Summary
The TICKET table cannot be considered a relation. For a table to be a relation, each attribute value in each row must be a single value (Eessaar). However, the TICKET table does not satisfy this condition since the Name and Address columns have more than one value in their respective attribute domains. A further examination of the table shows that the Confirmation column uniquely identifies each record. The Confirmation, which is the primary key, satisfies part of the relation condition, requiring all the rows in a table to be uniquely identified by at least one attribute. Furthermore, all the column values are from the same domain, each with a unique name, which also satisfies part of the conditions to be a relation.
Converting the Ticket Table to a Relation
In order to normalize the TICKET table, the Name column is split into two columns: FirstName and LastName. This split would ensure that each cell contains a single value. The problem in the Address column is rectified by splitting the TICKET table into two to create another table named ADDRESS table, which will have the columns Confirmation, streetNo, streetName, City, State, and ZipCode. ADDRESS’ primary key is the Confirmation attribute since it uniquely identifies its rows. A foreign key is then used to link the ADDRESS table and the TICKET. Referential integrity would require that the foreign key in the new ADDRESS relation be the TICKET’s primary key. The Confirmation column is the foreign key in the new ADDRESS relation and the primary key in the TICKET relation.
ER model for the Revised Tables
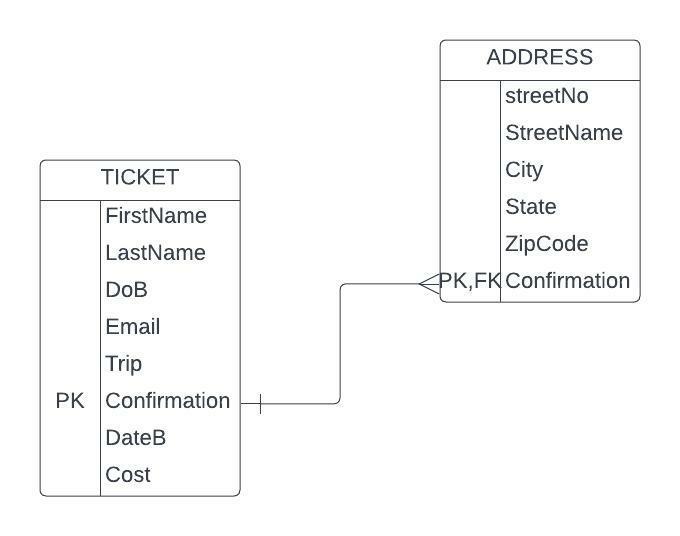
In conclusion, the revised tables are in 3NF since all attributes are single-valued in both tables, and all non-key columns are entirely functionally dependent on the primary keys in both tables. There are no transitive dependencies, and the new tables can be considered a relation.
Work Cited
Eessaar, Erki. “(PDF) the Database Normalization Theory and the Theory of Normalized Systems: Finding a Common Ground.” ResearchGate, 2016, Web.