Obesity
Obesity is the presence of too much fat in the body (Obesity Information 2014). It is determined using the body mass index (BMI). The BMI shows if a person is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
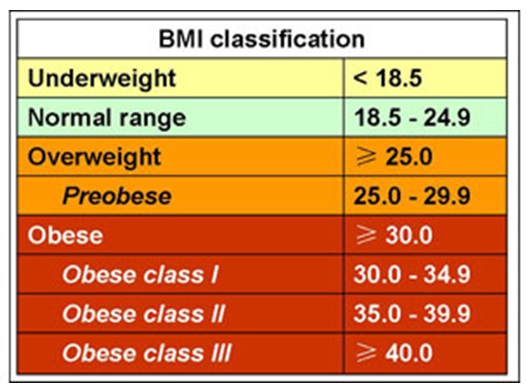
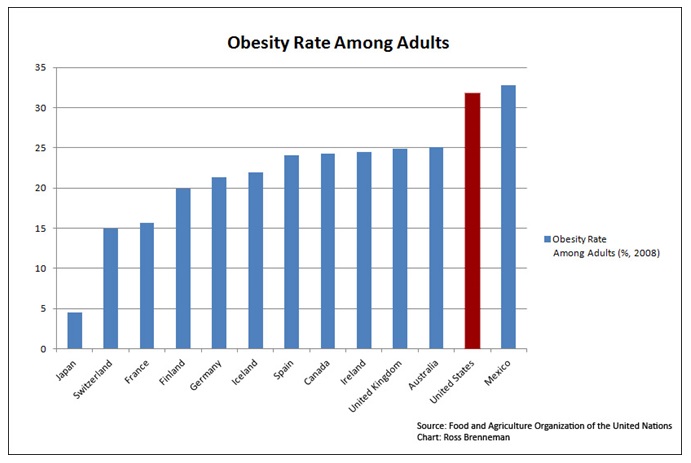
According to the WHO, in 2008 about half a billion people were obese worldwide (WHO: 10 facts on obesity 2014). The total of obese and overweight people in the same year was 1.4 billion. Out of this number, about 2.8 million die annually (WHO: 10 facts on obesity 2014). Hence, obesity is a major factor in most of the leading killer diseases worldwide. Further, the majority of the world’s population live in countries where obesity is prevalent. It is thus categorized as a global epidemic.
Inflammation
Inflammation, on the other hand, is a process that occurs when the body seeks to expel harmful substances from within it or correct the damage done by such substances (Medical News Today 2014). When the body detects that it is under attack by harmful stimuli, it deploys its defense mechanism to counteract the attack. The signs that appear on the outside of the body are often indicators of an ongoing fight in the body. Inflammation is thus an immune response from the body.
It manifests in form of redness, a burning sensation, tumor, pain, and lost functionality (Medical News Today 2014). Under certain circumstances, it is beneficial to the body since it helps heal tissue damages such as wounds. In other words, the healing process of a wound results from inflammation.
However, it should be noted that there are circumstances under which it becomes harmful to the body.
For example, the body can detect a harmful stimulus and initiate the self-defense process, which instead turns into a continuum of inflammation processes. It can become self-perpetuating when one case of inflammation causes another case of inflammation and the process goes on.
It occurs in three distinct stages. The first stage is irritation, followed by suppuration (the discharge of puss in the case of wounds), and finally granulation (Medical News Today 2014). It is important to note that without this process, there would be no healing of wounds and other infections. As such, although most treatment regimens attempt to reduce inflammation, care should be taken so that the beneficial aspects of inflammation are encouraged in order to hasten to heal.
Inflammation falls into two categories, which include acute inflammation and chronic inflammation. The former lasts only several days while the latter can persist for months or even years (Medical News Today 2014). Acute inflammation occurs as a result of tissue damage (injury) or bacterial infections and causes the healing of the condition. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, occurs because of viral infections, persistent pathogens, or an overactive immune system (Medical News Today 2014). Chronic inflammation leads to the destruction and death of tissues (Medical News Today 2014).
The Link between Obesity and Inflammation
Research shows that obese people are more susceptible to inflammation (National Council on Strength and Fitness Trainer’s Tools: Obesity and Inflammation 2014). The reason behind this relationship is that obese people have higher levels of white blood cells and these cells are the major players in the body’s immune system (Gregor & Hotamisligil 2011). In other words, white blood cells are responsible for protecting and healing the body through the inflammation process. If a person has higher levels of these cells, the probability of experiencing inflammation is higher than under normal circumstances. A range of 4,500 to 10,000 white types of blood cells per microlitre of blood is normal (Gregor & Hotamisligil 2011). However, in obese people, this number increases even up to 20 times. This increase translates to numerous cases of inflammation being reported in overweight and obese people.
Obesity, Inflammation and other Illnesses
Obesity is known to cause chronic inflammation. Obesity-induced inflammation hampers the secretion of adipokines, which plays a major role in metabolic processes of the body (National Council on Strength and Fitness Trainer’s Tools: Obesity and Inflammation 2014).
As a result, the body becomes vulnerable to metabolic diseases. The danger of obesity-induced inflammation lies in its chronic nature (Gregor & Hotamisligil 2011). In the case of cardiovascular diseases, obesity-influenced inflammation leads to the production of chemical modulators by all organs in the body (National Council on Strength and Fitness Trainer’s Tools: Obesity and Inflammation 2014). This multi-organ action eventually upsets the optimal functionality of most of the organs and leads to the buildup of dangerous substances such as atherosclerotic in blood vessels.
Thus, the link between obesity and illnesses such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and arthritis among others exists due to the chronic nature of obesity-induced inflammation. Research is still ongoing to decipher the links between obesity, inflammation, and other illnesses. However, the current evidence generally shows that there is a strong relationship among them.
Recommendations
The University of California San Francisco Medical Centre recommends the following in dealing with obesity and its complications (UCSF Medical Center 2014).
- Patients should work with professionals to tailor their diets to their specific needs. Low calorie diets (LCDs) 500-1,000 calories/day or very low calorie diets (VLCDs) 400-800 calories/day are recommended.
- Patients should exercise regularly since exercise is the key to attaining physical fitness and/or normal BMI <25kg/m2.
- Patients should avoid weight loss drugs. Instead, they should use drugs such as Fastin (metabolism catalyst), Orlistat (hampers fat absorption by up to 30%), and Phentermine (an appetite suppressant).
- Bariatric surgery is also recommended if necessary. It is considered an extreme measure, but it is handy in some cases.
References
Gregor, M & Hotamisligil, G 2011, ‘Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity’, Annu Rev Immunol, vol. 29 no. 4, pp. 15-45.
Medical News Today 2014, What Is Inflammation? What Causes Inflammation?, Web.
National Council on Strength and Fitness Trainer’s Tools: Obesity and Inflammation 2014, Web.
Obesity Information 2014, Web.
UCSF Medical Center 2014, Obesity Treatment | Conditions & Treatments, Web.
WHO: 10 facts on obesity 2014, Web.