The case study has been developed on one of the top UAE insurance companies named “Oman Insurance Company”, Dubai. According to the requirements of combining information technology and information system relating to the internal and external environmental elaboration and development purpose, critical analysis of technological background and overall judgment of competency regarding the selected industry purpose, Oman Insurance Company of UAE has been chosen for its versatile insurance services with a wide array of using upgraded technological surface.
Thus, the forthcoming analysis of each of the requirements will introduce a number of inquiring schedules as below:
- Observation of overall company view with related association of technology in each aspect of operations and methodology.
- Overview of industrial background with critical evaluation technique like SWOT and PEST analysis.
- Internal and external analysis of Oman insurance to identify strategic competency in terms of technology.
- Influential factors affecting the systematic development of the company.
Thus, to run the entire research work, it is very much essential to know about Oman insurance company as the selected factor to idealize its present external and internal information system and technological cues.
Company view
Oman Insurance Company is an UAE-based Insurance Corporation having approximately 10 branches in all states of Emirates with a very strong and established existence as in top position in Dubai. According to the website of Oman Insurance Company (2008) it can be found that the company has been formed up in 1975 that offers some insurance services like- life insurance including entire, term, annuity, endowments, unit-linked etc. and non-life insurance considering property, personal, liability, agricultural, business intermission, financial, marine, aviation, goods transportation, railways, all liabilities of constructors etc. products as well as additional mileage of tailoring of preparing special coverage. After a long period of its establishment, the company is providing such kinds of service to a number of insurers and to successfully wheel its operational programs, it uses a number of tools and techniques offered by INSIS (Insurance Information System) and Fatada Company Ltd.
From the Website of Oman Insurance Company (2008) it also found that establishing itself as a financially sound and professionally managed corporation, the year 2007 had recorded a huge success of earning Dhs 1.5 billion premium turnovers and technical reserve of Dhs 517 million by Oman. It is very much serious in the promised customer-oriented service by delivering better quality offer. Thus, the company has been positioned as the prime insurance organization in case of gulf in having a fanatical call center to serve exclusive facilities to its premium holder. Rather than, it is a single company of providing financial services for gulf by occupying an establishment of R & D department for benefiting the improvement of forthcoming insurance goods and methodologies for satisfying the specific customers as well as some of the slow served insurance which needs the population of gulf.
Regarding the employment issue, Oman is proving its competency by involving much high quality and experienced employees who are capable of deal with a large variety of clients in the route of surveys, conferences, meetings, seminars and ceremonies of being get together continuous intervals. Additionally, it serves daily domestic magazines named “l Aman” which is served for the purpose of increasing customer interaction.
Being specialized with its products, services and individuals, OIC has been specially identified as a quality concerned company having an extra systematic mechanism for continuously improving own performance by the year 2000. Fadata™ Ltd (2008) provides the information that it has recorded as first UAE Company for the acquisition of Dubai Quality Award for the financial sectarian performance for the same year. In this way, it also won ISO901:2000 certification, Sheikh Khalifa Excellence Award, Dubai Quality Gold Category Award from the year 2000 to 2003. In this light, it has also won Life Insurer, Social Responsibility, Training Initiative etc. forms of awards in 2005, 2006 and 2007.
Therefore, OIC occupies a vision of becoming a world-level provider of financial service having a public purpose concern and a model for excellence. Griffin, R. W. (2006), argued that to maintain a harmony with this broader objective, the company embodies its value generation in regard to the trustworthiness of its human resources. For it they are aiming to “Protect” their target markets as:
- P for Proactive
- R for Reliable
- O for Openness
- T for Team oriented
- E for Excellence
- C for Committed
- T for Trustworthy
Finally, its mission compasses are related with every day activities by granting it to perform and in shifting its OIC image into a “World-class” corporation by the following promises:
- Acceleration of mental peace in the time of uncertainty.
- Value addition service in the served goods or services.
- Maintenance of strong partnerships with trade-related vendors and bodies.
- Incremental stakeholder value by persona, process and technological assimilation.
Scope of the required proposition in Oman’s perspective
After analyzing this short overlook of Oman Insurance, it can be understood that Oman is positioning and building its representation with not only the traditional strategic focus ensuring wealth and property but also macro-focused used of technological sophistication in each of its selected attributes.
At 1st, in this regard its call center service is mentionable which induces the following value-added services:
- Swift product judgment.
- Rates and quotations.
- Use of personal phone lines by travel, home, mobile and other equivalent insurance policies.
- Renewals of policies.
- Cooperation in processing claims.
- Management of problems and complaints.
- Instant investigation of balance by an account statement.
Then, its management believes that OIC’s giant success comes out because of proper application of INSIS software application as:
- Stack of technology.
- Customer and object subsystem.
- Product and policy administrational system.
- Unit Linked Extension for life insurance policies.
- Remuneration system for agents.
- Settlement of claim.
- Module for claiming process.
- Analytical reporting.
- Data security and general referencing system etc.
Further, market integration lies in its loyal involvement with Fadata Corporation as a high technically expertise supplier of system modules and other needed software. Fadata™ Ltd (2008) argued that this activity turns into the initiative of utilizing automated life portfolio which is a flexible resolution practice as maintainable for meeting all of their requirements as a perfect module for the overall IT infrastructural recognition of Oman.
In case of Middle East’s insurance market, a high growth can be located during the year 2008 because of enlargement of demand level for private health care insurance as well as the explosion of Islamic complaint insurance and the growing concern of inducing life insurance as the industrial “Best Strom”.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001) stated that since external environments are more complex, turbulent and becoming global, it is turning to adopt for those companies for adopting with that environment. For achieving this capacity, firms tend to involve in a process called environmental analysis on continuous basis basically involves four activities by which technological association can be tailored according to their own need. This can be exemplified as below:
- Through scanning, companies can identify early signals of potential IT changes in general environment by detecting such changes that are already underway. It is very much important for UAE insurance companies as it is highly impulsive. A relevant report has discovered that while world’s average insurance premium reached $550 per capita, the insurance market of GCC could be worth out of bed to $20 billion.
- Monitoring engages the ability for detecting the meaning of several environmental events influencing IT.
- By forecasting, companies can develop feasible projections about what might happen, how quickly and as a result of technological changes how the first two steps would be modified.
- Finally, assessing will determine timing and significance of the technology throughout the firm’s strategic management team.
A number of drivers in this industry can strongly influence the variation in utilizing technological advancement a lot which can be regarded as economic, demographic, social, legal, global and most virtually technological figures. Thus, the environmental analysis using those variables can be shown by discussing SWOT, PEST and competitor analysis as below:
SWOT analysis of UAE insurance industry
David, F., (2008) provides the importance of the SWOT analysis for the insurance industry.
Strengths: A number of factors that work as a catalyst of strengthening this industry can be recognized as:
- Involvement of Insurance Information System encounters many facilities for serving a high-quality customer service.
- With various product assortment relating to life, motor, health, cargo, hull, general accident, fire, liability, engineering and personal issues, the UAE insurance companies are now capable to compete with world-class top insurance and financial institution.
- Introduction of call center as very important service by imitating many impulsive opportunities to meet customer requirements, many local insurance firms have positioned positive brand feelings in people’s mind.
- Nowadays, some top-level insurance firms are receiving the magnificent support and effort from specialized hardware and software system integration companies with an extensive introduction of information system incorporation and wider information technology programs as an additional feature of competitiveness.
- Significantly Middle East has recorded a top achievement in growth for professional Takaful insurance.
- Many successful companies are now orienting effective training and certification programs which will be helpful to stabilize and effective human resources for gaining more premiums.
Weaknesses: Some of the weaknesses that the insurance market is facing are below:
- Traditional attitude of some people to view insurance as gambling.
- Although having a number of systematic developments, this industry has been regarded as a “non-exclusive” sector from the governmental consideration.
- Investment opportunities are decreasing day- by- day in this sector.
Opportunities: Increasingly, this industry is being subjected to numerous opportunities, as:
- Global expansion in utilizing Takaful insurance as a present growth of $7.4 billion and $14 billion within the year 2015 while this zone is optimizing for setting up the highest growth in this criteria.
- Scope for getting major support for increasing community of clients for the previous year has been notified which makes this industry a special watershed year for this region.
- The last year has also been forecasted for rising home and auto insurance services at an optimum level for the coming period.
- All the scopes and diversification of the industry will be very much helpful to attract brilliant advisors and talented personalized resources for UAE insurance business.
- Statistics have shown that in 2004, the country owned around 4.3 million of total population involving about 3 millions expatriates. Ren, H., Dobson, I., & Carreras, B., (2008) argued that it is also occupying the most diversified populations located in Middle East of local Emirati of 19%, Arab and Iranian of 23%, South Asian of 50% and others of 8% as Westerners and East Asians. Besides, Abu Dhabi is the largest and densely populated Emirate having total population of 1.4 million while Dubai has 1.2 million, Sharjah has 570000, Ajman 200000, Ras Al Khaimah 190000, Uman Al Quwain 55000 people in 2005. This sort of high population can be served by multiplied insurance materials.
Threats: Finally, UAE insurance businesses are not beyond potential threats. Such as:
- Non- investment recommendations of those companies may fall themselves in a situation of financial shortage.
- Need of experienced and forecasted claims for insurance.
PEST analysis of UAE insurance industry
Porter, M. E. (2004), argued that the modern political, demographic, social, technological factors are reformulating this industry’s historical potential. This can be experimented by a PEST analysis as below:
Political factors: Recently, UAE government considers its domestic insurance sector as a less attractive one. For this, many public companies tend to opt for health insurance from some insurers in order to offer employees with that aspect in straight competition with Daman which has the right for the government-regulated plans for intelligence in both private and public issues and billing with general public providers. The year 2008 has also revealed modern rules and regulations relating health insurance as well as Takaful market.
Economic factors: The past year’s study has recommended UAE insurance business not make expectation of gaining profit- making purpose from claims of investment as a core business motive. Thus, the health insurance organizations should forecast future benefits by maintaining the inflow of bills to the ultimate insurers. A study result by Standard and Poor rating Services disclosed that the GCC insurance industry can build up the properties to $20 billion.
Socio-cultural factors: UAE is Muslim based country while male consists 70% and women only 30% of the total population. The worldwide climb up of insurance companies can also be reflected in this zone with a number of global insurance companies that are successfully running their operation for providing satisfactory customer support.
Technological factor: Porter, M. E. (2004), said that technological changes affect many policies and procedures of this industry since players of health insurance are regarded to visualize their profits on technical services as this business’s basic view as “premiums minus claims equation”. From ITP DIGITAL, (2009) it can be found that topmost companies are also highlighted in implementing INSIS functional system in main process, object system, life insurance-linked extension, maintenance, data security etc. Lose of time and energy is also being controlled by software infrastructural modification for meeting diversified and changed customer demands. Similarly, projection of ERP system can introduce Oracle AIM methodology for operating several projects. Additionally, INSIS functions are leveraged enough for process efficiency IS integration, high control and productivity, important insight practice, actuarial and calculation by reporting alternatives and future growth support for insurance companies are demanding day-by-day.
Competitor analysis of UAE insurance industry
UAE insurance business market has already been saturated by a number of established public and private competitors as:
- Al Buharia National Insurance Company,
- Oman Insurance Company,
- National General Insurance,
- Neuron Qatar National Insurance Company,
- Lebanese Insurance,
- Mednet,
- AXA,
- Nasco Karogolan,
- Ras Al Khaimah Insurance,
- Al Wahba National Insurance,
- NAS,
- ALICO,
- Al Sagr Insurance,
- Tokyo Marine Insurance Company,
- Al Buharia,
- Good health,
- Al Dhafra etc.
Thompson, A. et al (2007) argued that the competitor analysis can be observed in the light of 5 forces model of competition that recognizes that along with those direct competitors, suppliers and buyers could become competitors as following:
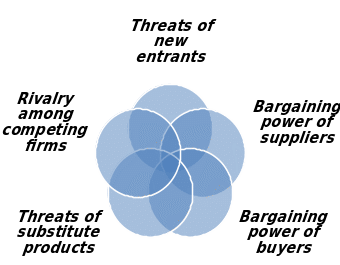
Threats of new entrants: UAE insurance market is not exceptional in this regard as it is unfortunate as the new entrants frequently have the potential to be quite threatening to incumbents. Thus, here exists a valid threat that few inexperienced newcomers may move to the market with less capable level of premium that will be unsuccessful in covering the medical costs as well as a threat for insurers which can simply damage the market. Skinner, S. J., Ivancevich, J. M. (2003), argued that a new firm’s entry into the market has two major tasks:
- barriers to entry encompass economies of scale as marginal improvements in efficiency as an incremental size increase, product differentiation as life, marine, health, automobile, engineering, liability etc. form of policy, capital requirements necessary resources for investment as a reluctance of current investment recently, switching cost regarding customer’s taken service from other company, access to distribution channel and government policy.
- Expected retaliation from the existing firms.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Fatada’s expertise is one of the major suppliers of UAE insurance companies. If Fatada can exert power over firms, those will be unable to recover costs and prices that will reduce profitability:
- Bargaining power of buyers: Involves demand for high quality, service, and call centers with lower premiums.
- Threats of substitute products: A number of national and international banks and financial companies are also providing services for security of life and property.
- Rivalry among competitors: This competition exists among national and global, private and public institutions and generally local insurances of each Emirate.
Competitor analysis components
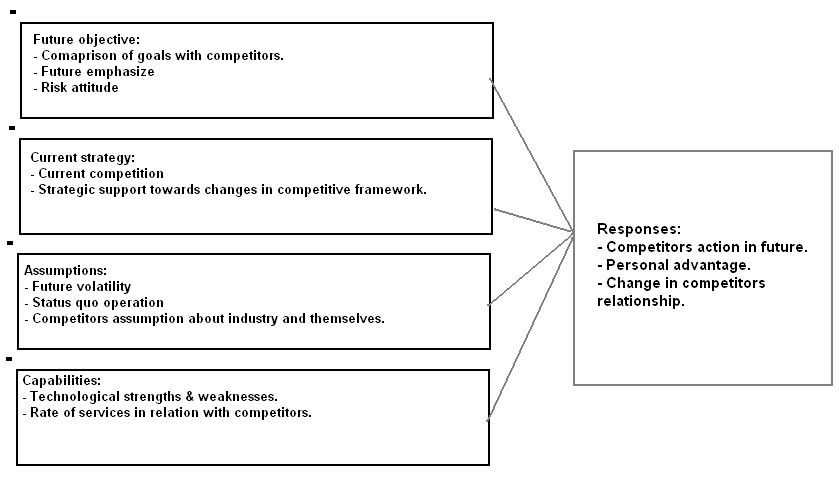
Skinner, S. J., Ivancevich, J. M. (2003), mentioned that by overviewing all the components regarding future objective, current strategy, assumption, capabilities and responses, it can be unstated that the use of IT or IS will be influential for making competitive advantages in terms of product differentiation, fast service, project management, insurance account management, payment control, scheduling and processing, accounting records and reinsurance processes in current and future perspective.
The components of internal analysis can be motivated to competitive advantage and strategic competitiveness of developing the utilization of IT/ IS program as following:
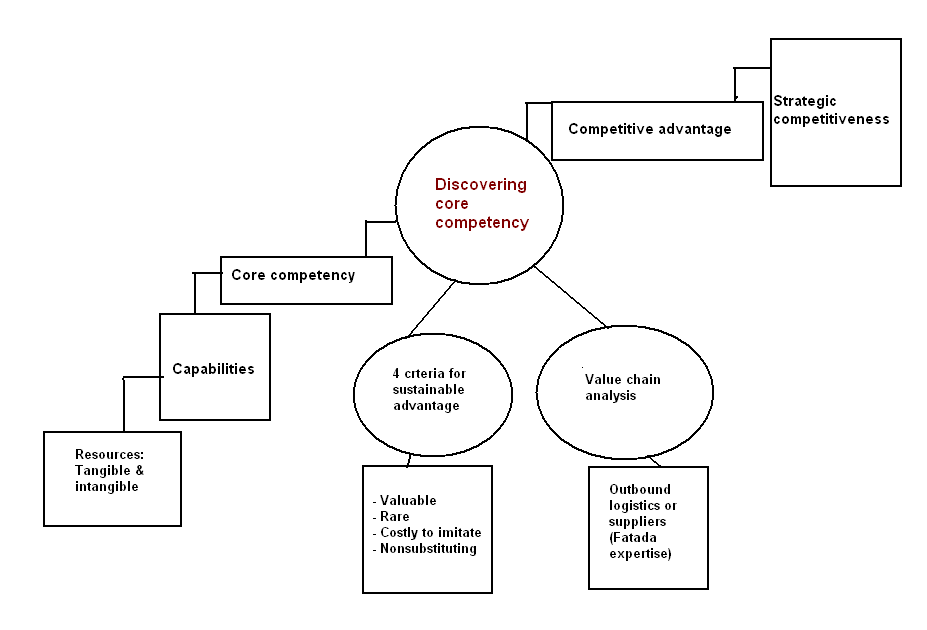
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), provides the internal analysis diagram, from it can be identified that customer value is the source of Oman’s potential to earn above-average return. What it intends to create value for facilitating the new insurance supportive programs including products and ideas for satisfying the definite and other below-average insurance decides to choose its business-level strategy as differentiation and organizational structure. Here, core competencies like high-quality goods, swift services Gap analysis, data migration, life insurance products configuration etc. are actually value-creation through which the company seeks strategic competitiveness and huge returns. By, initiating leveraged INSIS systems for increased efficiencies to the insurance business, close association of IS, complete coverage regarding this process from horizontal and vertical integration, useful observation, powerful and accurate calculation and global application are very much supportive for Oman to set its strategic competitiveness.
The 1st inputs of the diagram indicate some of the tangible and intangible resources obtained by the firm, such as:
- Financial resources– It indicates Oman’s capacity to borrow capital from external sources as well as the ability to generate internal capital. For this issue, it achieved Dhs 1.5 billion for premium turnover, Dhs 2.36 billion pf shareholder equity and total assets of more than Dhs 4.69 billion.
- Organizational resources– Involving the firm’s formal reporting structure which is automated facilitated by INSIS support associated with planning, controlling and coordinating system.
- Physical resources– The approximate 9 branches in each of the Emirate of UAE including plant and equipment.
- Technological resources– Act as the most important catalyst of Oman’s success in gaining customer’s loyalty and goodwill for offering quality goods and services through a proper subscription of upgraded technology and software for life, health and other general insurance simulation. It had also recorded Dhs 517 million as technical reserve.
- Human resources– This also plays a major part in conducting with clients at a simultaneous interval.
- Innovative resources– Creative idea amplifies in the new dimension of call center, R & D efforts and outsourcing decisions.
- Reputation resource– It includes reputation with customers, perception of product quality, brand value, reputation with suppliers, efficient, supportive, effective and beneficial relationships.
Hill, C., and Jones, G., (2007) mentioned that in relation to the question of organizational capabilities which refers to the capacity to develop resources that have been purposely integrated to achieve a desired end state. Thus, the internal capabilities of Oman enable it to create and exploit external opportunities by developing sustained advantage while utilizing insight as well as adroitness. Those capabilities are based upon developing, carrying and exchanging information systems and knowledge through the firm’s human resources and management procedures. It can be stated as:
- Employment of INSIS with the unification of entire set of technological systems for timeline of everyday activity’s swiftness and elaboration of monthly balance sheet.
- Implementation of insurance integrated solution for managing current business, accounting records and ERP application for managing financial situation.
- Professional knowledge for adopting the rapidly diversified IT market in order to obtain efficiency.
All that factorial impact of IT to build up Oman’s internal capabilities can be shown as:
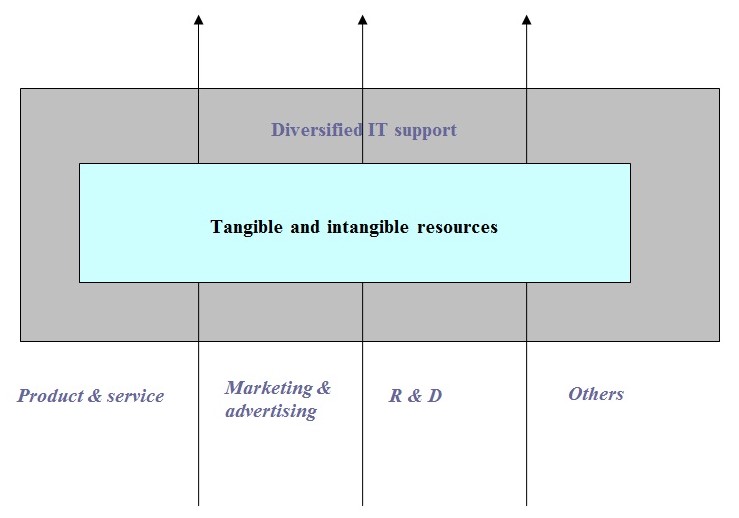
And finally, core competencies are the mentioned resources and capabilities that serve as a source of competitive advantage for the firm over competitors. Thus, it distinguishes a competitively by reflecting its personality. An important question is- “How many core competencies are required for Oman to have a competitive advantage?” Response to this question will essence its running strategy on the basis of home service as well as outsourcing which all are interrelated to build up value- chain of the firm, as below:
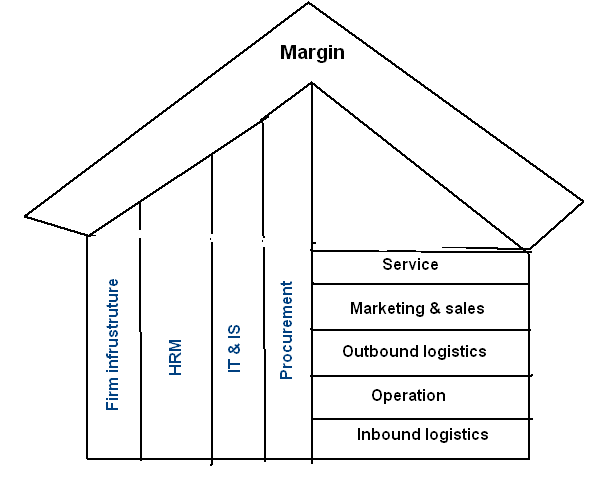
Need of outsourcing for formulating internal core competency
Saloner, G., Shepard, A., and Podolny, J., (2001), argued that sometimes, a firm within a specific industry seeks the strategic value that can be captured through effective outsourcing which means the purchase or utilization of a value-creating activity from external supplier. In this issue, the strategic view of Oman insurance largely focuses on outbound logistics by an effective implementation of Fatada intellectual and INSIS programming.
From Fadata ™ Ltd (2008), the firm hires facilities from the following fields:
- Project management- It is used for supporting all commercial perspectives inducing vertical service proving matter.
- Insurance account management- It enables to act each of the processing of pre- accounting for collection of premium involving necessary accessories like:
- Control of payment- Used to keep a notification of entire due payments that is further used for addressing customers, agent and agent supervisor by systematic automation.
- Scheduling of payment- Used to keep track of all transactions from due to refused or paid.
- Processing of payments- Here, the premiums are being isolated into fractions by insurance mathematics. The allotment of premium and corresponding data schedule permits cost/ benefits explanation.
- Accounting records- Result of payment processing can be joined to this chart based on systems for creating records by normal software ledger.
Similarly, Oman gets support from INSIS from the following field:
- Modification of reinsurance and co-insurance projects by complete automated administration with the help of proportional and non-proportional treaties by involving RI clause, ceding of premium, ceding of claim and ceding of loss reserve. Additionally, web-based Java software helps it in selling insurance goods and addressing marketing activities along with custom proposal, quotation serving and binding regarding absolute invoicing and recording.
- Skinner, S. J., Ivancevich, J. M. (2003), expressed that document management software is a management and solution of workflow offering full automation for document chain, processing of task and controlling decision control for operating effectiveness.
- Prolonged search for solution of insurance problems.
- Supplying modern package of current business for flexible advantage in next period by presenting enforceable management.
Strategic focus at Oman insurance
Johnson, G. & Whittington, R. (2006), said that by employing personal resources, capabilities, core competencies and outsourcing a number of technical advantages, Oman insurance company has clearly disposed of itself as a pioneer of implementing differentiation strategy. With this, the unique attributes and characteristics of its insurance goods provide value to the customers. Kotler, P. (2006), argued that because a differentiated product can satisfy unique needs of customers, it should maintain its pricing strategy up to that standard level. The overall dimensions of Oman in seeking and utilizing differentiation strategy are as following:
- By undertaking all types of general risks, it offers the facility of customized insurance services.
- It has proven its significance by establishing exclusive call center. It posses an R & D section to innovate new insurance materials and low- volume products.
- Talent and qualified workforce are its other characteristics by which manpower is being successfully used to obtain and retain customers.
- Highly responsive concern towards problem.
- Automated life portfolio.
- Strong IT infrastructure than many other similar insurance firms in UAE.
- Updated software formulation.
- Employment of tools for OS/ dB/ Development.
- Informative website in order to acknowledge customers about current products and services.
- Oracle internet development suit.
- Networking and Ethernet.
- NT servers.
- Life insurance tools and procedures discussion and configuration with INSIS.
- Third party integration module by GL, AP, AR etc.
- Customized software.
- ERP implementation for motor, property, personal, financial, agriculture, aviation, marine, goods transportation, railway and risk for developers etc. forms of non- life insurance.
- Close integration with IS.
- Use of manual and automotive documentation.
- Larger MIS issue etc.
After disclosing the overall internal graphics of the company, it can be summarized that Oman insurance company can finally be analyzed by an “effect/ probability/ action” grid in which simulation of a specific project (life insurance) by information technology can be exemplified as follows:
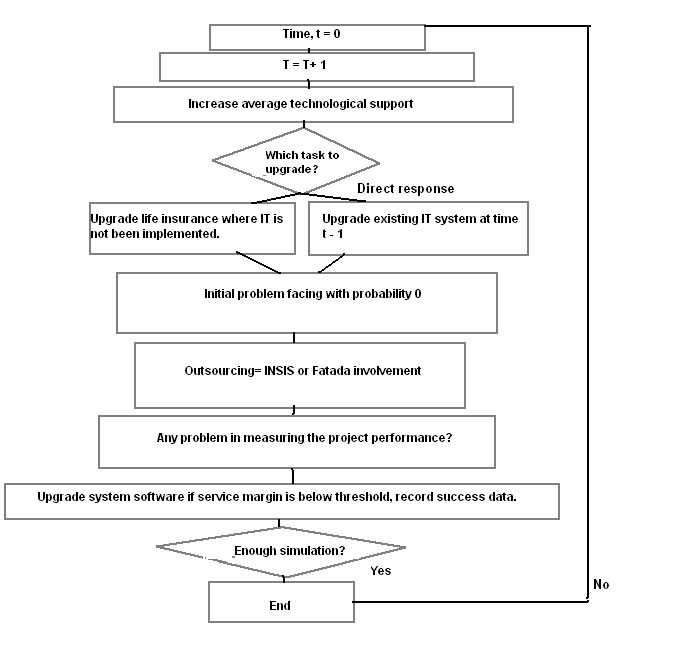
In this flowchart, specific time can be estimated for implementing automated simulation in life insurance projected. Ren,H., Dobson, I., & Carreras, B., (2008) held that next, the decision for average IT support can be taken considering existence and time. After considering outsourcing, problem identification and margin, final decision for enough simulation is to decide.
Task – 4
The 4th task is concerned with entire discussion of internal and external issues regarding the system development of the company. So, to elaborate this relationship, it is necessary to have a clear view of system development which can be defined as a conceptual framework that can be utilized in project management which explains the phases included in an IS development project from a primary viability study by taking care of the entire implementation. Or it is the engineering of system and software linked to the development of many processes for improving systems while the mechanisms used to modify the systems by generally computer and technological methodologies. So, this concept is constructed for structuring, planning, and controlling the entire external and internal information system by software management system. A number of factors like- resources, capabilities, core competencies, strategic competitiveness and other value development efforts can have a major influence on this SDLC.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), argued that system development model can be developed by a number of processes like- waterfall model, RAD, JAD, fountain model, build and fix, spiral as well as synchronized and stabilize model of which must generally follow the following phases for feasibility:
- The 1st phase will evaluate each of the components of internal and external environment by idealizing deficiencies. For this, interviewing and consulting services will be applicable.
- Deficiencies will be noticed for present systems with adequate requirements for improvement.
- Designing of new system concerning the internal resources and capabilities.
- New system development by installing new components and techniques. Trained users and performance testing is obligated with top most adjustments.
- Use of new system may be introduced by systematic replacement of previous one or closing it down.
- After running up of one, exclusive evaluation, maintenance and updating are essential.
Therefore, the environmental impact on the system development process is elaborated below:
- Planning or initiation stage: For generating a top-class view of current insurance planning for product, policy, call center and employment efficiency, desired goal must be determined. Feasibility study is needed for presenting the plan to the top management to raise funds. Each of the projects should be tested in terms of 3 criteria, as- economical, operational and technical. Additionally, references will be required for spotting and disseminating by Management information team since this stage is termed as analysis stage.
- Gathering of requirements and analysis: Here, the primary objective is to identify any fixed problem in the industry or internal capacity. Breaking down the project into number of parts with diagram projection will be helpful to locate the problem more significantly.
- Design: This will measure screen layout, rules of operation, process diagram, premium policies, accounting records and other documentation. The result will then be useful for the completely new or converged system.
- Coding: At this phase, both subsystem and modular codes will be associated. However, it will be joined together with after processing units under examination for adding them with main project accompanied with scenery goals, targets, timing and budgeting plan for full package of software.
- Testing: The result of previous phase can be examined in various ways while system, unit, and customer-oriented testing are also accepted. It is often a difficult situation referring to the question of subject and quantity in case of iteration that is not simply an element of waterfall model, but happens to some extent. Some types of testing can be data set, unit, set, black and white box testing, module, system, integration, automation, user agreement and regression testing.
- Operations and maintenance: This phase involves the changes and inducements before sunset of the main system. Maintenance is an abstract part of this process. Since, important replacement of individual occurs within the company, it should adopt new system implementation in order to upgrade the system.
Kotler, P. (2006), expressed that management of positioning control will be dependent upon threshold of Work Breakdown Structure or WBS for describing the targeted project of Oman for enabling the project manager to appropriately describing the project task. This would reveal the addressing of WBS in the categories of:
- Planning
- Acquisition
- Delivering
- Monitoring
All of those aspects would be effective enough to direct the overall placement of Oman from a creative and facilitated point of view. Such as:
- It will appear as a programmatic quotation for each project task by providing flexible and stable route for attaching projects into a reliable adjustment through the scope of development.
- Each phase has a specific objective with functional recommendations, deliverables, and useful control procedure for efficient MIS team though the project supervisor will face complexity in monitoring each phase while operating it.
- Control will be helpful for issuing transparent statement for the target result a through out research.
- WBS is also effective in recognizing top stages and milestones of the task in a narrative model. Upper section is helpful in identifying complete issue and time line with necessary description. Middle section is a guideline for WBS task strategy while each task must have time and origin opposing the activity.
- Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., Gilbert, D. R. (2006), argued that tasks will also have specific documents, decisions and analyses by relying on software and system engineering with close coordination relative to the external or internal project linkage. Here, outside contractors can be used to get services like- preparation and submission of results and suggestions for review purpose, better- level design dedication, set- up configuration, training, logistics, migration of data, documentation, maintaining, SW and HW supply etc. with external resources.
- Functional, product, modified product and allocated baseline will be required as a significant milestone.
- Similarly prototyped software, development for end- user, RAD, JAD, and XP etc. can be used in lieu of SSM analysis.
Thus, a successful implementation of this process will be frequently useful for Oman insurance company as it consists of many logical stages for the company’s R & D to build up an information system with requirements, feasibility, training and customers’ wide acceptance. This can be the key component for ensuring the image of consistent high-quality image for the company brand in the customers’ mind by exceeding their expectation by cost assumption, working efficiency, developed IT infrastructure and cheaper cost imagination.
Bibliography
Bodie, Z. Kane, A. and Marcus A. J. (2005), Investments, 5th edition, Tata McGraw-hill publishing company limited, New Delhi; ISBN: 0-07-048662-X.
Chernev, A., (2007), Strategic Marketing Analysis, 2nd edition, Brightstar Media, ISBN: 978-0979003912.
David, F., (2008), Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases, 12th edition, Prentice Hall, ISBN: 978-0136015703.
Dibb, S. Simkin, L. Pride, W. M. & Ferrell, O.C. (2001), Marketing Concepts and Strategies, 4th ed., Boston, USA: Houghton Mifflin.
Fadata ™ Ltd (2008) Oman Insurance Company, UAE, Web.
Griffin, R. W. (2006), Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), Strategic Management, 4th Edition, South-Western Thomson Learning, Singapore, ISBN: 0-324-041891-2.
Hill, C., and Jones, G., (2007) Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach, 8th edition, South-Western College, ISBN: 978-0618894697.
ITP DIGITAL, (2009) Top Gulf Companies, Web.
Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2006), Exporing Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases, 8th edition, London: FT Prentrice Hall.
Kotler, P., Armstrong, G. (2006), Principles of Marketing, 11th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi, ISBN: 81-203-2825-6.
Kotler, P. (2006), Marketing Management, 11th edition, Prentice Hall, NJ, ISBN: 0-13-0336297.
Porter, M. E. (2004), Competitive Strategy, Export Edition, New York: The Free Press, ISBN-10: 0743260880.
Oman Insurance Company (2008) Oman Insurance Company Wins the Shaikh Khalifa Excellence Award, Web.
Ren,H., Dobson, I., & Carreras, B., (2008) Long-Term Effect of the n-1 Criterion on Cascading Line Outages in an Evolving Power Transmission Grid, Web.
Skinner, S. J., Ivancevich, J. M. (2003), Business for the 21st Century, Homewood, Boston, ISBN: 0-256-09222-2.
Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., Gilbert, D. R. (2006), Management, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, ISBN: 81-203-0981-2.
Saloner, G., Shepard, A., and Podolny, J., (2001), Strategic Management, 2nd edition, John Wiley, ISBN: 9780471380719.
Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, 13th edition, Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, New Delhi, India.