Costs of Production
Cost of Goods Sold
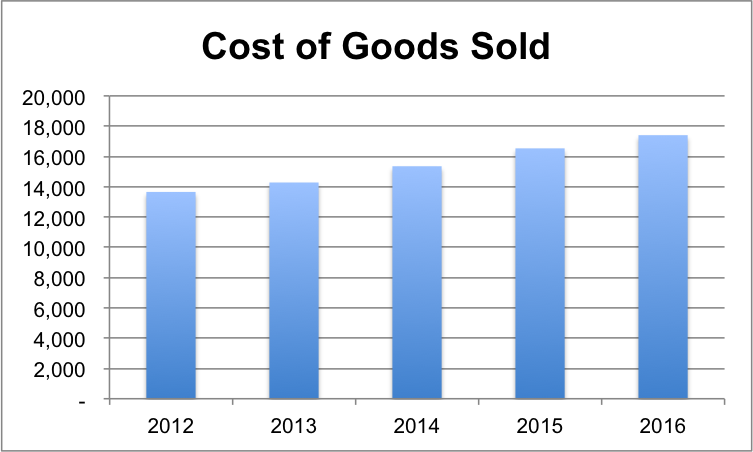
Nike’s cost of goods sold (COGS) is provided in Table 1, showing the company’s COGS have increased in the last five years, mainly due to the increase in the price of raw materials including thread and leather. The major portion of COGS included inventory costs. The cost of warehousing and transport also affected the company’s COGS.
Table 1: Cost of Goods Sold. Source: (Nike Inc B, 2016).
Total Operating Expenses
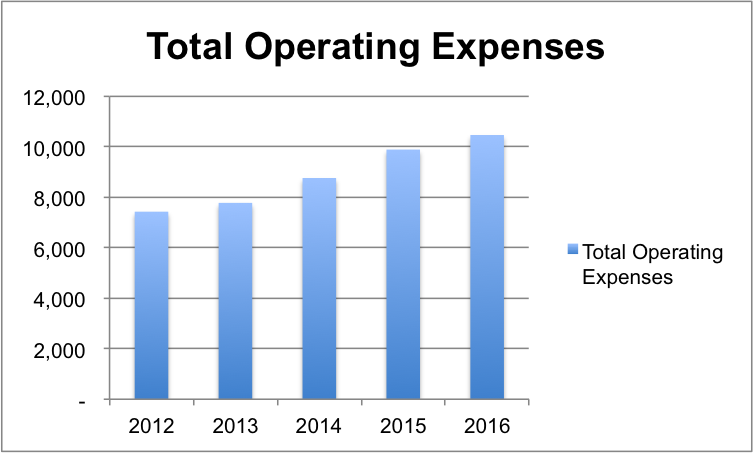
The company’s total operating expenses for the last five years are provided in Table 2. These expenses, which include labor cost, have increased over that time period.
Table 2: Total Operating Expenses. Source: (Nike Inc B, 2016).
Net Income
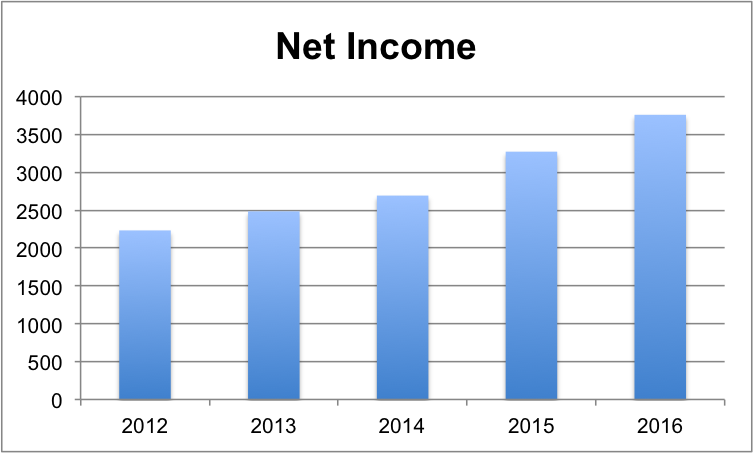
The company’s sales increased at a higher growth rate than its COGS and total operating expenses in the last five years, allowing the company to report higher net income in each of the last five years (See Table 3). The COGS and operating expenses significantly affect the company’s profitability because its operations are highly labor intensive. The increase in the price of raw materials has a negative effect on the product’s price. The increase in the product’s cost reduces the company’s profitability.
Table 3: Net Income. Source: (Nike Inc B, 2016).
Classification of Costs
Cost analysis of Nike indicates that there are two types of costs reported by the company: fixed costs and variable costs. The fixed costs are not affected by the company’s sales but the company cannot avoid them. On the other hand, the company’s sales determine the total variable costs. They vary according to the level of business activity. The following tables provide classification of fixed and variable costs as reported by the company.
Table 4: Variable Costs. Source: (Nike – Form 10-K 2016, 2016).
Table 5: Fixed Costs.
Overall Market
Global Market Share
The global athletic footwear market is highly diverse and not concentrated. Many famous brands dominate the global athletic footwear market. These leading companies have international operations as they have various production units located in different countries. However, small manufacturers also sell their products in local markets. The global market share of companies is provided in the following table.
Table 6: Athletic Footwear Global Market Share 2015. Source: (Athletic footwear market share worldwide by company in 2015, 2016).
Nike’s Market Share
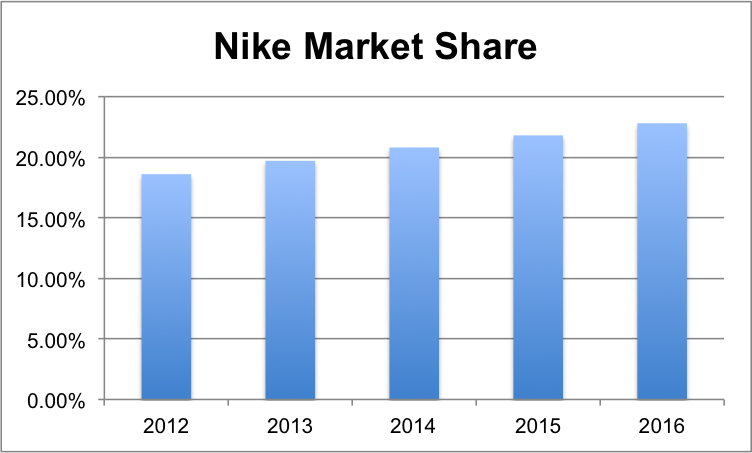
Nike has the highest market share in the global athletic footwear market. It could be noted from the information provided in Table 7 that the company’s market share increased in the last five years, and it could be expected that the company’s business will grow at the same pace in coming years.
Table 7: Athletic Footwear Nike Market Share 2012-16. Source: (Forecast of Nike’s global market share in athletic footwear from 2011 to 2020, 2016).
Barriers to Entry
The athletic footwear market is highly competitive, with many customers and manufacturers. The industry is at the maturity level as companies operate at a low-profit margin. A few companies, including Nike, Adidas, Reebok, and Puma, lead the industry. There is tough competition between these companies as they compete on the basis of their product designs and price. Although start-up costs are low, the market structure is complex, making it difficult for new companies to sell their products. The complexity makes it difficult for new companies to use traditional distribution channels. Retailers are also reluctant to display new brands. The existing companies enjoy economies of scale and they produce high-quality products.
Market Structure
The market structure is determined by using 4-Firm Concentration Ratio. The steps are shown as following.
Table 8: 4-Firm Concentration Ratio.
The market share of the top four companies is 40%, which falls in the range of 1-60%. Therefore, it could be concluded that there is monopolistic competition in the athletic footwear market.
Recommendations
The intense competition in the global market puts pressure on companies to reduce their fixed costs. Nike should also increase its operational efficiency, increasing production and lowering total costs. Nike has a strong position in the market. It has the opportunity to expand its retail network in new markets in Africa and Asia. The company can benefit from an increase in its production by selling its products in these new markets. The company can also benefit from the increase in demand for athletic footwear. Price elasticity is low, implying that the company’s sales are not affected by changes in its prices. It can increase its sales by introducing new designs and improve the quality of its products.
References
Athletic footwear market share worldwide by company in 2015. (2016). Web.
Forecast of Nike’s global market share in athletic footwear from 2011 to 2020. (2016). Web.
Nike – Form 10-K 2016. (2016). Beaverton: Nike Inc.
Nike Inc B. (2016). Web.