inflicted through their operations all over the world. “Health and environmental laws require companies like Toyota to ensure that manufactured cars do not emit high levels of hydrocarbons and CFCs whilst the final consumers use those, amounting to potential damage to health” (Huynen, Martens, and Hilderink, 2005). Toyota as a company has always emphasized on business ethics and has always strived to meet the demand of the stakeholders by executing its corporate social responsibility policies (Toyota, 2010). According to Toyota Motor (2010), Toyota’s CSR policy outlines the extent to which the company should reduce damage to the environment and public health. The CRS policy outlines that, “for the sake of both the company’s CSR policy and governmental legislations, health issues remain one of the key potential impacts of globalisation over Toyota’s business” (Huynen, Martens, and Hilderink, 2005).
Effect of Hydrocarbon Emissions on Health and Toyota’s Responses
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) suggested that approximately “forty-seven per cent of hydrocarbon emanations emerge from on-road and off-road automobiles. Petroleum products used by cars contain hydrocarbons which in turn merge with NOx, and sunlight to form ozone, a very dangerous type of air pollutant and a major element of smog” (EPA, 2010). “The tanned mist of smoke, which badly affects countless city regions, causes burning sensation and harm to eyes, skin, and lungs; these also desiccate the defending membranes of the nose and throat, prying with the body’s capacity to defend infections” (CleanAir Systems, 2010). Hydrocarbon emission rates in developed countries especially in European countries are increasing on a daily basis. Similarly, illnesses such as respiratory problems, brain damage, arrhythmia, heart problems, lung diseases and premature deaths among others have consequently increased (EPA, 2010).
In order to reduce the appalling health effects resulting from emanations from their products, Toyota undertook a number of plans that were geared towards supporting measures to curb global warming, curtailing energy consumption and conservation through innovations in production technology. Execution of these plans helped Toyota to attain 40 percent environment-friendly technologies in the period 1991-2009 and led to 40,000 ton CO2 emission reduction (Toyota, 2010). The figure below depicts diminution in CO2 emanation for the period 1991 to 2009 by Toyota Company.
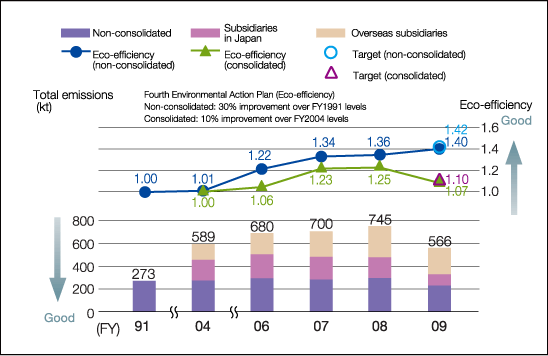
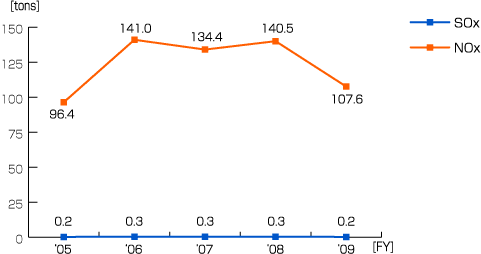
Toyota launched technologies which collect SOx back from air. This has lead to significant reduction of discharges of SOx in the environment. This technology concentrated on replacing detrimental fuel with bio-fuels such as bioethanol (Toyota, 2010). On the contrary, greater use of city gas for the co-generation systems increased the amount of NOx released to the environment. The figure below shows the trend of SOx and NOx emanations from 2005 and 2009.
According to GreenCarSite (2010), Toyota Prius Hybrid is currently the company’s most popular environment-friendly cars with 104g/km CO2 emanation rate and 65.7 mpg. Its highly striking features and low emitting rates have made it one of the most preferred cars of recent times and this contributed to increased sales for the company. Toyota has sold 21,769 Prius cars in October 2010 for which Toyota experienced great augmentations in profit (GreenCarSite, 2010).
Toyota has innovated Toyota FFV which is one of the most eco-friendly cars, “it cut down conservative fuel application by substituting it with E85 ethanol” (Landahl, 2009). “FFV was successful product in entire European Market; especially it facilitated to boost the Sweden market in 2008 due to its internal combustion engine; however, Toyota initially introduced nearly 70,000 E85 vehicles and about 150 E95 busses” (Landahl, 2009).
Environmental Issues
“Everybody involved in the car manufacturing companies keeps the environmental concern in mind, starting from the lower level employees who gather waste materials for recycling to the top-level management who speaks with politicians on global warming issues” (Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2006). Annual report for Toyota Corporation 2009 states that, “Toyota is outstanding for initiating environment-friendly transportation elucidation for individual markets instigating non-economic purpose to the society. Another being an issue of corporate social responsibility reduction of carbon emission also has significance in increasing profit of the companies”. Various automobile industries have been unable to compete in the automobile industry because of inability to control harmful emission and comply with strict the rules and regulations. Companies such as Ford could not compete in the market because their car models were not environmentally friend, their old model Ford Pinto was faced out in the (Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2006).
Natural solutions can be found to the problem of global warming which is caused by emission of carbon. This harmful carbon is mostly emitted from use of petroleum products in automobiles. Carbon emission can be reduced by about 90% though use of Bio-ethanol which is produced from sugar cane, sugar beet, and cereal crops. (Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2006). At the same time, ‘Biodiesel and biofuel have prospective future, because these fuels are carbon-neutral with all the CO2 discharged through use of the fuel, so, car-manufacturing companies now heavily relied on the Bio-ethanol, and other biofuel considering their responsibility to save the environment from adverse impact of carbon emission” (Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2006).
Firms in Automobile industry have been striving to come up with environmentally friendly car models through use of latest technology. This is due to the pressure mounted on them with the regulatory authorities. As reported by the government body, US Environmental Protection Agency, “hydrocarbons were the forerunner to ground-level ozone, which created for imperfect fuel combustion and from fuel evaporation and it is a grave air pollutant in urban areas across the US” (US Environmental Protection Agency, 1999). This calls for the need to reduce the emission of hydrocarbons. The pie-chart below shows proportion of the emission from different sources in 1999.
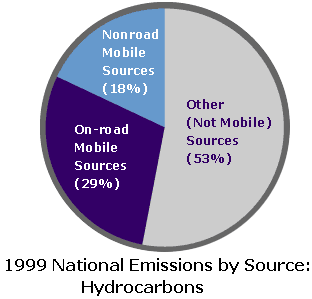
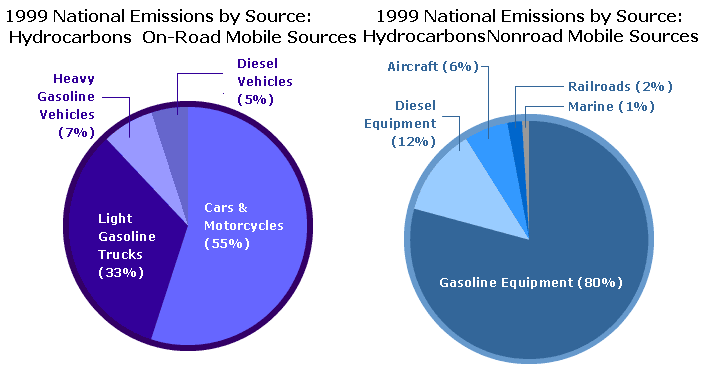
Corporate Social Responsibility
CSR is about how companies manage the business processes so as to produce an overall impact on the society. Social responsibility becomes an integral part of the wealth creation process which if managed properly should enhance the competitiveness of business and maximise the value of wealth to the society. A downswing in the economy creates a better opportunity to practise CRS very well. President of Toyota, Tetsuro Toyoda reported that “in 2003, Toyota introduced the Global Environmental Commitment in order to explain its environmental concern. It has developed its technology to decrease utilizing raw materials, energy consumption, and minimize environmental risk factors” (Toyoda, 2005).
The annual report for Toyota outlines that CRS has helped the company to promote different technological experiments and thereby adopt technologies models and practises which are in harmony with the environmental concerns. This has seen the company enhance affable relationships with individual and corporate bodies for this purpose (Toyota Corporation, 2009). For example, “innovative re-use of wastewater in the car manufacturing procedure has facilitated the company to decrease water consumption (up to 18%) and discharge (up to 19%) by 2006, and the company has commitment to minimize water consumption up to 23% in its environmental action plan” (Toyota Corporation, 2009). In addition, “Toyota invest huge amount of money for celebrity endorsement to protect the environment from greenhouse effect by creating positive image of hybrid vehicles” (Toyota Motor, 2010).
Comparison with Other Companies
Companies in the automobile industries have worked towards coming up with models to prevent high-level fuel consumption. They have become even more aggressive by reducing prices of such model as in the case of Honda. Innovation of the environmental friendly hybrid model has greatly helped Toyota to gain support from the community. Further, it has helped it gains a large market share. Other than the production of environmental friendly models, the company as also organized promotional program to make people aware of environmental eco friendly cars. This strategy assisted the company to develop better co- operation and co- ordination with the public and societal institutions and to increase the market share of Prius in the UK market (Rodriguez & Page, 2004). The chart below shows the market share of hybrid cars.
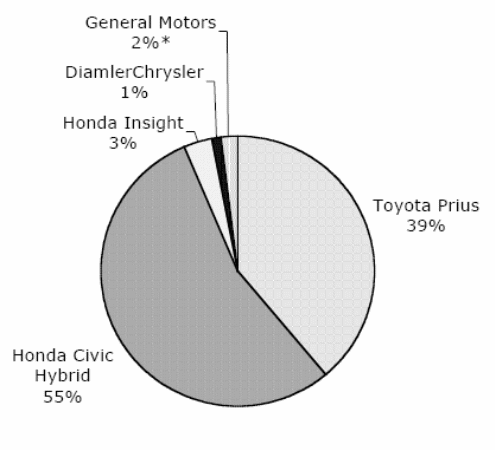
Generally, automobile firms invent environmental friendly cars so as to uphold the market position by increasing net sales. For instance, “Famous car manufacturing company Jaguar Land Rover has reduced water consumption effectively by 28% between 2002 and 2007, carbon productions by 21percent between 2003 and 2008, and waste to landfill by 39 percent between 2002 and 2007. The demand of new brand XJ, 3L V6 Diesel increases due to decreasing CO2 emission” (Rodriguez & Page, 2004).
Core Initiatives of Toyota to Reduce Carbon Emission
Invention of the hybrid motor vehicles played a significant role in protecting environmental damage as well as public health. This enabled Toyota to develop different products for different markets. Therefore, it has manufactured hybrid Plug- in car (PHEV) targeting customers who want to use an environmentally friendly vehicle. Further, “Toyota has introduced several models of eco friendly trucks such as, GENEO (8FG/D) produced with electronically controlled fuel injection system, which is able to reduce Co2 emission by 57%, NOx and HC emissions by 99%” (Toyota Motor, 2010). These eco-friendly cars have also helped reduce fuel consumption by 30% (Landahl, 2009).
Globalization of Toyota: Conclusion
The paper starts by discussing globalization, its advantages and disadvantages. It tackles the relationship between foreign direct investments and globalization. More specifically it discusses the impact of globalization on Toyota. Further, the paper addresses the health concerns which emerge from globalization. The paper also looks at the health problem which results from emanation of hydrocarbon. The second part of the paper focus on corporate social responsibilities. It looks at how corporate social responsibility can help improve performance of a company. It also compares the CRS of Toyota with other companies in automobile industry.
From the above study, it is clear that Toyota has come up with several innovations such as cars with hybrid engines and plans that would help it faces challenges which arise from globalization. It has greatly modified their output to be environmentally friendly. Further, it has worked towards educating the public on the benefits of the eco-friendly cars through promotional campaigns. Toyota should increase expenditures in research and development. This will help in creation of more new eco-friendly, creative, and differentiated vehicles.
Reference List
Audretsch, D. B. & A. Thurik, R. (2000) What’s New About The New Economy? Sources of Growth in the Managed and Entrepreneurial Economies. Web.
Capon, N. & Berthiaume, R. (2007) Toyota Marketing Strategy for Plug-in Hybrids. Web.
Chudnovsky, D. & López, A. (1999) Globalization and Developing Countries: Foreign Direct Investment and Growth and Sustainable Human Development. Web.
CleanAir Systems (2010) Hydrocarbon Emissions. Web.
EPA (2010) Technical Factsheet on: POLYCYCLIC AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS (PAHs). Web.
GreenCarSite (2010) Toyota Prius Hybrid 1.5 VVTi. Web.
Huynen, M. M., Martens, P., & Hilderink, B. H. (2005) The health impacts of globalisation: a conceptual framework. Web.
Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2006) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. 8th ed. London: FT Prentrice Hall.
Landahl, G. (2009) Incentives Promoting Clean Cars. Web.
Martens, P. & Raza, M. (2010) Is Globalisation Sustainable? Web.
Rahman, K. M.A. (2008) Globalization and the Climate of Foreign Direct Investment: A Case for Bangladesh. Journal of Money, Investment and Banking, 28(5). Web.
Rodriguez, A. & Page. C. (2004) A Comparison of Toyota and Honda Hybrid Vehicle Marketing Strategies. Web.
Toyoda, T. (2005) Environmental Policies. Web.
Toyota Corporation (2009) Annual Report 2009: The Right Way Forward. Web.
Toyota Motor (2003) Toyota’s Global Strategy —Moving toward Global Motorization. Web.
Toyota Motor (2010) CSR Initiatives. Web.
Toyota Motor (2010) Reduction in the volume of CO2 Emissions. Web.
Toyota Motor (2010) Toyota Environmental Activities Grant Program. Web.
US Environmental Protection Agency (1999) Mobile Source Emissions – Past, Present, and Future. Web.