Introduction
Nike should integrate information systems to improve efficiency and effectiveness of its operations.
Information technology leverages primary and secondary activities of an organization.
Manual systems have proved to have retrospective effective on the performance of organizations.
The adoption of information systems enhance value chain activities of diverse departments.

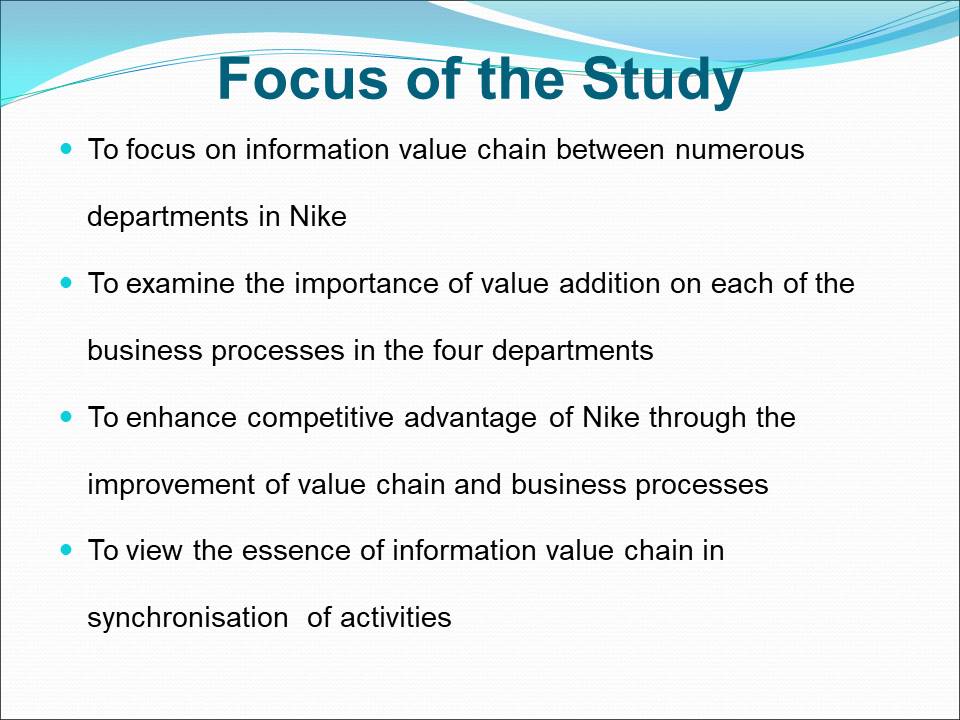
Focus of the Study
To focus on information value chain between numerous departments in Nike.
To examine the importance of value addition on each of the business processes in the four departments.
To enhance competitive advantage of Nike through the improvement of value chain and business processes.
To view the essence of information value chain in synchronisation of activities.
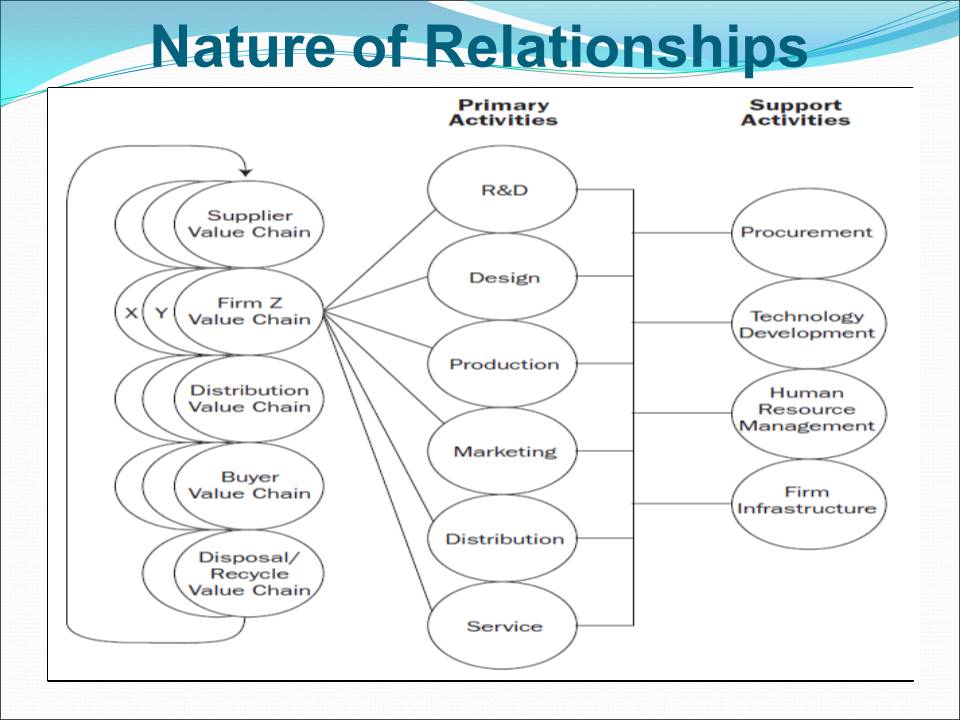
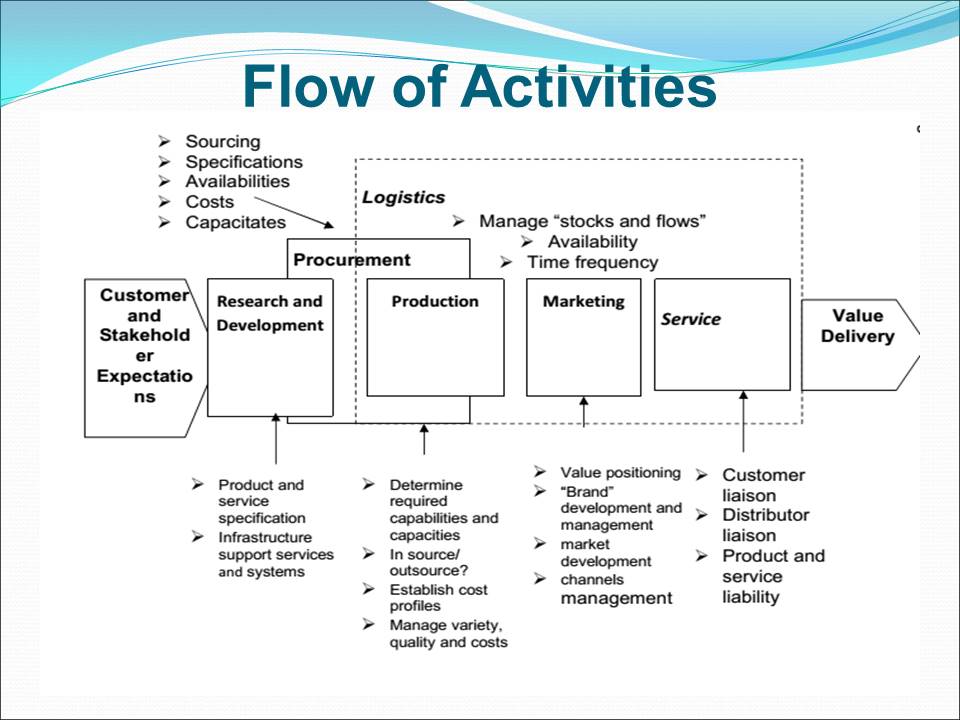
Value Chain Activities
Comparative analysis of traditional and modern approaches in each department elucidates value chain activities.
Primary activities such as research, development, design of products, marketing, and accounting happen in respective departments.
The concept of information value chain bestows strategic advantage in competitive markets.
Supplier, distribution, disposal, buyer, and firm value chain activities are core activities in business cycle.

A Ten Step Traditional Method
- The application of manual system in coordinating primary and secondary activities among departments.
- Separation of primary activities according to the respective departments.
- Establishment of the products needed in the market based on manual research and development.
- Collection of primary data using old method such as postal services.
- Manual analysis of primary data collected.
- Expensive and cumbersome way of generating invoices created massive inconsistencies.
- Poor synchronisation of activities made preceding activities influence subsequent activities.
- To enhance functions of the finance and sales and marketing departments, employment of many staff was a necessary strategy.
- Reduction in cost-effectiveness of operations significantly increase operation costs.
- The shipment of products took long because of the manual processes involved .


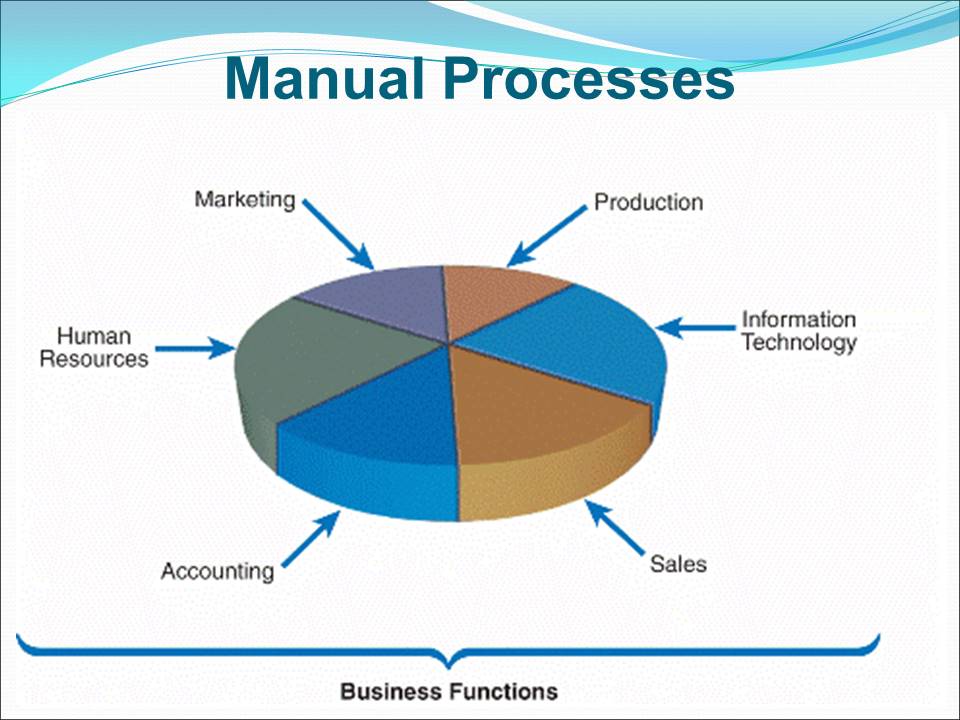
Problems of the Manual System
Lack of real-time communication between departments delayed delivery of products.
Manual accounting system caused massive errors and did not provide real-time information.
The sales and marketing department did not present the right information about marketing environment.
The processes of generating order was inefficient owing to poor communications between departments.

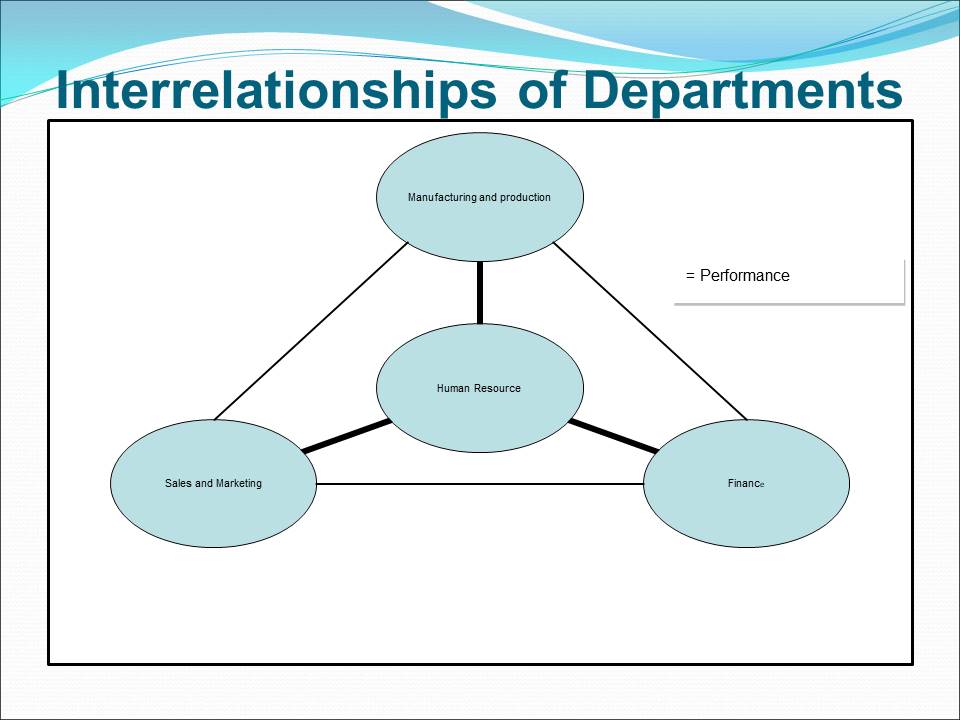
Improving the Business Chain
The manufacturing and production department and the sales and marketing department are areas that require improvement.
The manual system has problems in aspects such as research and development, design, production, sales, and marketing.
Improvement of the manual system requires integration of the information value chain and business processes.
The improvement of the functions in each department enhances competitive advantage of Nike.

Steps to Modernise the Manual System
Modernise operations of manufacturing and marketing departments.
Marketing department require real-time information for it to keep abreast with market trends.
Real-time provision of information aids sales and marketing department perform its core functions.
The core functions include collection of data, analysis of current market trends, and examination market variables.
Integration of management information system into the Internet enhance real-time analysis of data.

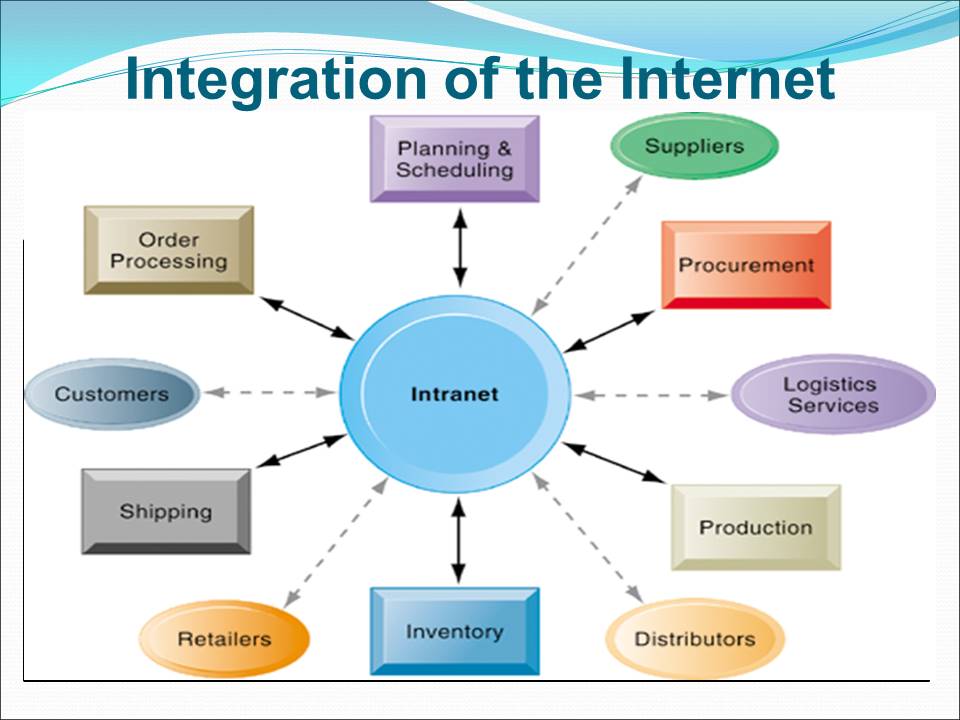
Requirements
Hardware devices such as mobile phones, laptops, and computers amongst others.
Networking system, which allows the transmission of high speed data.
Software such as Microsoft windows and Linux operating systems.
Customer relationship management software, which promotes real-time communication.
The Internet and website, which allow real-time communication between departments.

Importance of Professional MIS
Management information system (MIS) promotes efficiency of manual processes.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) promotes execution of business operations.
Transaction processing system (TPS) is able to process, store, organise, and share the processed data for business decision-making.
Decisions support system (DSS) enable managers to make critical decisions.

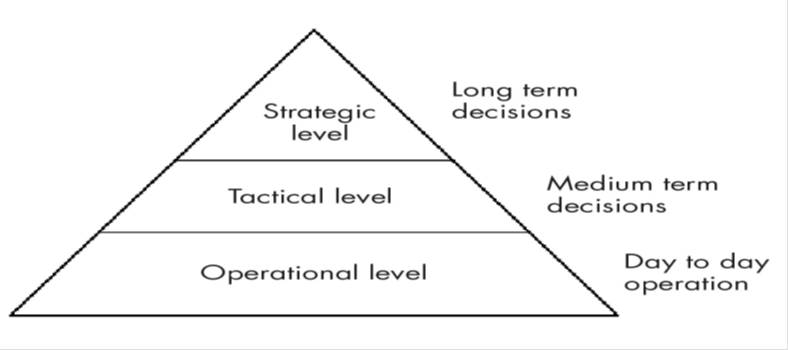
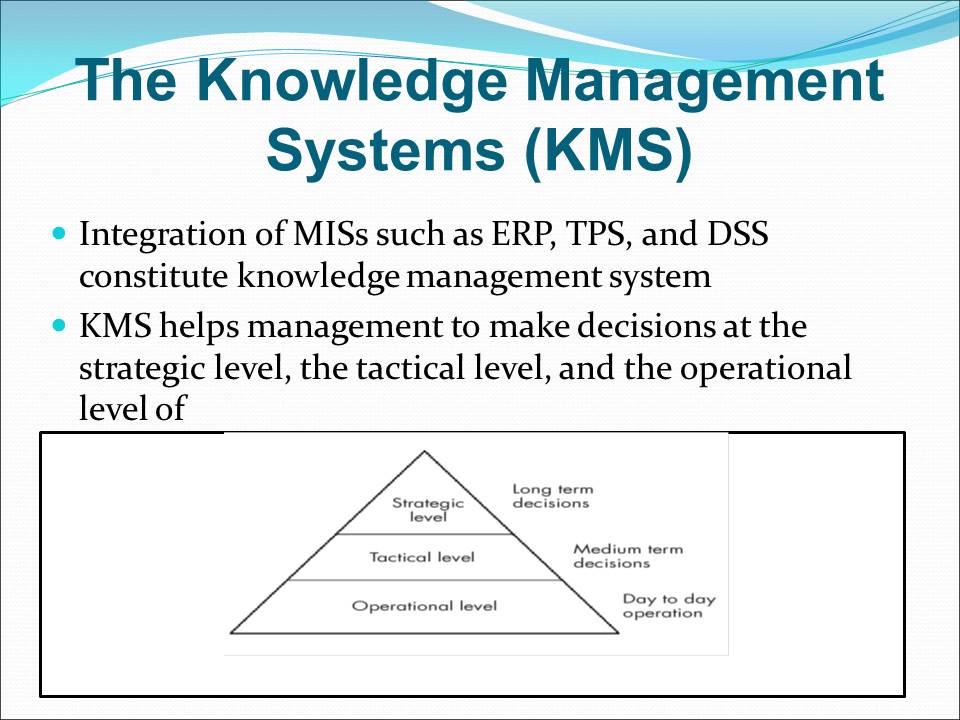
The Knowledge Management Systems (KMS)
- Integration of MISs such as ERP, TPS, and DSS constitute knowledge management system.
- KMS helps management to make decisions at the strategic level, the tactical level, and the operational level of:
References
Arnott, D., & Pervan, G. (2008). Eight key issues for the decision support systems discipline. Decision Support Systems, 44(3), 657-672.
Barua, A., Konana, P., Whinston, A. B., & Yin, F. (2004). An empirical investigation of net-enabled business value. Mis Quarterly, 28(4), 585-620.
Dennis, A., Wixom, B. H., & Tegarden, D. (2005). Systems analysis and design with UML version 2.0. New York: Wiley & Sons.
Evans, J. R., & Berman, B. (2001). Conceptualizing and operationalising the business-to-business value chain. Industrial Marketing Management, 30(2), 135-148.
Goldschmidt, P. G. (2005). HIT and MIS: implications of health information technology and medical information systems. Communications of the ACM, 48(10), 68-74.
Jasperson, J. S., Carter, P. E., & Zmud, R. W. (2005). A comprehensive conceptualization of post-adoptive behaviors associated with information technology enabled work systems. MIS Quarterly, 29(3), 525-557.
Lee, C. C., & Yang, J. (2000). Knowledge value chain. Journal of management development, 19(9), 783-794.
Lewis, B. R., Templeton, G. F., & Byrd, T. A. (2005). A methodology for construct development in MIS research. European Journal of Information Systems, 14(4), 388-400.
Luftman, J., Kempaiah, R., & Nash, E. (2006). Key issues for IT executives 2005. MIS Quarterly Executive, 5(2). 1-23.
Marakas, G. M. (2003). Decision support systems in the 21st century. New Jersey New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
March, S. T., & Hevner, A. R. (2007). Integrated decision support systems: A data warehousing perspective. Decision Support Systems, 43(3), 1031-1043.
Melville, N. P. (2010). Information systems innovation for environmental sustainability. MIS Quarterly, 34(1), 1-21.
Shim, J. P., Warkentin, M., Courtney, J. F., Power, D. J., Sharda, R., & Carlsson, C. (2002). Past, present, and future of decision support technology. Decision support systems, 33(2), 111-126.
Tallon, P., Kraemer, K. L., & Gurbaxani, V. (2001). Executives’ perceptions of the business value of information technology: a process-oriented approach. Journal of Management Information Systems, 16(4), 145-173.
Turban, E., Aronson, J., & Liang, T. P. (2005). Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems. Pearson Prentice Hall.