Abstract
Network design is a sequential process that requires a thorough analysis of the needs of the business enterprise. The physical and the logical layout structure of the network have to match the design and the business needs in that particular context (Bordetsky & Hayes-Roth, 2007). The main objective behind the design of this particular network is to enhance the sharing of resources and provide access to the internet. Having a clearly stated objective plays a significant role in determining the strategy to that is during network design. Evaluation of the business requirements, goals, and objectives forms the preliminary stage in network planning, design, and implementation. The design requirements are also important during planning and design (Meyer, 2003).
Design requirements for the network for the proposed network
Design requirements of a network depend on the business needs. One of the significant design requirements for the network is to have a provision for the access of multiple email addresses. It is also important for the network to have access to the internet for communication purposes. Another significant design requirement that needs to be incorporated into the network it has to host at least two workstation computers, which have been configured to share resources such as the printer and the point of sale application. Network security is not a major concern; therefore low-level security measures similar to the home networks are efficient (Deal, 2008).
Network planning and design
Network planning entails coming up with a logical and physical layout of the network components. In this case, there are no complex issues because the network requires hosting only two workstations. Variables such as network availability, reliability, performance, standards compatibility, and scalability play a significant role during the design phase (Hummel, 2009). The configurations of the two workstations have to facilitate the sharing of resources and have access to the internet.
The physical layout of the network
The most effective approach for connecting two workstations is peer-to-peer topology. However, to expand the network in the future, the use of star topology having a central switch or a hub is preferred (Meyer, 2003). An eight-port switch is suitable for this connection since the business is less likely to expand to accommodate more than eight workstations. To minimize the costs that are associated with switching and transmission, the location of the switch and the workstation will be close to eliminating the need for devices that are used to combat signal attenuation such as repeaters and interconnected switches. The Ethernet cables used will be of high-quality category, preferably CAT 6 550 MHz UTP (Untwisted Pair) cables. The physical layout diagram for the network is as shown below.
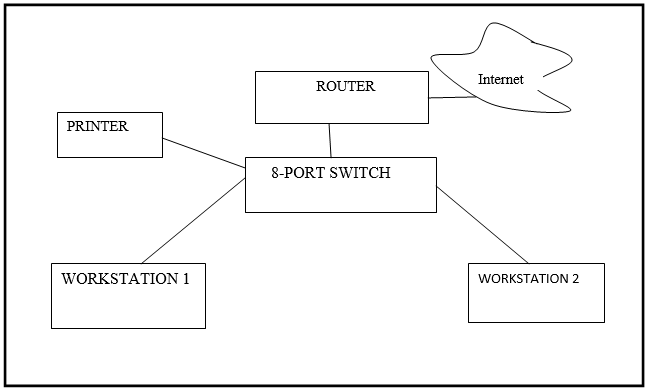
The star topology is preferred because it eliminates issues associated with network failures. For instance, if a workstation breaks down, the functionality of the network is not impaired, thereby enhancing reliability (Tamara, 2005). The star topology is also easy to implement and troubleshoot compared to other network architectures, which are more complex and require complex configuration methods for their effective functioning. This reduces the initial implementation and recurring maintenance costs (Meyer, 2003).
An Internet Service Provider will be in charge of providing access to the internet. The choice of the ISP will depend on the monthly subscriptions, terms and conditions, the required hardware, and the complexity in setting up the network to have internet access. The most basic hardware required to guarantee internet connectivity is a router. Other third-party hardware and applications are usually at the expense of the Internet Service Providers.
One workstation will host the printers and other shared applications, after which the necessary configurations are done so that they can be accessed by the other workstation. Printers that have Ethernet compatibility are most preferred because they are less complex to configure (Meyer, 2003).
The logical layout of the network
There is no need to segment the network because its size is small and not complex. This means IP version 4 address is suitable to assign IP addresses to the various network devices (Bordetsky & Hayes-Roth, 2007). There is no need to subnet the network. Having the router as the default gateway, its IP address is set to 192.1680.0.1. The IP addresses of other network devices have to be static to enhance security.
One approach to enhancing network security is disabling wireless broadcasting by the router. It is also important to encrypt the SSID of the network to enhance security in cases whereby there will be wireless broadcasts (Hummel, 2009).
Hardware requirements
The hardware requirements mustn’t exceed the allocated funds limit for the network project. Therefore, a thorough analysis and evaluation of the network components are vital, without jeopardizing the functionality of the network.
The table below outlines the required hardware needed for the implementation of the network
Table 1: List of hardware requirements.
Software requirements for implementation of the network
Network management applications are also required in this context. The business significantly relies on billing applications. This means that it requires a billing application installed on the workstations to facilitate the carrying out of business activities. It is also important that the various applications be compatible for use in a Windows platform. Various billing applications can be web-based or licensed off the shelf. Licensed billing applications are more preferred compared to web-based billing applications due to security issues. The following table outlines the software requirements for the network implementation project.
Table 2: software requirements.
In addition, $ 500 will incur expenses that relate to the provision of the internet to the business. This will entail all the costs incurred for the ISP to install necessary and configure fully functional internet access for the network. This brings the total budget for the network project to about $ 3197. The only recurring charges that the business will have to incur are the payment of monthly subscriptions for internet access to the Internet Service Provider. In this case, the amount is $ 100.
References
Bordetsky, A., & Hayes-Roth, R. (2007). Extending the OSI model for wireless battlefield networks: a design approach to the 8th Layer for tactical hyper-nodes. International Journal of Mobile Network Design and Innovation (IJMNDI), 2(2), 5-12.
Deal, R. (2008). Cisco Certified Network Associate study guide (exam 640-802). New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Hummel, S. (2009). Ezine Articles. Web.
Meyer, M. (2003). Mike Meyers’ A+ Guide to PC Hardware. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Tamara, D. (2005). Network+ Guide to Networks. Boston: Cengage Learning.